Increased blood hematocrit in a child
In the children's blood test there are indicators that are understandable to parents, for example, the level of hemoglobin or the number of red blood cells. However, there are in the form and indicators, the value of which is unknown. And if they are also elevated, it causes anxiety. One of these indicators is hematocrit. What does this mean in a child's blood test, what should be the normal hematocrit, and why is it elevated?
Why determine hematocrit
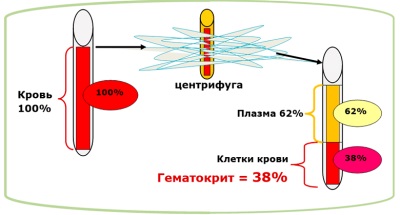
Evaluation of hematocrit allows you to see how much blood cells occupy, that is, determines the thickness of the blood. He evaluates all blood cells at once, that is, leukocytes and platelets, as well as red blood cells. But, since the red blood cells prevail among all the formed elements, it is their content that most influences the hematocrit.
Norm for children
Hematocrit is measured in percent and for each age this indicator will be different. The norm for children are such results:
|
Have a newborn |
56% |
|
On the fifth day of life |
53% |
|
From the tenth day of life to the end of the first month |
49% |
|
From 1 month to a year |
45% |
|
In children 1-5 years |
35% |
|
In children 5-10 years |
37% |
|
In children 10-15 years |
39% |
|
In children over 15 years |
47% |
An excess of the norm is indicated if the hematocrit is more than 62% in a newborn infant and infant, and in children older than a year before adolescence, it exceeds 44%.
Causes of hematocrit increase
High hematocrit does not always indicate a disease. This parameter of a clinical blood test may also increase when exposed to various external or internal factors, when the internal balance in the children's body is disturbed, which causes the activation of compensatory mechanisms. In such cases, changes in hematocrit are temporary and do not affect the general condition of the child.
Pathological causes of high hematocrit include:
- The state of dehydration. This is a fairly common cause of increased blood density, caused by loss of plasma, which can be observed with an insufficient amount of fluid drunk, overheating, vomiting or diarrhea, and intense sweating during exercise. As soon as water is lost by the tissues, the body compensates for its deficiency with liquid from the blood (plasma), which leads to an increased number of blood cells in the bloodstream.
- Chronic hypoxia. When cells and tissues lack oxygen for a long period, it stimulates the increased formation of red blood cells to eliminate oxygen deficiency. As a result, the number of erythrocytes in the bloodstream rises, which causes a high hematocrit. At the same time the volume of blood remains unchanged. This situation is possible with chronic lung diseases, diabetes, heart defects, passive smoking, staying in the mountains (mountain air contains less O2).
- Erythremia. Such a tumor disease affecting the bone marrow causes more blood cells to form in it. They are increased in the amount of peripheral blood and will be determined in a higher percentage.
- Prolonged use of certain medications. To drugs, because of which the hematocrit rises, in the first place include hormonal and diuretic drugs.
- Burns, injuries and bleeding of different localization. The consequence of such effects will be the loss of blood for the most part due to plasma, so the hematocrit in the general analysis will be higher.
- Kidney diseases which in a child can be both acquired (tumors, polycystic and other) and congenital. Due to the increased loss of fluid in the urine, such pathologies provoke blood clots and an increase in hematocrit.
What is dangerous high hematocrit
Overlapping clots of small vessels leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to important organs, including the brain and heart. In the worst cases, stroke, gangrene of the extremities, respiratory failure or heart attack are possible.
What to do
Having detected an elevated hematocrit in a child, you should consult a pediatrician, because such a change in the blood test may not be dangerous and be a sign of a serious illness. The doctor will be able to correctly decipher the analysis, determine the cause of the increase in blood density and prescribe a treatment that will help return the hematocrit to a normal indicator. In therapy, blood thinners and other drugs can be used. Parents will be advised to give the child more drink, limit the foods rich in animal fats or iron in the child’s menu.