Flat epithelium in the urine of a child
For parents, the health of their children is always a priority, so when they feel worse, they go with the child to a pediatrician who prescribes urine and blood tests. Any changes in the results of such studies may cause concern and anxiety. Is it necessary to worry if a large number of epithelium is detected in the baby’s urine and why can it be excreted in the urine?
What is analyzed?
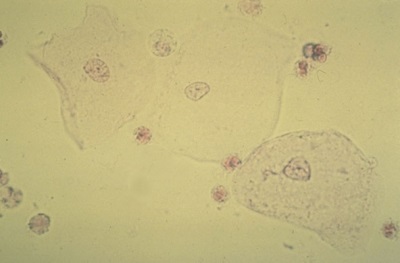
The determination of the number of epithelial cells in the urine is carried out during urinalysis. This takes into account not only the number of cells, but also their type, since the epithelium can be flat, renal or transitional.
Most often it is the flat epithelium that enters the urine, since the cells of the urinary system - the urethra and the bladder - are lined with such cells.
Do newborns have epithelium - normal?
In the urine of a newborn infant, not only a large number of flat epithelial cells can be detected, but also transitional or renal epithelial cells. This is not considered a sign of disease, since the baby’s urinary system is still adaptable to existence outside the mother’s womb, therefore, in the neonatal period (up to 2 weeks after birth), the appearance of epithelium in the urine should not be disturbed.
Norm
Cells of the squamous epithelium enter children's urine from the bladder and urethra, since they constantly exfoliate from their mucous membranes. In this case, the normal number of such cells is up to 3 units in the field of view of the microscope.
Causes of deviations
A sharp increase in the number of flat epithelial cells may indicate such changes in the child’s body:
- Inflammatory disease of the urinary tract. The child may develop cystitis or urethritis.
- Inflammation of the external genital organs or improper collection of a urine sample for analysis.
- Kidney disease, including congenital.
- Blood supply disorders of the excretory system.
- Urolithiasis or increased excretion of salts in the urine.
- Retention of urine inside the bladder, as a result of stress, neurological pathologies or special actions of the child.
- Reflux of urine from the bladder up the urinary tract.
- Prolonged use of drugs that contribute to the deposition of salts and spasms of the urinary tract.
- Purulent processes in the body, poisoning and other intoxications.
Did you collect urine for analysis?
An increase in such a figure as squamous epithelium may be caused by irregularities in the procedure for collecting the analysis, since epithelial cells are able to get into the urine sample from the child’s genitals.
To ensure that the result does not turn out to be false, it is important to thoroughly flush the external genital organs before collecting urine. In addition, an average portion of urine should be collected for analysis, and the capacity for biological material must be sterile. It is necessary to deliver the received urine sample to the laboratory within 1-2 hours.
Recommendations
It is known that often diseases of the organs of the excretory system are asymptomatic or resemble other diseases.
If a large number of epithelium is detected in the analysis of the child, parents should be alerted by such symptoms as increased body temperature, pain in the lumbar region or abdomen, weakness and lethargy, restless behavior of the infant and regurgitation, problems with urination. Any of these symptoms should be a reason to contact a pediatrician, urologist or nephrologist.
What other types of epithelium are in the urine of a child?
In addition to flat epithelial cells, the transitional epithelium, which is also called cubic or cylindrical, can be determined in a child's urine sample. It represents the cells of the mucous membranes of the bladder, ureters and renal pelvis. Another type of epithelium that can get into the urine of a child is renal.

If these types of epithelial cells are present in individual urine in children's urine, then at normal levels, other indicators of urine analysis are normal. If a child has an increased number of renal epithelium, and there is also leukocyturia, erythrocyturia, cylindruria, or proteinuria, this is the reason for a detailed examination of the kidneys.