The rate of red blood cells in children
In assessing the health of a child, laboratory methods are of great importance, among which the main one is blood test. After receiving the results of such an analysis, the physician will necessarily evaluate the sedimentation rate and the number of red blood cells, also called red blood cells.
Such cells are very important for maintaining the health of children, therefore any problems with their education or disintegration affect both the state of health and the development of the child. For this reason, parents should know how many red blood cells a child of a particular age should be normal for, why the number of such cells can vary and what to do if a blood test showed an excess of the norm or a shortage of red cells.
The role of red blood cells
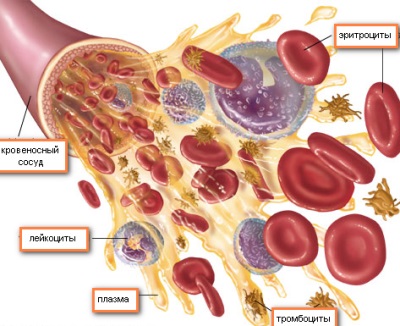
The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body. In addition, they "take" carbon dioxide from the tissues and deliver it to the lungs to be removed from the body. Performing functions like erythrocyte staining ensures the presence of a protein called hemoglobin inside these cells.
Daily new red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow. After entering the bloodstream, they circulate in the blood for about 120 days, after which they begin to "grow old" and as a result are destroyed in the spleen and liver. Since normally the formation and disintegration of red cells occurs continuously, the number of red blood cells is also constant.
In addition to participating in tissue respiration, red blood cells are important for:
- Transfer of amino acids.
- Enzyme transport.
- Autoimmune and immune responses.
- Maintain acid-base balance.
- The blood clotting process.
We recommend to watch the informative video on the function of red blood cells in the human body:
How to determine the number of red blood cells
What affects the number of red blood cells
The main factor on which the number of red cells depends is the age of the child. The newly born babies have more red blood cells in their blood than a child of 2 years or 3 years. For this reason, in order to properly evaluate the results, the patient’s age must always be marked on the form.
Other factors whose exposure to red blood cells becomes more or less are:
- Stress and exercise.
- Partial pressure of oxygen
- Different diseases.
Table by age - normal values
The normal number of red blood cells at different ages in children is as follows:
|
Have a newborn |
From 5 x 1012/ l to 7 x 1012/ l |
|
On the fifth day of life |
From 4.5 x 1012/ l to 6 x 1012/ l |
|
From the 10th day of life |
From 4.5 x 1012/ l to 5.5 x 1012/ l |
|
In infants over the age of one month |
From 4 x 1012/ l to 5 x 1012/ l |
|
A year or older |
From 4 x 1012/ l to 4.5 x 1012/ l |
|
From the age of 15 |
From 4 x 1012/ l to 5.5 x 1012/ l |
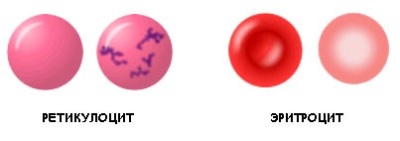
Reticulocyte
So called young forms of red blood cells, which are normally present in small quantities in the blood of each person. They are counted in a ppm blood test.
The maximum number of reticulocytes is observed in newborns (10-40 ‰), but from the fifth day after birth, their number decreases, and sometimes they are not determined at all (the norm for a child under a month is 0-15). In infants 1 month and older, reticulocytes are found in the amount of 5-13 ‰, and from 5 years of age - 3-10.
An increase in the number of reticulocytes is observed after bleeding and during the treatment of anemia. Also, the identification of these erythrocyte precursors in large numbers is characteristic of hemolytic anemia, thalassemia, malaria, and bone marrow damage by a tumor.
Erythrocyte indices
In addition to the total number of red blood cells in modern clinical analysis and determine other indicators associated with red blood cells. They are called erythrocyte indices. Such indices are calculated values that can be used to judge the shape, size and other physical characteristics of red blood cells. It helps in the diagnosis of anemia.
There are such indices:
- The average volume of the red blood cell. This parameter allows you to estimate the size of red cells and is designated in the analysis as MCV.
- Red cell distribution width. This parameter shows how big the difference is in the size of the red bodies. Its designation is RDW.
- The average content of hemoglobin. This parameter (MCH) determines how much hemoglobin is contained in 1 erythrocyte.
- The average concentration of hemoglobin. On this parameter, denoted as MCHC, judge the saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin.

Red blood cell count
Below normal
When a reduced red blood cell count is detected in a child, it is called erythropenia. If the child drank a lot of fluid before taking the test, erythropenia will be relative and will not affect the health of the baby. Erythropenia due to disease is called absolute. It provokes:
- Insufficient formation of red cells in the bone marrow. This is due to nutritional deficiencies (with B12 and iron deficiency anemia), a bone marrow tumor, exposure to radiation, toxic substances, medications.
- Accelerated destruction of red blood cells after entering the bloodstream. It can occur under the influence of infection, autoimmune reactions, poisons, drugs and other damaging factors. This cause of erythropenia is observed in hemolytic disease, whooping cough, collagen diseases and other diseases.
- Blood cell loss due to frequent nasal bleeding, fractures, surgeries, ulcerative lesions of the intestines, as well as kidney disease, in which red blood cells enter the urine.
You can suspect erythropenia in a child because of his lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue, pallor, weakness, reduced appetite and other symptoms.
If you do not consult a doctor with such signs of red blood cell deficiency, hypoxia affecting the internal organs of a child can lead to disruption of their work, reduced immunity and even developmental delays.
Above normal
In addition, erythrocytosis occurs in children who live in highlands, as well as in those who suffer from passive smoking.
We recommend to see the release of Dr. Komarovsky’s program on clinical blood analysis. It describes in detail all the indicators that need to be paid attention to in the diagnosis of diseases of the child:
True erythrocytosis, the cause of which is the greater number of red blood cells, is often due to the excessive formation of such cells in the bone marrow. A similar situation is observed in erythremia, chronic respiratory diseases, congenital heart defects, Cushing disease and kidney tumors with increased production of erythropoietin.
Pathology is manifested by reddening of the skin, the appearance of burning pain in the limbs, an increase in blood pressure, an enlarged spleen, and other symptoms.
If, together with the doctor, you don’t find out the cause of the increased number of red blood cells and do not start the correct treatment, the child’s blood will become more viscous, which can lead to the appearance of blood clots and deterioration of the blood supply to various organs, including the brain.