Elevated neutrophils in the blood of a child
Studying the blood test of a child, the number of leukocytes is given special attention, because their increase often indicates an infection or acute inflammation in the children's body. However, it is equally important to evaluate the leukocyte formula, which shows which white blood cells are higher than normal. These are often neutrophils, because they are normally represented in the peripheral blood in large quantities, and increase when exposed to various external factors. What do the high neutrophils detected in the child mean and how to normalize their number?
What level is considered elevated
Neutrophils represent the largest group of white blood cells, whose main task is the fight against pathogens. There are several forms of such leukocytes:
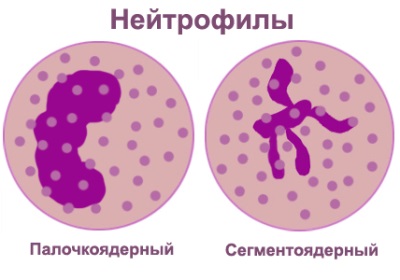
- Young (also called "metamyelocytes" and "myelocytes") - absent in the normal leukogram.
- Band neutrophils (sticks) - young cells, the content of which in newborns should not exceed 12%, in children under 5 years old - 5%, and in children over five years old - 4%. This is the upper limit of normal for this type of neutrophil.
- Segmental - the most numerous neutrophils, which are mature cells.
Their upper limit of normalcy in childhood is represented by the following indicators:
|
The newborn in the first days of life |
70% |
|
In infants from the 5th day of life to 1 month |
55% |
|
In children older than 1 month to a year |
30% |
|
In children older than a year |
35% |
|
In children over five years old |
55% |
|
In children over 10 years old |
60% |
If the level of neutrophil cells exceeds these indicators, it is called "neutrophilia».
We recommend to watch the video, where a specialist of one of the metropolitan clinics covers the topic of neutrophils in detail:
Causes of Neutrophilia
It should be noted that the level of neutrophils directly depends on the cause - the stronger the effect on the children's organism, the higher will be such white blood cells.
A slight increase in the percentage of neutrophils occurs during physical or psycho-emotional stress, as well as after meals. If the cause of a high number of neutrophils is a disease, the cell level is directly related to the activity of the disease.

Pathological causes of neutrophilia include:
- Active inflammatory processes, such as arthritis, pneumonia, dermatitis, inflammation of the pancreas, appendicitis, and others.
- Bacterial infections, including purulent (formation of an abscess or cellulitis).
- Some viral infections.
- Infections that caused protozoa or fungi.
- Tumor processes.
- Extensive burns.
- Poisoning.
- Diabetes.
- Trophic ulcer.
- The use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids.
- Acute blood loss or erythrocyte hemolysis.
Also, neutrophils are detected in an increased amount in the postoperative period.
Leukocyte Shift
In addition to increasing the number of neutrophilic leukocytes, doctors also estimate at the expense of what forms of these cells an increase in their percentage occurred. Diagnose:
- Shift Formula Left - stab cells are raised, and also young forms are present. This result is typical for severe intoxication, purulent infections, anemia (post-hemorrhagic or hemolytic), leukemia, and burns. If the displacement is small, it can be caused by intense training or emotional stress.
- Shift Formula Right - the number of sticks is low, and the percentage of segmented cells is increased. A similar pattern is less common than a shift to the left. It happens with anemia, polycythemia, leukemia and other pathologies.
See the release of Dr. Komarovsky’s program on clinical blood analysis. In it you will hear the answers to many questions that interest you:
What to do
If a child’s blood test showed an elevated level of neutrophils, parents should contact a pediatrician who will immediately send a baby for a re-examination, because the level of such leukocytes can be determined incorrectly due to the non-observance of such rules:
- The child must donate blood on an empty stomach. If it is an infant, then it should not receive food 2-2.5 hours before blood collection. Only a little bit of drinking water is allowed, as it does not affect the level of white blood cells.
- The child should be calm. It is best to have the mother come with the baby for blood sampling a little in advance, so that the crumb sat for a while in the corridor. This will eliminate the effect on the result of temperature drops.
- Exercise should be avoided immediately prior to collection. (do not allow the child to run in the clinic corridor) and the day before.
If a blood sample was taken taking into account such advice, but the leukocytosis is still caused by a high level of neutrophils, the doctor will order an additional examination. First of all, it will be aimed at identifying an infection or an active inflammatory process.
As soon as the cause of neutrophilia is detected, the baby will be given the necessary treatment. When the children's body with the help of the drugs used to cope with inflammation or an infectious process, the level of neutrophilic leukocytes also normalizes.