The rate of neutrophils in the blood of children
Leukocytes are important blood cells that protect the child from various external or internal adverse factors. Such cells are on guard for children's health and are responsible for immunity. The largest group of these white bodies is neutrophils. What are these leukocytes responsible for and what should be the normal neutrophil count in childhood?
The role of neutrophils
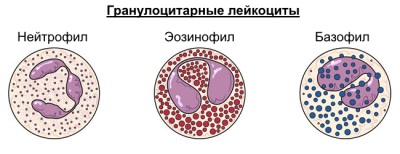
These white blood cells, which, together with basophils and eosinophils, are referred to as granulocytes (they contain granules with enzymes and antibiotic proteins), designed to capture harmful bacteria and other small particles. They are able to move to places of damage and inflammation.
When a neutrophil absorbs a foreign cell or particle, it dies with the release of active compounds that damage bacteria and increase inflammation, thereby attracting other immune cells to the site of infection. Dead neutrophilic leukocytes, along with tissues that have collapsed during the inflammatory process, as well as microbes that cause inflammation, form a purulent mass.
How to determine the level of neutrophils
To find out how much neutrophils are contained in a child’s blood, it is possible from a general blood test if the leukocyte formula is determined in it.
Such cells are calculated as a percentage of all leukocytes. To the result of the analysis was reliable, it is important to consider the following nuances:
- Neutrophil count may increase after a meal., therefore, the analysis is advised to take on an empty stomach. The child can only drink a little clear water before the blood is taken, and if blood is taken from the baby, then it should not be fed two hours before the test.
- The amount of leukocytes is affected by physical activity, and psychoemotional stress.
- The number of neutrophils may be unreliable due to temperature changes, for example, if a child entered the office to donate blood immediately after being in the cold.
We recommend to see the release of the program of children's doctor Komarovsky, which highlights the question of what is a clinical blood test:
Types of neutrophils
All neutrophilic leukocytes, found in peripheral blood and determined during tests, are represented by the following forms:
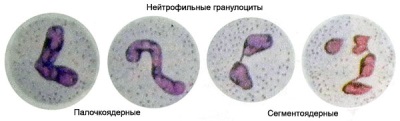
- Young neutrophils. In the analysis form they can also be seen as “metamyelocytes” and “myelocytes”.
- Band neutrophils ("Chopsticks"). These are young cells, inside of which there is a rod-shaped nucleus.
- Segmental cells. These are mature neutrophils with a segmented nucleus, represented in the largest number among all neutrophilic leukocytes.
Norm for children
Normally, there are no young neutrophils in the child’s blood, and their appearance is called shift the formula to the left. As for stab neutrophils, their number is small, and an increase in their percentage is also attributed to a shift to the left.
The norm "chopsticks" consider:
|
Have a newborn |
From 5% to 12% |
|
From the fifth day of life |
From 1% to 5% |
|
In children over 5 years |
From 1% to 4% |
The rate of segmented neutrophils for different ages is as follows:
|
Have a newborn |
From 50% to 70% |
|
On the 5th day of life |
From 35% to 55% |
|
One month old baby |
From 17% to 30% |
|
One year old child |
From 20% to 35% |
|
At the age of five |
From 35% to 55% |
|
In children older than ten years |
From 40% to 60% |
Neutrophil level change
Above normal
If the neutrophils in the blood go up, it is called neutrophilia. Minor neutrophilia is triggered by non-hazardous factors, such as food intake, stress or exercise. High neutrophilia in children often indicates an active inflammatory process or infection with pathogenic microbes.
This increase in white blood cells is detected in appendicitis, pancreatitis, otitis, pneumonia, sepsis and other infections caused by bacteria. With a fungal or viral infection, these cells rise much less frequently. Also, the cause of neutrophilia can be burns on a large area of the body, poisoning, taking certain medications, leukemia, trophic ulcers, bleeding and other pathologies.
If a child has an increase in neutrophils, and repeated blood tests confirmed this, the doctor will look for inflammation and infection, and if such causes are not confirmed, other diseases. After diagnosis and the appointment of a suitable treatment (for example, a course of antibiotics when infected with bacteria), the level of neutrophils will soon return to normal.
Below normal
The absence of stab neutrophils can be a sign of aplastic anemia, as well as a consequence of chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Low neutrophils are also found in anaphylactic shock, infection by fungi, lesions of the pancreas, high spleen activity and tumor processes. Separately allocate congenital neutropenia, which the child inherits from the parents.
In addition, neutropenia also occurs. benign. This feature is detected in children of the first year of life and does not manifest clinically. By 2 years of age, the level of neutrophils in such babies is normalized independently.
If the analysis revealed a neutrophil deficiency, it is important to immediately show the child to the doctor, as this is often a sign of a decrease in his defenses. As soon as the reason for the decrease in the percentage of such leukocytes is clarified, the child will be given treatment, as a result of which the neutrophil count will be restored to normal values.