Neonatal screening of newborns - genetic analysis of blood from the heel
Examination of newborns to identify their hereditary diseases is called neonatal screening. Such an analysis helps to detect diseases that are not determined in utero, but it is important to start treating them as soon as possible. The newborn must be examined for the presence of phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis, galactosemia, adrenogenital syndrome and congenital hypothyroidism.
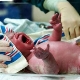
Such screening involves the selection of blood from the heel of an infant on the fourth day of life (if the baby is premature, then on the seventh day). It is necessary to take blood in three hours after the child has eaten.
Why blood is taken from the heel?
Since the fingers of a newborn baby are still very small, the blood for screening is taken from the heel. Heel crumbs rubbed with alcohol, then the skin is punctured one to two millimeters. Slightly pressing on the heel, an analysis form is applied to it, soaking the circles marked on it through.
Why 3 hours before the analysis can not be eaten?
In order for the test results to be reliable, it is important that the crumb did not eat anything three hours before the manipulation. About this warn all moms.
If we ignore this condition, then, according to many moms, additional experiences are provided related to possible false-positive analysis.

How many days to wait for the results?
The test results will be available within ten days after blood collection. Parents are informed about them only in case of deviations from the norm. If the performance of the baby will be increased, he is prescribed a re-examination of the disease, the likelihood of which there is a baby.