Acetone (ketones) in the urine of a child
Childhood illnesses are always a cause for parents. If the child is lethargic, complains of nausea, refuses to eat, and later he gets vomiting, be sure to check the urine of the baby. You should determine if it contains acetone. Why can acetone appear in baby urine, how to find out and what is important for parents to take? Let's figure it out.
What is it?
Acetone is a compound formed in the human body during the breakdown of fat molecules. This compound refers to ketone bodies. At first, ketones appear in the blood of a child - this condition is called ketonemia or acetonemia, but can also be called ketoacidosis. When the ketones accumulate in the blood very much, they begin to penetrate into the urine of the child.
Signs that indicate the likelihood of acetone in the urine:
- Your child always eats with appetite, but suddenly refuses even his favorite dishes.
- The baby looks weak and lethargic.
- He complains of headaches or pains in the navel.
- The child says he feels sick.
- Baby tends to sleep.
- The child has a fever, but there are no other signs of acute respiratory infections.
- There were bouts of vomiting, which are constantly repeated.
We carry out the test
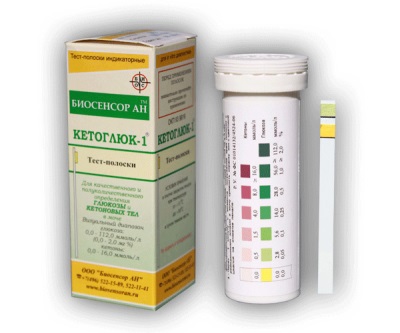
To detect acetone in children's urine use special test strips that change color after contact with urine.
The reagent-coated strip should be lowered into a jar in which the baby’s urine is collected (use only fresh urine, preferably morning urine). Then it is removed and dried, and then compared with the color scale, which the manufacturer of the strips attached to their packaging. So at home you can quickly determine if there is acetone in the baby’s urine and how much it contains.
Do not forget that the indicator strip can be used only once, and the test strips should be kept closed and not touch them with your fingers.
Norm
Normally, acetone in pediatric urine is absent. If the acetone concentration is at least 0.5 mmol / l, the test strip will show the result "+".
The smell of acetone in urine
The urine of a child with acetonemia acquires a characteristic odor, which is compared to a fruity one. It resembles the aroma of apples that are perepreply. The smell can be from subtle to very pronounced, and this has no direct connection with the severity of the baby’s condition. Parents can feel the same smell from the child (from the mouth).
Additional symptoms of acetonemia
In addition to the smell of acetone in a child with an increase in the level of ketone bodies in the blood there will be such signs:
- Nausea;
- Vomiting - often repeated, sometimes indomitable;
- Pallor and dry skin, dry tongue, decrease in the amount of urine and other symptoms of dehydration;
- Abdominal pain (spastic);
- Drowsiness, lethargy, possible convulsions (rarely);
- Increased body temperature;
- Enlarged liver in size;
- Detection of acetone in the general analysis of urine;
- Reduced glucose level in biochemical blood tests (also reduced amount of chlorides, increased level of fats);
- Leukocytosis and increased ESR in clinical blood analysis.

Acetonemic crisis
So doctors call the child’s condition, when the child is experiencing vomiting and lack of appetite, and acetone is detected in the baby’s urine. It often appears in children aged 1 to 5 years, as a physiological condition, but can also be a sign of serious diseases.
Acetonemic syndrome
So called often repeated crises. In this case, the syndrome can be primary (it develops in children with a predisposition) or secondary (appear on the background of somatic diseases, infections, operations, injuries).
The reasons
The formation of a large number of ketone bodies in the blood happens when the concentration of glucose in the body decreases, if there is little of it from food or a lot of waste. Also, excessive consumption of fatty or protein foods can lead to acetonemia, since some products are called ketone-rich because they can provoke a rise in the level of ketones in the blood.
Acetone ingress into children's urine can be caused by:
- Significant physical activity.
- Long cry.
- Any somatic or infectious disease, especially flowing with fever.
- Increased excitability of the child.
- Overwork
- Unbalanced diet. Problems can be caused by overeating, an abundance of fatty foods, the use of artificial food additives.
- Helminthic invasion.
- Dysentery
A separate cause of acetone in the urine is considered diabetes, in which ketone bodies are also formed in the blood, but an increase in sugar level is observed and there is a lack of such an important hormone as insulin.

Why does it most often occur in children?
The main reason for the frequent occurrence in children of acetone in the urine is a small amount of glycogen in the children's body. In addition, children are more mobile and need more energy.
Since glucose acts as the main source of energy for the child’s body, and if it is not sufficiently supplied or the glucose depot (glycogen) is consumed too high, it is also quickly consumed, energy begins to be extracted from fat. Acetone is a by-product of fat breakdown. Accumulating, it irritates the emetic center of the child’s brain, which provokes repeated vomiting and loss of appetite.
What if urine acetone is elevated?
It all depends on the level of acetone, which is determined in the child, as well as the condition of the baby:
|
Acetone Test Result |
Child condition |
Parenting |
|
+ or from 0.5 to 2 mmol / l |
The child drinks and eats. |
The situation can be improved independently. The child should be given a lot of sweet drink and saline solutions. |
|
++ or from 2 to 5 mmol / l |
The child does not refuse to drink. |
Treatment can be carried out at home with constant monitoring of the child. In the case of deterioration or refusal to drink you need to go to the hospital. |
|
+++ or over 5 mmol / l |
The child refuses to drink, his condition worsens. |
Urgently take the child to the doctor. |
Having missed the moment when acetone is formed in a small amount, a state occurs when the ketone bodies become so large that it leads to bouts of vomiting. In this case, the child refuses to eat and drink, and hospitalization will be the only way out.
Faced with an acetonemic syndrome in a baby once, parents should be ready to repeat and purchase glucose in ampoules, bottles or tablets for a first-aid kit. You should also always have raisins and rehydration preparations at home. To prevent episodes of acetone in the urine, you should give the baby sugary drinks during physical exertion, stressful situations, illness, and other situations provoking acetonemia.
Treatment
Since the main cause of acetone in the urine lies in the lack of glucose, the first actions of parents in detecting this condition should be to compensate for the lack of this simple carbohydrate. To do this, the child must be given glucose from an ampoule (40%) or a bottle (5-10%) or given glucose in tablets.
If there are no such funds at home, raisins steamed in a thermos will help out. Pour a tablespoon of this type of dried fruit with a glass of boiling water. After 15-20 minutes, the infusion can be given to the child.
To neutralize those ketone bodies that have already appeared, give the baby an alkaline non-carbonated mineral water and rehydration solutions. It is also recommended to give your child vitamin PP in ampoules, as a drink, or tablets, so that glucose is better absorbed.
Important points:
- Let us drink warm, so it will be better and faster absorbed.
- Drinks should be small - 5-10 milliliters. At the same time, they should be given often - every 5-10 minutes.
- Daily drinking volume is calculated based on the weight of the child - for each kilogram the child should receive 120 ml of liquid.
- A single dose of glucose is also calculated based on the weight of the baby - for each kilogram of the child’s weight, 5 mg of glucose is given (1 ml of 40% solution contains 400 mg, 1 ml of 5% solution contains 50 mg). This portion of glucose is given to a child three times a day.
- If the child does not drink from the spoon, you can give him liquid from a syringe without a needle.
Diet and nutrition
During the crisis, it is recommended not to feed the child at all or give him light food, thus reducing the load on his body. In this case, the drinking regime should be given great attention.
As soon as vomiting stops, the child can begin to be fed with such products:
- First day: crackers, baked apples, porridge without butter.
- Second day: add vegetable dishes, eggs, low-fat cottage cheese.
- The third or fourth day: you can add lean meat, a little vegetable oil in the gruel, biscuit.
- Fifth day: we begin to give yogurt and kefir, in which there are no additives.
Cook all the food or boil it. Give the child a small amount of 5 times a day or more. Try to add vegetables to each meal.

The appearance of acetone in the blood and urine of the baby can be prevented by using the correct diet and drink. If a child has spent a lot of strength, for example, he ran, cried, became nervous, fell ill with a fever, it is important to immediately give him a warm sweet drink.
What can not eat?
These groups of products must be eliminated during the crisis, and after it, give the baby such food in small quantities:
- Products containing vegetable fats.
- Fish fat.
- Broths on meat or fish.
- Fat meat.
- Oily fish and caviar.
- Dairy products.
- Chocolate and caffeinated beverages.
- Bread and muffin.
- Legumes
- Mushrooms
- Offal.
- Sour fruits and vegetables - it is better to abandon spinach, oranges, tomatoes, eggplant, kiwi.
- Smoked products.
- Products with flavor enhancers and other food additives.
- Fast food.
What can you eat?
The basis of feeding a child with acetonemic syndrome should be:
- A variety of cereals.
- Baked or fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Lean meat
- Skim cheese.
- Milk.
- Eggs
- Dried fruits.