Basophils in the blood of a child
White cells in the blood of a child are represented by several species. One of them is basophils, whose name is due to the staining of leukocytes with special dyes. Such shaped elements, although contained in the peripheral blood in a small percentage, are very important for maintaining the health of the child. What is their function, what is the level of basophils in healthy children and why can it change?
Why do we need basophils
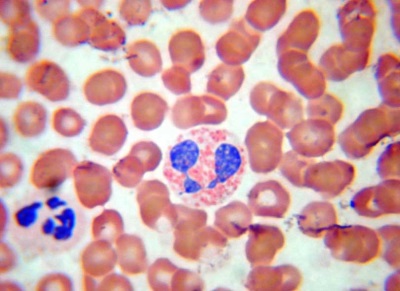
This type of leukocyte refers to granulocytes along with neutrophils and eosinophils, since there are granules inside these cells.
In the basophils in these granules are compounds, among which are histamine, prostaglandins, serotonins and many other substances involved in inflammatory and allergic reactions. Such cells do not last long in the blood (only a few hours), and then settle in the tissues and are there for about 10-14 days. After transition from the bloodstream to the tissue, basophils are called "histiocytes" or "mast cells."
Basophilic leukocytes are actively involved in immediate type allergies (anaphylactic reactions). In addition, due to the content of heparin, basophils are important for the regulation of blood clotting. Getting to the site of inflammation, colliding with an allergen, infectious agent or toxin, basophilic leukocytes release into the bloodstream the contents of their granules, resulting in increased vascular permeability, blood flow increases and other granulocytes are attracted. Basophils also have the ability to absorb foreign particles.
Norm in children
Elevated level
The reasons
Basophils also increase in many chronic pathologies and during infection with worms. Prolonged inflammation or allergies are factors that stimulate the formation of basophils in the bone marrow and their increased flow into the bloodstream.
An increased percentage of basophils is found in diseases such as:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Polycythemia.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Hepatitis.
- Chronic leukemia.
- Chickenpox.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Tumor processes.
- Diabetes.
- Poisoning.
If the child was treated with hormonal drugs, basophils in his analysis will also be increased. In addition, an increase in these leukocytes is provoked by the removal of the spleen, exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation, or iron deficiency.
What to do
If a child has a basophilic leukocyte count of more than 1% of all white blood cells, then the baby should be shown to a doctor. The pediatrician will assess the general condition of the child, complaints and other parameters of the blood test, after which he will look for the cause of elevated basophils (first of all - an allergy or inflammatory process).
Lack of basophils
A decrease in the percentage of basophilic leukocytes in a leukogram for many children is considered a variant of the norm. If the result of a child’s blood test shows a complete absence of basophils, this is not considered by doctors to be any diagnostically important criterion. A similar picture is observed under stress, during recovery from infectious diseases, after chemotherapy or with endocrine pathologies, however, changes in such diseases will not be limited to basophilopenia.
We recommend viewing the record of Dr. Komarovsky’s program on clinical analysis of a child’s blood: