The rate of ESR in the blood of children and what to do with an increased value
Thanks to the analysis of the child’s blood, it is possible to determine whether the baby is healthy or has any diseases. This is especially important if the disease is hidden. To identify such hidden pathologies, all children are routinely sent for tests at a certain age. And blood analysis of children pay increased attention.
One of the important indicators determined in the laboratory in the study of blood, is the ESR. Seeing such a reduction in the form of a blood test, many parents do not know what it means. If, moreover, the analysis revealed an increased ESR in the blood of a child, this causes anxiety and anxiety. To know what to do in case of such changes, you need to figure out how to perform an ESR analysis in children and how its results are interpreted.
What is ESR and how does it determine its value
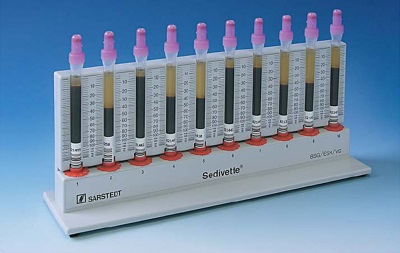
The abbreviation ESR reduces the “erythrocyte sedimentation rate,” which is found during a clinical blood test. The indicator is measured in millimeters per hour. To determine it, blood connected to the anticoagulant (this is important so that it remains liquid) is left in the test tube, allowing its cells to settle under the influence of gravitational forces. After one hour, the height of the upper layer, the transparent part of the blood (plasma) above the blood cells that have settled down, is measured.
Now in many medical institutions, the determination of the ESR is carried out in the automatic device.
Table of values of norms
When a blood test is being decoded, all indicators are compared with regulations that depend on the age of the children. This also applies to the sedimentation rate of red blood cells, because the ESR immediately after birth will be the same; at the age of 2-3 years or 8-9 years, the indicator will be different.
Standard ESR are such results:
The newborn in the first days of life | 2-4 mm / h |
In an infant up to a year | 4-10 mm / h |
In children older than one year | 4-12 mm / h |
Increase rate in the age of 27 days of life to two years is considered the norm. In children of this age, the ESR can reach 12-17 mm / h. In adolescence, the results differ in girls (the rate is considered to be up to 14 mm per hour) and in boys (normal ESR is 2-11 mm per hour).
Why it is below normal
Deviations from normal ESR are often manifested by an increase in this indicator, and a decrease in the rate at which erythrocytes settle down is observed much less frequently. The most common cause of such changes is increased blood viscosity.
Lower ESR occurs when:
- Dehydration, for example, due to acute intestinal infection.
- Heart defects.
- Sickle anemia.
- Acidosis (lowering blood pH).
- Severe poisoning.
- Sharp weight loss.
- Steroid medication.
- Increased blood cell count (polycythemia).
- Presence in the blood of red blood cells with a modified form (spherocytosis or anisocytosis).
- Pathologies of the liver and gallbladder, especially manifested by hyperbilirubinemia.
Causes of increased ESR
High ESR in a child does not always indicate health problems. This indicator may change under the influence of various factors, sometimes harmless or temporarily acting on the child.However, quite often an increase in ESR is a sign of the disease, and sometimes very serious.
Non-hazardous
With such reasons characteristic a slight increase in ESR, for example, up to 20-25 mm / h. TThis indicator of ESR can be detected:
- When teething.
- When hypovitaminosis.
- If the child is taking retinol (vitamin A).
- With strong feelings or stress, for example, after a long crying baby.
- With a strict diet or fasting.
- When taking certain medications, such as paracetamol.
- With obesity.
- With an excess of fatty foods in the diet of crumbs or nursing mothers.
- After vaccination against hepatitis B.
In addition, in childhood can be identified as the so-calledIndrome increased ESR. It has a high indicator, but the child does not have any complaints and health problems.
Pathological
In diseases, the ESR rises much more than the norm, for example, to 45-50 mm / h and higher. One of the main reasons for more rapid erythrocyte sedimentation is an increase in the amount of protein in the blood by increasing the level of fibrinogen and the production of immunoglobulins. This condition occurs in the acute phase of many diseases.
Also a common cause of higher ESR is the appearance of immature red blood cells during inflammatory diseases. All of these changes lead to more rapid sedimentation of blood cells, resulting in increased ESR.
Increased ESR observed with:
- Infectious diseases. An elevated rate is often diagnosed with bronchitis, ARVI, scarlet fever, sinusitis, rubella, cystitis, pneumonia, parotitis, as well as with tuberculosis and other infections.
- Poisoning, for example, caused by toxins in food or heavy metal salts.
- Helminthiasis and giardiasis.
- Anemia or hemoglobinopathy.
- Injuries to both soft tissue and bone. ESR also increases during the recovery period after surgery.
- Allergic reactions. ESR is increased in both diathesis and anaphylactic shock.
- Joint diseases.
- Tumor processes, for example, with leukemia or lymphoma.
- Endocrine pathologies, for example, in diabetes mellitus or thyrotoxicosis.
- Autoimmune diseases, in particular, with lupus.
ESR in case of infections
It should be remembered that for the diagnosis of infection take into account not only changes in the blood, but also the clinical picture, as well as history. In addition, it is important to note that after recovery, the ESR indicator remains elevated for several months.
About the rate of ESR and the causes of elevated rates, see the following video.
Symptoms
In some cases, the child does not bother at all, and a change in the ESR is detected during a routine examination. However, often high ESR is a sign of the disease, so the kids will have another symptom:
- If red blood cells settle faster due to diabetes, the child will experience increased thirst, increased urination, weight loss, the appearance of skin infections, thrush and other signs.
- With increased ESR due to tuberculosis the child will lose weight, complain of indisposition, cough, chest pain, headaches. Parents will notice a slight fever and a poor appetite.
- With such dangerous reason to increase the ESR as oncoprocess, the baby's immunity will decrease, lymph nodes will increase, weakness will appear, and weight will decrease.
- Infectious processesat which ESR rises most often, will manifest a sharp rise in temperature, increased heart rate, shortness of breath and other signs of intoxication.
What to do
Since the most often high ESR signals the doctor about the presence in the child's body of the inflammatory process, the change in this indicator should not be ignored by the pediatrician. In this case, the actions of physicians are determined by the presence of any complaints in the child.
As a rule, the disease activity and the level of ESR have a direct relationship - the more extensive the inflammation and the more pronounced the disease, the higher the ESR will be. And therefore, indicators of 13 mm / h or 16 mm / h are not as alarming the pediatrician as ESR 30, 40 or 70 mm / h.
If the child does not have any manifestations of the disease, and the ESR in the blood test is high, the doctor will send the child for further examination, which will include biochemical and immunological blood tests, chest x-rays, urinalysis, ECG and other methods.
If no abnormalities are detected, and increased ESR, for example, 28 mm / h, will remain the only alarming symptom, the pediatrician after a while will send the baby to retake the clinical blood test. Also, the child will be recommended to determine the C-reactive protein in the blood, which is judged on the activity of inflammation in the body.
If an increase in ESR is a symptom of any disease, the pediatrician will prescribe a drug treatment. As soon as the child recovers, the indicator will return to normal values. In case of an infectious disease, antibiotics and other medications will be prescribed for the child, and in case of allergies, the baby will be given antihistamines.
In any case, parents should understand that an increase in ESR is not an independent disease, but is only one of the symptoms. In this case, treatment should be directed to the reason due to which the red blood cells settle faster.
How to take an analysis
To avoid false positives (increased ESR without inflammation in the body), it is important to pass a blood test correctly. On the ESR affects quite a lot of factors, so that when passing the analysis it is recommended to conduct it on an empty stomach and in a calm state.
- You should not donate blood after an X-ray examination, eating, crying for a long time or physiotherapy.
- It is desirable that the child should eat before the blood draw no later than 8 hours.
- In addition, two days before the survey, very high-calorie and fatty foods should be excluded from the child’s diet.
- On the day before the analysis, the child should not be given fried or smoked dishes.
- Immediately before taking the baby’s blood, it is necessary to calm him down, because whims and experiences provoke an increase in ESR.
- It is not recommended to come to the clinic and donate blood immediately - it is better that the child rested for some time after the street in the corridor and was calm.
We recommend to see the release of the program Dr. Komarovsky, which details the topic of clinical analysis of blood in children.