Echo EG (Echoencephalography) of the brain in children
Head injuries are incredibly widespread in childhood. Falls, fights, jumps, visits to rides - all this at times increases the likelihood of a head injury. In addition, the children's brain is very vulnerable and often subject to congenital and acquired ailments. Therefore, issues of correct and timely diagnosis come out on top.
Echoencephalography or Echo EG is considered one of the most informative and safe ways to examine the brain in children. From this article you will learn how to carry out such a procedure, what it shows and how to prepare a child for such an examination.
What it is?
Echoencephalography combines two types of research - ultrasound and EEG. The doctor receives information about the state of the brain during echoEG due to ultrasound and electrical impulses. Ultrasound waves are fed to different parts of the brain, which tend to be reflected from different tissues and media in different ways. The reflected ultrasound signal is converted into an electric one and fixed on the screen of the device.
In newborns and children up to one and a half years, research is carried out using the neurosonography method - an ultrasound scan is made an ordinary sensor through unclosed "springs". Older children, who have already closed "springs" and bones of the skull have become more durable, have been shown to carry out an echo.
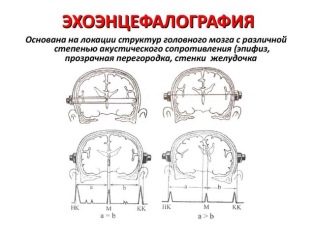
Echoencephaloscopy (EchoES) has been used in medicine since 1956 and, despite the constant improvement of research methods and equipment, remains very popular. As a result of exposure to ultrasound with the subsequent conversion of the signal into electrical, it is possible to obtain three types of data:
- base complex - impulses reflected from the meninges and skull bones;
- final complex - impulses reflected from the inner surface of the skull;
- middle M-complex - directly impulses of the body of the brain and its middle parts.
It is clear that the most important indicator is the M-complex. The remaining pulses are measured to identify it. When the M-complex is shifted from the midline, it is said that the child has brain pathologies and disorders of the central nervous system.
Indications and contraindications
There are not so many contraindications for carrying out an echoEG of the brain in children - the presence of fresh wounds and surgical sutures on the scalp. If this is not the case, the procedure is performed for patients of any age and gender.
The survey is not included in the list of mandatory screening, and therefore conduct it for medical reasons. These include:
- regular severe headaches in a child;
- bouts of dizziness, loss of consciousness, loss of balance without apparent mechanical causes;
- confused consciousness in a child, delirium;
- vomiting and nausea that are not caused by food indigestion, poisoning or gastroenterological illness;
- loss of coordination of movements of the limbs, head.
If the child fell and hit his head badly, the doctor, having detected signs of traumatic brain injury, may well prescribe an echoencephalography to determine the degree of dysfunction of the brain and the location of the lesion.
Is it harmful?
Echo echo does not belong to harmful examinations, which include CT and partly MRI. Ultrasound does not harm the brain structures, does not violate the metabolism of neurons.Mom may not be afraid - modern medicine does not have data on the harmful effects of ultrasound on humans. Rumors of harm are greatly exaggerated and are lined up mainly on the basis that scientists do not yet have a large statistical base for studying the remote consequences of the use of ultrasound. The method has been used for just over 20 years, and it takes much more time to collect such a base.
The damage that allegedly exists is mainly described in women’s forums by people who are far from medicine and have a poor understanding of what exactly is being said. But the harm that a mother can expose a child by refusing to undergo an Echo EG can be very serious and obvious: the lack of an accurate diagnosis will not allow doctors to prescribe the baby the correct and timely treatment, on which his health and life can directly depend.
How is it done?
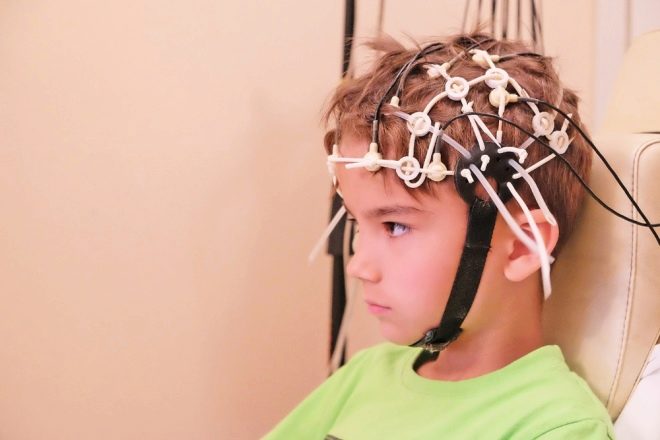
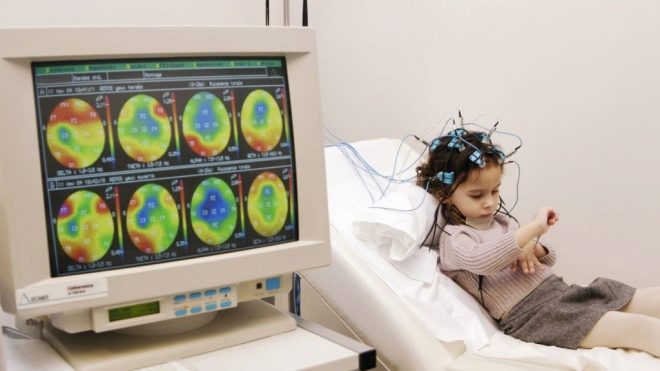
To obtain an echogram, special equipment is used, which is installed in a separate small office with good light and sound insulation. Small children are placed on the hands of mom or dad, large ones can be diagnosed sitting on a chair or lying on a couch with their heads elevated.
A special cap with sensitive sensors is put on the child’s head. Ultrasound is directed using two sources attached to the temporal part of the head above the ears. The study lasts no more than 20 minutes. In relation to infants, it is desirable that they are asleep at the time of the survey.
The procedure is painless. The child will not feel any discomfort.
Training
Before the examination you need to wash the baby's head. In the doctor's office, he should get with clean hair. There is no need to come for an examination on an empty stomach. The child must be fed and calm.
If we are talking about babies, be sure to feed him before the procedure. An older child can be fed before leaving the house. If you undergo an examination on an empty stomach, the lack of glucose in the blood, which appears in a state of hunger, can significantly affect the state of the brain, the results will be inaccurate, erroneous.
A day before the examination, exclude from the diet of the child all the products that can stimulate the central nervous system - tea, coffee, cocoa. Be sure to tell your doctor about what medications the child is taking at the given dosage. There is no need to stop taking medicines before the examination.
Prepare a big child psychologically. Explain to him that nothing terrible will happen.
You can imagine the survey game, saying that the cap on his head will be exactly the same as that of astronauts or superheroes before the responsible task of saving the world.
Decryption
When deciphering the echogram, doctors pay attention to the increase in the amplitude of echo pulsations, as well as the median M-echo, the displacement of which, as we already know from the median values, may indicate an asymmetry of the hemispheres and brain regions. Normally, a healthy baby M-echo shifts no more than 0.5-1 mm. Also, there are areas with increased echogenicity and a ventricular index, which in a normal state of the brain in a child is approximately 1.8.
It is impossible to decipher the echogram of the brain by yourself. This is done by experts. But parents should know what pathologies can be identified by the results of the passage of such a study:
- tumors and neoplasms are usually accompanied by a shift of the M-echo towards the healthy hemisphere, if the shift is significant, malignant tumors may be suspected;
- if, after injury, a child is found to have a 4-8 mm M-echo offset, doctors suspect a brain hematoma, if the displacement exceeds the 7-8 mm mark, an urgent neurosurgical operation is scheduled to save the little patient's life;
- a slight displacement of the M-line (about 3 mm) usually indicates a brain contusion;
- a significant displacement of M-echo may manifest meningoencephalitis, as well as its complicated form with the occurrence of an abscess;
- in hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain), the M-line splits into peaks, and the severity of these peaks indicates the severity of dropsy;
- in violation of cerebral circulation and hemorrhages in the brain, there is not only a shift, but also the appearance of multiple areas of increased echogenicity.
In most cases, Echo EG results require additional diagnostics. For example, CT or MRI to clarify the pathological condition and its causes.
You will learn more about how an Echo EG is performed on a child in the following video.