What to do with elevated fibrinogen during pregnancy?
Disorders of blood clotting can cause a tragedy for the parturient, because it is important that the bleeding quickly after the birth of the baby quickly stopped. That is why during pregnancy a woman checks blood clotting indicators, including fibrinogen analysis. About what it is, and what to do if its quantity is increased, we will tell in this article.
What it is
The mechanisms of blood clotting are quite complex and multi-stage. At each stage, different substances that are synthesized by the body contribute to the formation of a thrombus.
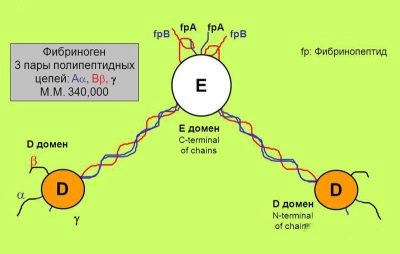
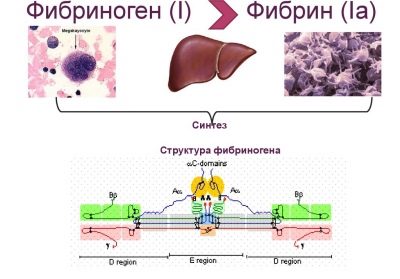
Fibrinogen is a plasma protein dissolved in the blood. As soon as the organism has a need to bring the coagulation system into combat readiness (a person has cut himself, got burned, he is undergoing an operation), fibrinogen begins to disintegrate under the action of thrombin, a special enzyme.
As a result, a fibrin monomer is formed, which precipitates in the form of filaments, with which the wound is “bound” by a thrombus, preventing further blood loss. Fibrinogen is produced by the liver. The concentration of this important protein is an informative indicator of hemostasis. If the blood plasma is completely free of fibrinogen, it becomes serum.
During pregnancy, the amount of blood circulating in the body of the future mother increases, due to this its composition may change. therefore a blood coagulation test is important for managing pregnancy and the choice of tactics of delivery.
In order to prevent massive bleeding that threatens a woman’s life, it is important to know how long her blood can clot, and accurate knowledge of the amount of fibrinogen in the blood of a future mother helps her doctors.
The greatest danger during childbirth is the birth of the placenta, which is always accompanied by bleeding of greater or lesser intensity.
How is the analysis done?
The level of fibrinogen is determined in a comprehensive analysis, which is called a coagulogram or PPMK analysis. The analysis is considered necessary during pregnancy and during the prenatal period, no matter how planned the birth is planned - naturally or by caesarean section.
There is no separate analysis for fibrinogen concentration. - its values are studied together with other substances and criteria for blood clotting.
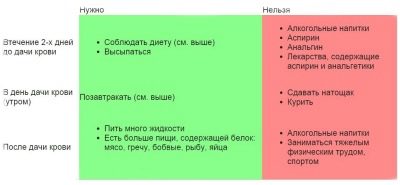
A blood sample is taken from the future mother's vein. Before analysis for several days you should avoid fatty and spicy foods, and you should also eliminate all stress factors, feelings, because under the influence of stress, the qualitative composition of blood changes due to changes in the hormonal background of the woman.
Blood should be taken on an empty stomach, if the laboratory visit is scheduled for the morning, then the last meal should be the night before.
Before analyzing it is important not to burden yourself physically, rest more. If a pregnant woman could not give up the bad habit of smoking, then an hour before taking a blood sample should refrain from smoking, since nicotine affects blood clotting factors, and the result of the analysis may not correspond to reality.
With the blood taken in the laboratory, numerous metamorphoses will occur - to begin with, its fluid component is released from it, which provides fluidity - plasma. It determines the amount of fibrinogen and other components of clotting.
There are several ways to detect fibrinogen.Test systems that are currently in service with virtually all laboratories may act differently: paint fibrinogen in a certain color, determine its weight, and evaluate it by chemical composition.
Most often, reagents that cause processes similar to natural processes in it are added to the resulting plasma. Fibrinogen begins to "cooperate" with thrombin, yarns of febrin monomer are formed, and it is them who are weighed and evaluated by laboratory technicians.
Sometimes the yarns obtained are dissolved in a colored solution and the degree of color and concentration of the substance are evaluated. Actually the way of analysis should not worry much about the future motherAfter all, all test systems that are currently used give quite accurate results.
Norms
The body of a woman begins to prepare for childbirth in advance. Even if a woman is about to give birth for the first time, and her body has never experienced anything like it, genetic “memory” tells you what to do and when.
That is why in pregnant women, the level of febrinogen in the blood plasma is increased compared with non-pregnant women and men. Gradually, the concentration of this protein substance increases, especially in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. In this way, the body prepares for the imminent blood loss that will accompany the birth of a new person.
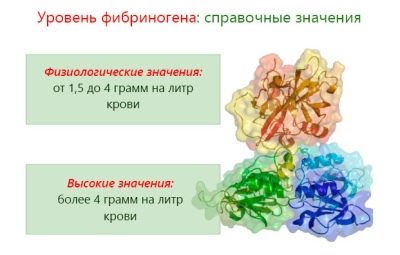
The normal values of febrinogen during pregnancy, therefore, differ from the values adopted as the norm for other categories of patients.
Table of normal values of fibrinogen for pregnant women:
|
Obstetric term (weeks) |
Fibrinogen concentration - minimum |
Fibrinogen concentration - maximum |
|
1-13 |
2.12 g / l |
4.33 g / l |
|
13-21 |
2.90 g / l |
5.30 g / l |
|
21-29 |
3.00 g / l |
5.70 g / l |
|
29-35 |
3.20 g / l |
5.70 g / l |
|
35-42 |
3.50 g / l |
6.50 g / l |
A slight decrease in fibrinogen in the first trimester of pregnancy is considered to be completely normal.
By reducing blood viscosity, the body creates more favorable conditions for the initial stage of development of the baby in the womb.
New blood vessels that connect the baby and the mother's body can not be loaded, the blood should be more liquid and flow faster. That is why the body reduces the amount of fibrinogen.
From the second trimester, as can be seen from the table, the plasma protein concentration values begin to rise. By this point, the vessels of the placenta, the umbilical cords are fully formed, they no longer need a sparing mode of operation, and the body of the future mother should be prepared for childbirth.
In the third trimester, an additional increase in febrinogen in a woman’s blood is considered normal. However, exceeding the protein level above the established upper threshold can be an alarming sign.
Reasons for raising
If the coagulogram shows that febrinogen is elevated in the expectant mother, the attending physician will certainly try to find the true cause of the bleeding disorder.
With increased fibrinogen clotting time decreases, a clot forms faster. In terms of preventing bleeding, this is very good. But blood clots can be dangerous for a woman by themselves.
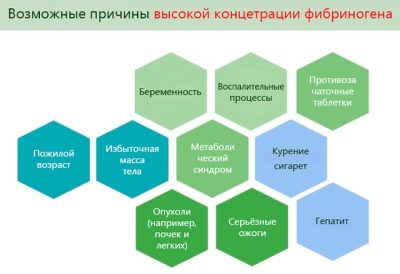
Most common The reasons why the level of febrinogen may be above the norm are as follows:
- Toxicosis. Any toxicosis, especially if it is pronounced and occurs with nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, causes mild (and sometimes not only mild) dehydration of the body. In response, the blood becomes more "thick."
- Inflammatory diseases, infections. If the future mother has any, then the viscosity of the blood also increases due to large losses of moisture.
- Stress and physical overload. If a woman is in a dysfunctional psychological environment, she is nervous, she produces a lot of stress hormones. Almost the same happens with excessive physical exertion.The body reacts to the appearance of these hormones in the blood with increased “alert”, and the blood coagulation system is also included in it. Fibrinogen rises.
- Thyroid function failure. The low content of hormones produced by this gland also affects the ability of the blood to clot, the blood becomes more “thick”, the risk of thrombosis increases.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Ailments can be both chronic and develop for the first time on the background of pregnancy. The analysis of the PCM in this case will not be the main, but important in the diagnosis.
- Oncological diseases. Recently, unfortunately, the number of detected malignant tumors in pregnant women is growing. What is the reason, hard to say. Specialists tend to consider as the main version of the global adjustment in the female body, which come along with the "interesting position."
Possible consequences
"Thick" blood has not benefited anyone yet. This statement is especially true for future mothers. Slightly excess protein fibrinogen in pregnant women is easily corrected and doesn’t cause great concern to health workers. However, a significant increase in plasma protein levels above the norm can cause serious consequences, both for the woman and for her child.
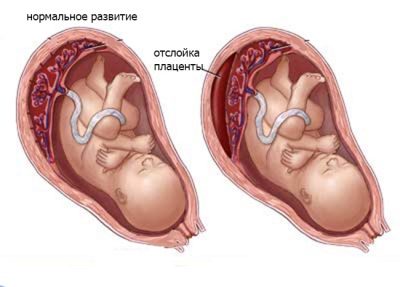
Among the most dangerous threats are spontaneous abortion and the death of the baby, thrombosis of the uteroplacental vessels and also the subsequent death of the child, premature detachment of the placenta, which again constitutes a mortal danger.
A woman can develop thrombophlebitis. In some cases, there is a high risk of pulmonary thrombosis, which can cause the death of the expectant mother.
"Thick" blood with a high content of fibrinogen does not allow the child to get all the necessary nutrients, due to what the intrauterine growth retardation can begin, and the lack of oxygen, which the baby also receives from the mother's blood through the mother-placenta-fetus system, can cause the development of a dangerous and serious condition - fetal intrauterine hypoxia.
Treatment
If febrinogen is elevated during pregnancy, this is not a reason to panic and beat all the bells. This only means that the woman needs additional examination and proper treatment.
First of all, the doctor must find out if everything is in order with the baby. For this woman will be offered to go unscheduled ultrasound scan. If the gestation period is large enough, a USDG will be prescribed to assess the speed and quality of uteroplacental blood flow.
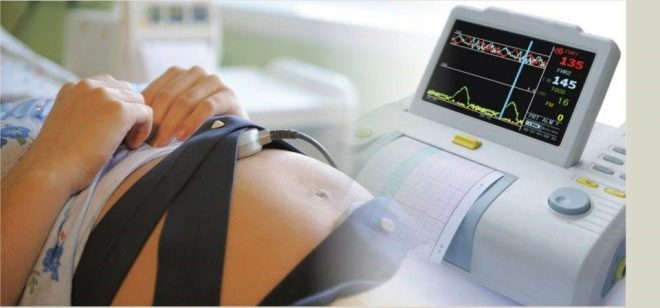
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the expectant mother will be asked to do unscheduled CTG to make sure that the crumb does not experience hypoxia and other problems.
To find the reasons for increasing febrinogen, a woman will be prescribed detailed blood tests. They must show whether there are inflammatory processes, whether everything is in order with the hormonal background.
With a slight increase, it is enough to adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother in order to gradually lower the protein concentration in the blood, and the coaglogram already assigned after a short time will not show alarming results.
Correction includes sufficient drinking regime. A woman should take as much water as the doctor will allow her to make the blood thinner, but not cause the formation of edema.
To do this, in the diet injected vegetables and fruits. with high content of vitamin C. Fresh tomatoes, sea buckthorn, cranberries, and viburnum berries “dilute” the blood well. If there is spring in the yard, fresh natural birch sap will help well (the juice in the cans has no relation to this birch sap).
At another time of the year, braised courgettes and cabbage come to the aid of the expectant mother.
If the “home” correction did not help, and the next blood test showed fibrinogen excess, the attending physician prescribes the B group's vitamins to the future mother, and in large doses.
At any stage of pregnancy can be assigned folic acid tablets, small doses of the most common aspirin. Usually such treatment is more than enough to reduce the level of febrinogen.
If, despite attempts to normalize the level of this plasma protein, the indicators of febrinogen do not decrease or its concentration rises, the woman is referred for consultation to a narrow specialist - a hematologist.
He will investigate the true causes of the pathology and prescribe one of the existing drugs - antiplatelet agents, which he deems necessary and acceptable for use during the child's bearing period.
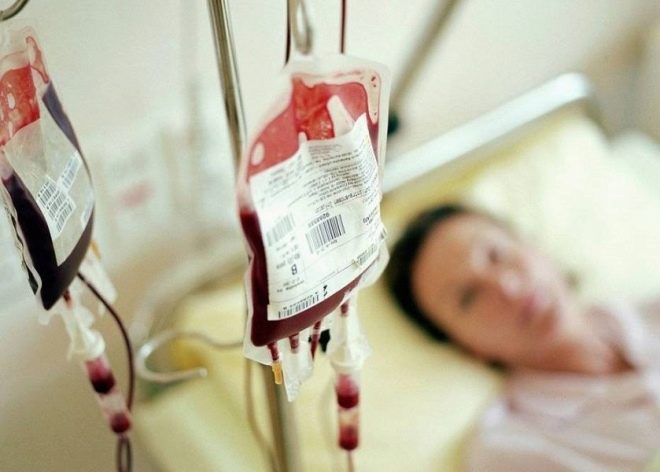
If before delivery it is not possible to lower the level of febrinogen in the blood, the birth process of the baby will take place under special control. In the delivery room, in addition to the obstetric team, there will be specialists in the field of hematology who will not allow tragic consequences in childbirth and will support the woman with medication and methods necessary in a particular situation, including replacement blood transfusions.
Reviews
Most of the expectant mothers, who left feedback on increasing the level of fibrinogen in the blood, noted that this happened to them only in the third trimester. More earlier enhancements happen much less frequently.
For the most part, doctors prescribed small doses of aspirin to women to thin the blood. Doctors recommend taking many women with this problem in parallel "Curantil" to improve uteroplacental blood flow.
Women who have had early bleeding disorders have been repeatedly treated for pregnancy with low molecular weight heparin during pregnancy. "Clexane"whose shots are put in the stomach.
Pregnancy in most cases can be successfully communicated to the due date. Treatment of children does not affect the state. For more information on what to do with increasing fibrinogen during pregnancy, see the following video.