How to determine if a child has a concussion: the first signs
Children actively explore the world, and therefore often fall. At the same time, according to traumatologists, they usually hit their heads and limbs, so a concussion in a child is a fairly common phenomenon at almost any age. In this article we will tell you how to recognize the first signs of such a trauma in a child and how to properly provide him with first aid.
What it is?
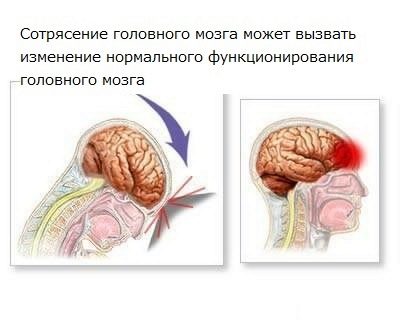
Brain concussion is called an injury by doctors, in which at the morphological level the tissue and the structure of the brain do not change, but neurological disorders do manifest. Concussion is temporary and, as a rule, short-term.
Almost 85% of TBI in tender children are given to brain concussion. The cause and circumstances of the injury are always about the same and lie in the mechanical effect on the skull: it can be either a blow to the head, or a blow to the head with something. Sometimes the cause is a violation of the axial load, for example, at a fracture of the spinal column, a sharp fall on the butt, a jump to the feet from a great height.
A child can get a concussion on children's rides, for example, on circular merry-go-rounds or a trampoline - all movements, including sharp acceleration, are associated with a reflex head dropping, in which the brain “hits” against the walls of the skull from the inside.
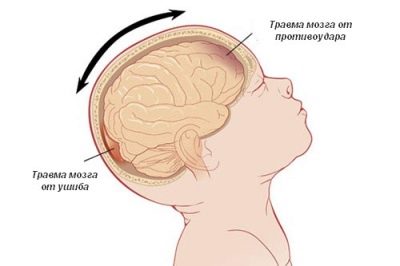
The fact is that the brain is located in the cerebral fluid, and between the walls of the skull and the brain tissue itself there is free space. In situations where the brain strikes from the inside of the skull, they directly speak of the presence of concussion. Some time after the impact, some functions and mutual consistency of different parts of the brain are temporarily disrupted.
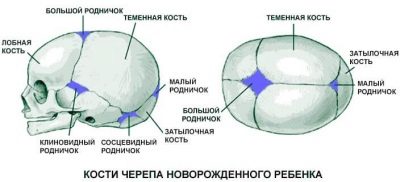
Most often, concussion is recorded in children older than 3 years. Up to this age, the baby's skull bones are softer. In infancy, concussion is not such a frequent diagnosis, as the cushioning properties increase due to a greater amount of cerebral fluid inside the skull and “fontanelles" that allow the bones of the skull to move when struck or otherwise affected.
In 1-2 years the fontanelles close, and the bones of the skull begin to harden rapidly. By the age of 5, they attain the strength of an adult by strength, and from that point on, tremor is a real threat.
According to children's traumatologists, most often concussion is recorded in children aged 7-9 years. Slightly less - in children from 3 to 6 years. More often parents of boys turn to doctors for help, because girls fall less often, they fight less, they do not seek to set a world record for jumping from the roof of a garage, etc.
First signs and symptoms
Due to the widespread occurrence of this type of trauma in childhood, every parent should be able to recognize and identify the first signs of a concussion in a child.
A concussion is a closed cranial injury, and therefore there may be no external damage to the child’s head. If a fall or a header occurs before your eyes, and you are confident in the very fact of injury, there may be fewer questions than in situations where a small child has struck, but cannot tell about it, and the parents will not let you fall or hit. reasons missed.
One of the first symptoms may be loss of consciousness. With a concussion, it can last for a few seconds or several tens of minutes. The child may faint even immediately after receiving the injury, and some time later. In many children, the symptom of loss of consciousness is absent altogether. Only a certain inhibition and stupidity is noticeable.
At home, it is easy to identify shaking by this sign: the child behaves differently, he looks confused, and he slowly reacts to the words addressed to him. In small children under one year of age, there may be either constant whining crying or unnatural drowsiness.
Children who, already by virtue of age, can clearly explain and express themselves, may have impaired memory. Most often, children do not remember the circumstances of the injury, at least - they can not remember the events that followed the coming to life after loss of consciousness. It is difficult to say whether the lost fragment of memory will return. Amnesia in this case is quite understandable and often irreparable. Lack of memories, however, will apply only to the event associated with the injury. Mom, Dad and the child remembers very well, you can not worry.
At home, parents suspecting a child with a concussion can even determine the extent of the injury:
- first degree - there is no loss of consciousness, the child well remembers;
- second degree - loss of consciousness did not occur, but it is confused, speech is disturbed, the child cannot partially or completely remember what happened to him;
- third degree - there was a loss of consciousness, memory is impaired.
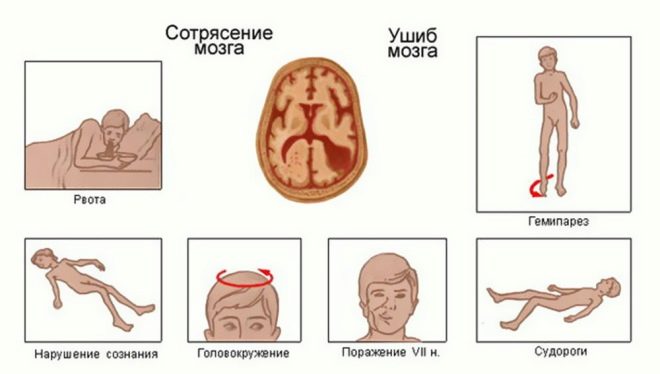
If the child did not lose consciousness, then parents can determine the concussion by the subsequent clinical picture typical of this type of injury:
- the child becomes lethargic, complains of headaches;
- nausea appears, and sometimes vomiting (usually single, but severe);
- strong weakness, dizziness, tinnitus;
- the child may sweat a lot (wet, cold palms, wet scalp);
- painful movements of the eyeballs in different directions;
- the eyeballs themselves may look unnatural (according to the type of discrepancy); if you carefully study the eyes of the child, you may notice a small nystagmus (eye trembling);
- sleep is disturbed (either the child cannot sleep, or he sleeps and does not want to wake up);
- nasal bleedings appear (not always and not at all).
With the appearance of at least 1-2 symptoms, it is necessary to measure the blood pressure of the child several times in an hour. With a concussion, the level of blood pressure is unstable.
The above symptoms are usually observed during the first days after injury. Then most of the signs disappear, only headaches, a feeling of increased tiredness, irritability and emotional instability can persist for a long time.
Parents should be aware that shaking in children under 3 years old most often occurs without loss of consciousness. The clinical picture in children is rather scanty. As a rule, when shaking, they first long, until fatigue, cry. Then they calm down and immediately fall asleep. They sleep for a long time, after which the child refuses to eat or eats little, neurological signs such as regurgitation may appear. After a few days the appetite is restored, sleep is getting better.
What is the danger?
Mild concussion is usually not dangerous for the child. A child's body can quickly compensate for all violations of the neurological plan without significant consequences in the future. However, repeated concussion, if the child has previously endured such a condition, may cause the development of post-traumatic encephalopathy. When it can disrupt hand coordination, and also often there is a splash of one foot.
The development of such post-traumatic disorders does not depend on the extent to which the concussion was the previous time and what symptoms accompanied it and whether they were at all. The manifestation of such violations is very diverse: it can be flashes of unmotivated aggression, hysteria, neurosis, or, on the contrary, periods of deep inhibition. The child may become familiar with headaches, intracranial hypertension, as well as problems with memory and remembering new information.
The danger of a concussion lies in the fact that other cranial traumas can be “masked” under it, which represent a more significant danger to the child. Therefore, only careful observation will help to distinguish concussion from brain contusion or other head injuries.
With concussion, all symptoms disappear within 3-7 days after injury, with more severe brain injuries, the clinical picture does not change or is burdened.
First Aid - What should parents do?
If you suspect a child's brain concussion should be transferred to a horizontal position. You can put a small roller under your feet so that they are a little higher in level. Under the head, you can put a small pillow.
If the child is of a conscious age, by all means do not let him fall asleep before the arrival of the Ambulance, which should be called immediately after the detection of the characteristic symptoms of a cranial injury. Lack of sleep is important for the initial assessment of confusion, which will determine the extent of injury.
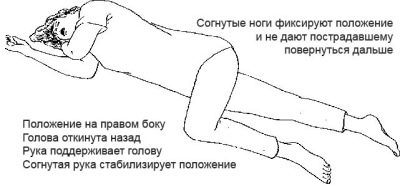
The child should lie on the right side. This is important in order to protect it from vomiting asphyxia, if it suddenly opens. A baby can be taken with handles on the left maternal hand, facing it and so hold it until the arrival of the medical team.
To avoid the effects of sudden convulsions, which can also occur quite spontaneously, the child’s limbs should be bent at right angles - hands should be placed on the chest, legs should be bent at the knees.
If a child has visual consequences of a fall on the scalp - cones, puffiness, ice wrapped in a towel can be attached to the injury site. If there is an abrasion or a wound, treat it with hydrogen peroxide, apply cold and wait for the doctor. It is possible that the child may require stitches in the hospital.
With a large wound, you should not wait for the time to assess other symptoms — you should ice over the edges of the wound without affecting it, and go to the emergency room.
When the child loses consciousness, they are placed on a flat and hard surface, lifting their legs and head, and they are given to smell ammonia. If there is no breathing, parents should be able to carry out pulmonary resuscitation, and when the baby recovers, do not let him move, speak or drink liquid before the arrival of the doctor.
How is the treatment?
At the stage of recovery, the child is shown peace, balanced nutrition, the absence of loud sounds, bright light, active movement. Usually, rehabilitation takes up to 3-4 weeks. It is recommended for this time to limit computer games, watching TV and reading books.
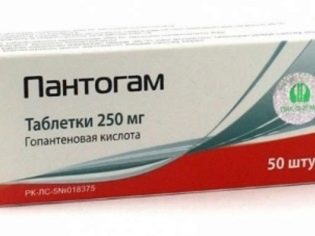
Vitamin preparations are prescribed for the child, as well as nootropics (“Pantogam», «Nootropil"). Infrequently, but it may take a hospital stay for 1-2 weeks. In the recovery period, a neurologist may prescribe a massage for the child and physiotherapy sessions.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
Renowned pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky, whose opinion is of great interest to parents, believes that one should not exaggerate the risk of concussion. If we are talking about a small child, then with a high degree of probability after the fall he will not have any concussion. But there will be a lot of scream from fright and a lot of spent parental nerves. After an hour or two after the injury, the child is once again cheerful and has already forgotten what happened, he plays, takes care of the usual children's affairs and asks for food, he has no concussion.Parents can not panic.
Moms and dads are the best doctors in the world who know the peculiarities of the development of their child, and therefore they are the first who can detect signs of a concussion of the brain according to the changed behavior of the child.
Komarovsky believes that in all cases except an open injury, the observation tactic is the best.
If the kid fell asleep after the injury, he shouldn’t interfere, says Yevgeny Olegovich. But once every two hours, the mother must still wake up the child and check how well his thinking processes work. This helps a simple question - where is mom, how is the child's name, how many fingers do you show, etc. If there is no answer or the answers look more like nonsense, you should immediately call the "emergency room".
Treating brain concussion is not so difficult, but still it is better to prevent injuries. Komarovsky strongly recommends that parents watch their children more closely for a walk, not to encourage self-indulgence with swings and slides, the use of rides for other purposes, it is also better to avoid trampolines.
At home, you need to take care that there is a non-slip mat in the bathroom and there are no poured and untidy puddles on the tile floor.
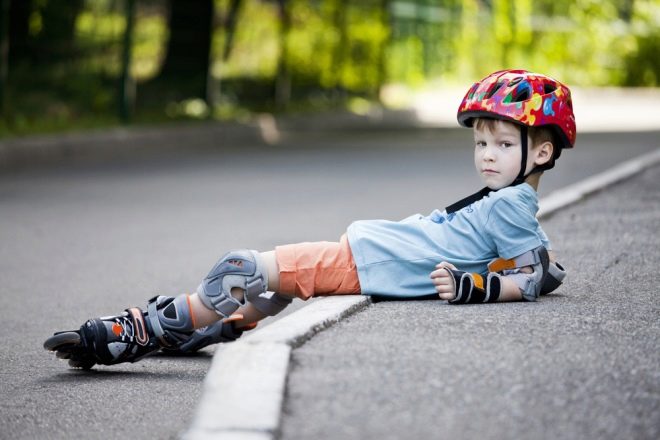
The child should ride a bicycle and roller skates with a protection and a helmet.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you more about brain concussion in a child in the next video.