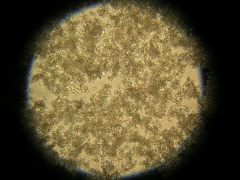
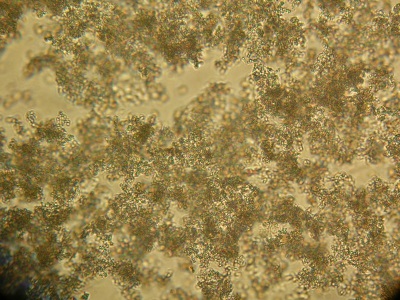
Phosphates in the urine of a child
Urine tests are shown for both healthy children and babies with signs of various diseases. At the same time, changes in analyzes do not always indicate serious diseases. Let's find out why phosphates can appear in children's urine and with what it can be connected.
What is it?
Such a name are salts of phosphoric acid. Their excretion in the composition of urine is called phosphaturia.
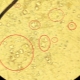
Amorphous phosphate crystals
Amorphous substances are substances that do not have a clear structure, with respect to salts, they say about inclusions in urine without a clear form. They are often detected in children, because in childhood the metabolic processes are not fully established and the balance is often disturbed. If such phosphates appeared in the urine of the child and there are no other changes in the analyzes, usually only a diet is prescribed for the correction of the indicator.
Norm
Small amounts of phosphates, which are found in the clinical analysis of urine, are a variant of the norm. Most often they can be detected in the urine of children under five years of age. If “+” or “++” is marked on the analysis form, there is no need to worry - such indicators are acceptable.
Have baby
The appearance of excess phosphate salts in the urine of the infant can be either a sign of malnutrition in the child (if he uses complementary foods) or a nursing mother, or a symptom of kidney disease or disorders of calcium and phosphorus metabolism.
Symptoms
In most children, excretion of excess phosphate in the urine is not accompanied by any symptoms. Often the only sign of phosphaturia is that the baby’s urine may become turbid or contain flakes.
The reasons
The main reason for the detection in children's urine of a large concentration of phosphate salts is eating disorders. In older children, a lot of phosphates in the urine can be caused by the use of carbonated drinks with phosphoric acid.
Among other problems that cause an increase in the number of phosphates in children's urine are called:
- Rickets;
- Infectious processes in the kidneys;
- Congenital pathologies of the kidneys;
- Diabetes.
Treatment
The main treatment for phosphaturia is a change in the nutrition of the child. In the diet of the baby should be limited to foods containing calcium and phosphorus. Also reduce the consumption of foods that can stimulate gastric secretion and stimulate the nervous system. The therapeutic diet for this pathology is number 14.
Diet
In most cases, after the correction of nutrition, the excretion of excess phosphate in the urine stops. In the daily menu of the child should be protein foods, for example, lean fish and meat.
Proteins in the diet are calculated based on the amount of 1 gram for each kilogram of child's weight. Also, give the kid dishes of cereals and vegetables, sour berries and fruits. If there are no contraindications, the child is shown plenty of drink.

In the diet of the child with excessive excretion of phosphate in the urine limit:
- Dairy and dairy products, cheeses;
- Fresh pastries and pastries;
- Salted and canned foods, as well as smoked meats;
- Fatty fish and fatty meats;
- Sweets (caramel, marmalade and chocolate);
- Eggs (they are given only boiled and in small quantities);
- Products that include cocoa;
- Fried food.
Nevertheless, it is impossible to completely exclude products that are a source of phosphorus, since this element is very important for the musculoskeletal system.
Folk remedies
When phosphaturia recommended decoctions based on cowberry, berries of mountain ash, oat straw, mint leaves and other plants. However, before giving any such remedy to a child, you should talk about its use with a doctor who observes your baby.
Possible consequences
The main risk of phosphaturia is the formation of stones in the urinary tract. Note that these stones have a porous structure and a soft texture, so they are quite easy to crush and remove from the body.
If you do not get rid of phosphate stones in time, they can cause hydronephrosis, renal colic, infections or kidney tumors.
Prevention
To avoid disturbances in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, it is important to balance the baby’s diet, enrich his food with the necessary vitamins and other nutrients, and also monitor the baby’s sufficient drinking regimen.