Low hemoglobin in infants
Hemoglobin in an infant can be reduced for several reasons. And before you panic, seeing the figure below the norm in the form of a blood test, parents should find out how it is dangerous for babies and how to raise hemoglobin in a child under one year old.
What hemoglobin is considered reduced
Normally, the hemoglobin of a newly born baby is very high and amounts to 180-220 g / l, and from the second week of life it begins to decline, reaching 110-130 g / l by the age of 12 months.
The lower limit of hemoglobin in the blood of a child in the first year of life is considered to be the following indicators:
|
Have a newborn |
145 g / l |
|
In 1 month |
110 g / l |
|
In 3 months |
95 g / l |
|
In 6 months |
110 g / l |
|
In year |
100 g / l |
If the hemoglobin is lowered slightly, it will alert the doctor, but will not yet require treatment, since a small deviation can be corrected by some changes in the diet and lifestyle. If the hemoglobin level in children of the first year of life is greatly underestimated, for example, immediately after birth below 130 g / l or 9 months below 100 g / l, this is the reason for a more detailed examination to determine the cause of the decrease, and then prescribe a suitable therapy.
Reasons for the decline
The most common cause of low hemoglobin in the blood of a child is anemia, provoked by a lack of iron.
In infants, such a deficiency often causes anemia in the mother, which appears when of pregnancy or during breastfeeding. Because of this condition, the baby cannot accumulate iron during fetal development and loses it in breast milk, which leads to a decrease in hemoglobin level.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky about the level of hemoglobin in a pregnant and nursing mother, see the issue below:
Also, iron deficiency in infants can be caused by too late introduction of complementary foods, the refusal of a child older than 6 months from meat or fruit complementary foods, a vegetarian diet of the nursing mother and insufficient activity of the infant.
Other causes of low hemoglobin in babies younger than a year are:
- Complications of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Hasty circumcision of the umbilical cord.
- Prematurity
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Anemia caused by deficiency of vitamins B9 and B12.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Bleeding - both acute and chronic.
- Transferred operation.
- Genetic anomalies of erythrocyte formation.
- Infectious disease.
- Pathology of child development.
Symptoms of anemia
The following signs will help to suspect a too low level of hemoglobin in an infant:
- Drowsiness, drowsiness and the rapid appearance of fatigue.
- Pale skin color of the cheeks and palms.
- Moody behavior.
- Dry skin and peeling.
- Worse sleep
- Refusal of food.
- The appearance on the nails of white spots and stripes.
- The appearance of circles under the eyes.
- Increased body temperature without acute respiratory infections, allergies or other diseases.
- Frequent colds and SARS.
What is dangerous low hemoglobin
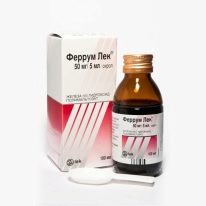
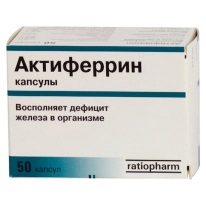
Treatment
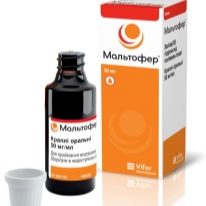
Medicines
Any of these drugs should be prescribed by a doctor, making sure that there are indications for their use and the absence of possible contraindications.
Giving the child iron supplements alone is unacceptable. In addition, some babies have side reactions when taking iron supplements, such as regurgitation, skin rash, vomiting, and others. In this situation, you should stop taking and talk about the side effects of a pediatrician for the selection of another medication.
What to eat
When breastfeeding to adjust the food should be mom, adding to it products that contain quite a lot of iron:
- Beef
- Liver.
- Low-fat pork.
- Grenades.
- Buckwheat groats
- Wheat and barley grits.
- Apples
- Lentils
- Pistachios and other nuts.
- Oatmeal.
- Beetroot.
- Dried apricots
- Blueberries
- Turkey
It is important to remember that the absorption of iron from food is improved under the influence of ascorbic or lactic acid. At the same time, iron contained in meat products is best absorbed. The presence in the diet of soy protein, polyphenols from legumes, nuts, tea, as well as excess dietary fiber and calcium, on the contrary, affects the absorption of iron.
When artificial feeding should be discussed with a pediatrician the question of the earlier introduction of complementary foods, in particular, fruit and meat puree.
Opinion Komarovsky
A popular pediatrician confirms that the most common cause of lowering hemoglobin iron deficiency anemia appears in an infant. He explains this by the depletion of iron stores in a child by the age of 5-6 months. For this reason, Komarovsky advises all infants at this age to undergo a clinical blood test, especially if the mother had low hemoglobin during the pregnancy period.
With regard to treatment, a well-known doctor claims that iron-rich foods only help prevent a decrease in hemoglobin or delay the progression of anemia. If the level of hemoglobin in an infant is already lowered, Komarovsky recommends that you adhere to the recommendations of your doctor and give your baby iron supplements.
The full release of the program by Evgeny Komarovsky, which details the topic of low hemoglobin in children, see below:
Prevention
To prevent a decrease in hemoglobin in a child under one year old, it is recommended:
- Treat anemia in the future mother during gestation. Women should pay attention to their diet, enriching it with iron-containing food, so that the fetus can accumulate enough iron by the time of birth. Also, if indicated, pregnant women are prescribed multivitamins and iron supplements.
- Breastfeed the baby, because my mother's milk contains iron, which is absorbed much better than from iron-rich milk formula. This is facilitated by the content in the mother's milk lactoferrin enzyme. Its presence not only helps to digest the gland from human milk, but also contributes to a better absorption of iron from complementary foods after its introduction (this leads to a recommendation to continue to breastfeed at least 1-1.5 years).
- Long regularly walk with the baby on the street. Thanks to these walks, the blood will be enriched with oxygen, which will be a stimulus for the production of red blood cells.
- Introduce complementary foods in a timely manner, starting at 6 months of age, when the infant’s own iron stores run out. At the same time, it is important to comply with modern recommendations, since the presence of semolina and cow milk in the diet of a child up to the year increases the risk of anemia.
- To make a baby blood test at 6 months to assess the level of hemoglobin. It is also recommended to check the content of ferritin, as this will help determine whether the crumbs of iron reserves.