The child has elevated red blood cells
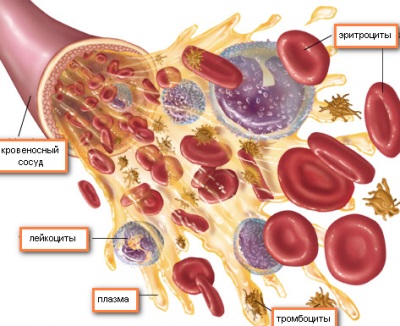
The most numerous group of blood cells are red blood cells. Their changes, which are assessed by a general blood test, help to identify various diseases in childhood and help the child in time for serious pathologies.
Most often, the number of red blood cells decreases, with which most pediatricians in their practice, including the popular doctor Komarovsky, face. However, there is an increase in their number, so many parents are interested in what the term “erythrocytosis” means and if it is dangerous for children, and also what to do if the child has elevated erythrocytes in the blood.
The release of the famous doctor’s program on clinical analysis of a child’s blood can be found in the video below:
What number of red blood cells is considered elevated
Red cells are called red cells, the main function of which is the transport of gases in the human body. These blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all organs and tissues, ensuring their nutrition and normal function.
The upper limit of the normal number of red blood cells at different ages is considered:
|
Newborns |
7 x 1012/ l |
|
On the 5th day of life |
6 x 1012/ l |
|
On the 10th day after birth |
5.5 x 1012/ l |
|
In infants in 1 month |
5 x 1012/ l |
|
In children older than a year |
4.5 x 1012/ l |
|
From the age of 15 |
5.5 x 1012/ l |
If the number of erythrocytes in the form of analysis is greater than the indicated numbers, this condition is called erythrocytosis. When it is detected, it is important to find out whether such an indicator is due to physiological reasons or is caused by some serious illness.
Types of erythrocytosis
Depending on the reason that led to quantitative changes in blood cells, there are two types of erythrocytosis:
- Relative. With such an increase, the real number of erythrocytes is not increased, and erythrocytosis itself is due to thickening of the blood and plasma loss, for example, due to dehydration due to sweating, diarrhea, very dry indoor air, vomiting attacks, high temperature and other factors.
- Absolute. Such erythrocytosis, which is also called true, is associated with an increase in the number of red blood cells. Most often it occurs due to the increased formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
The reasons
One of the non-dangerous factors provoking the appearance in the child's blood of an increased number of red blood cells is living in a mountainous area. In such a situation, the compensatory appearance of a larger number of red blood cells helps prevent altitude sickness.
If the child does not live in the mountains, a slight increase in the number of red blood cells is due to:
- Diarrhea or vomiting with intestinal infection.
- Increased body temperature with SARS or other diseases, a symptom of which is fever.
- Intense sweating on exertion or high temperature.
- Regular sports training.
- Stay in hot climates or in a room with dry hot air.
- Passive smoking of a child when one of the parents often smokes in his presence.
- The use of poor-quality water, in which there are impurities of chlorine, as well as the child's fascination with soda water.
Relative erythrocytosis can cause extensive burns, due to which the child loses proteins and plasma, and the blood condenses. In newborns, an increased number of red blood cells is often associated with hypoxia, which the infant experienced in the womb.
True erythrocytosis causes such diseases as:
- Erythremia. Her other names are Vaesa-Osler disease and polycythemia. With this pathology in the bone marrow, all blood cells are actively produced, but red blood cells are produced more than the rest. This is a benign tumor process that can provoke ionizing radiation, toxic damage to the bone marrow, or a gene mutation.
- Chronic respiratory diseaseespecially with obstruction. Due to prolonged hypoxia caused by frequent bronchitis, bronchial asthma and other diseases of the lung erythrocytes in the body of the child more is formed to provide the cells with oxygen in the volume they need.
- Congenital heart defects, especially from the group of "blue", in which there is a lack of blood circulation in the lungs (for example, Fallot's tetrad).
- Hypernephromain which more erythropoietin is produced in the kidney, a substance that stimulates the development of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Itsenko-Cushing disease. With this pathology, more corticosteroid hormones are produced that stimulate the bone marrow and inhibit the function of the spleen.
Symptoms
In most children, relative erythrocytosis does not show any specific symptoms. If it is caused by the development of a viral or intestinal infection in a child, the symptoms will correspond to the underlying disease.
You can suspect a true erythrocytosis in a child by:
- Purchase red skin. The skin tint in a child becomes pink first, and then darker, sometimes purple-bluish. At the same time, changes are noticeable on all parts of the body, as well as on mucous membranes.
- The appearance of pain in the toes and hands. This symptom is caused by impaired blood flow in small vessels, since blood viscosity increases due to the large number of red cells. Due to oxygen starvation, which develops in the tissues, burning stinging pains appear.
- The frequent occurrence of headaches. This symptom is due to the deterioration of blood circulation in small cerebral vessels.
- Enlarged spleen. The work of this organ is connected with the utilization of blood cells, therefore, with an excess of red blood cells, the spleen is overloaded, as a result of which the size of this organ increases.
- The appearance of a persistent increase in blood pressure. This symptom is inherent in erythrocytosis caused by renal pathology. At the same time, high blood pressure causes fatigue in the child, vision loss and other symptoms.

What is dangerous erythrocytosis
What to do with a higher value
If a high level of red blood cells is found in a child’s blood, this is always a reason for a more thorough examination. First, the child will be assigned a second blood test to ensure that there is no error. If the excess of the red blood cell rate is confirmed, the child will be assigned additional tests.
In the results of a general blood test, the doctor will pay attention to the structure and maturity of red blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin level and other indicators associated with red bodies. It is also important to take into account the changes in other blood cells - leukocytes (monocytes, neutrophils, etc.) and platelets.
At the present time in the diagnosis of diseases, manifested by a change in the number of red blood cells, use and so-called red blood cell indices. These include the average volume of red blood cells, the average content of hemoglobin in them and other indicators. They help in establishing the diagnosis.
For example, if a child has an increased distribution of red blood cells (this index is also called anisocytosis), the doctor will look for acute liver disease, folic deficiency anemia or bleeding.
When the cause of erythrocytosis is established, depending on the pathology, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment, and will also recommend parents:
- Give your child more drink. The volume of liquid drunk per day should be age appropriate, and purified non-carbonated water is considered the best drink.
- Monitor the balance of the children's diet. In the menu of a child with erythrocytosis should be enough vegetables and fruits, as well as other products that are sources of vitamins and mineral salts. In addition, some products are known to thin the blood, so give your baby lemon, sour berries, garlic, tomato juice, beets and ginger.
- Moisten and air the room in which the child resides.