Scale APGAR: interpretation of the scores of newborns in the table
The Apgar scale is used by obstetricians, as well as neonatologists, to determine the condition of the newborn in the first minutes after its birth. The results of such a survey are entered into the children's medical record and are taken into account by pediatricians, as well as by narrow specialists in the first year of the infant’s life. For parents, the Apgar scale is often incomprehensible. Let's look at what Apgar score is and how to decipher the points that are given to the newly born toddler.
Story
Anesthesiologist from America, Virginia Apgar, developed the assessment of all newborns more than 60 years ago, so the scale bears her name. The purpose of creating such a survey was the ability to quickly assess the condition of babies immediately after birth. The method turned out to be very convenient and simple, which allowed him to enter the obstetric practice. Nowadays, thousands of doctors in different parts of the world use the Apgar scale.
Indicators
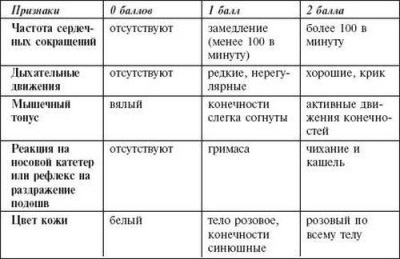
Apgar scores on such criteria:
- Skin color of the child (Appearance). This indicator is very informative, simple and allows you to identify circulatory disorders. If the body of the infant is completely pale or blueness is noted all over its surface, 0 points are put. Pale coloration is often detected with hemolytic disease. With a pink color of the body, but the blueness of the hands and feet the child is given 1 point. If karapuz body skin is completely pink, this is 2 points. Since the majority of babies have red skin color, and the blueness of the limbs is detected very often, this parameter most often underestimates the total Apgar score (children are rarely given 2 points).
- The heart rate of the baby (Pulse). The normal pulse rate for newborns is 120-140 beats per minute. In the absence of heartbeats, the score will be 0 points. If the pulse is less than 100 beats per minute, the crumbs put 1 point. With a heart rate in a newborn above 100 beats, they give 2 points.
- The presence of reflexes and reactions to stimulation (Grimace). For their determination, the baby is sucked from the nose mucus and look at his reaction or check other reflexes. The absence of reflex movements is estimated at 0 points, and for weak reflexes, represented by a grimace and movement, a baby is given 1 point. If the crumb in response to irritation is actively moving, loudly screaming, sneezing, coughing, this is estimated at 2 points.
- The state of muscle tone (Activity). Normally, in the newborn the muscle tone is increased, and the crumb actively randomly moves its legs and arms. If there is no muscle tone, and the baby’s limbs are hanging down, the parameter is estimated at 0 points. With a weak tone and a slight bending of the limbs, the child is given 1 point, and the activity and the presence of pronounced tone gives the right to put 2 points on this basis.
- Breath and cry of the child (Respiration). The normal rate of respiratory rate for a newly born infant is 40-45 per minute. If the baby cries out loud, it helps him to breathe harder and is a sign of good adaptation capabilities of the toddler. In the absence of breathing, the child receives 0 points. If breathing is irregular and shallow, and the cry is weak, this is 1 point. With normal breathing and a loud cry, the child will score 2 points. If a child asphyxia, it is this parameter that lowers the sum of points for Apgar.
Decryption
As noted above, the doctor assesses each of the indicators on a 3-point system: 0 - if there is no sign, 1 - if it is mild, 2 - if everything is normal and the sign is pronounced. All scores add up and get an overall rating.
Decipher the amount of points for newborns will help this table:
|
0, 1 or 2 points |
This is a critical indicator. A child with such an assessment during childbirth needs urgent resuscitation. In the future, it should be comprehensively examined and observed by specialists. |
|
3 or 4 points |
This is a satisfactory figure with moderate deviations from the norm. It is often determined in a premature baby. With such an assessment, the infant needs the close attention of doctors. |
|
5 or 6 points |
This is a satisfactory figure for which there are small deviations from the norm. A child with such an assessment also needs increased attention from medical professionals. |
|
7, 8 or 9 points |
This is the optimal value for the baby at birth. It pleases both doctors and newly minted parents. |
|
10 points |
This is the best indicator (maximum score) that a healthy kid often gets abroad, but he is not used by local doctors because of our mentality. Doctors are afraid to put the maximum, so as not to "jinx it" or believe that the majority of babies do not have an ideal state today. |
Survey algorithm
Assessment of the condition of the baby is performed twice - one test is performed in the first minute of life, and then a second examination is carried out in the fifth minute. The sum of points is recorded through the dash (as fractions), for example, 7/8 will mean that immediately after the birth the crumbs had 7 points, and after 5 minutes it was 8 points. If the indicator is 0/4, then this means 0 points at childbirth and 4 points in the fifth minute after birth. If necessary, a third examination is performed at the tenth minute.
The most common Apgar score for healthy babies is 8 points. In such infants, norms are noted (2 points) in three parameters and a slight decrease (1 point) in two indicators, for example, due to the blueness of the limbs and the pulse below 100. Maximum 10 points for children are very rare.
In most cases, the second / third assessment is higher than the first, which is characterized as a positive trend. This is due to the adaptation of the newborn to new living conditions. The crumbs make the pulse quicker, breathing returns to normal, the skin turns pink, a protective reflex and other reactions appear more actively. However, there is a decrease, for example, 9/8 or 8/7. In this case, medical observation of the baby increase.
What do the following points mean
Let's look at examples of Apgar ratings and their meanings:
|
8/9, 9/9 or 9/10 |
The baby is in very good condition and feels great. Close observation of obstetric staff after childbirth is not required. |
|
8/8 |
The child is in a normal condition, he feels well and quickly adapts to life outside the womb. |
|
5/7, 6/7 or 7/8 |
The health of the baby is average. The baby is weakened immediately after childbirth, but adapts well to new conditions. The baby doesn’t need close medical attention from the medical staff. |
|
7/7 |
The peanut is in a satisfactory condition. He does not need additional supervision of obstetric staff. |
|
5/5 or 6/6 |
The condition of the baby is satisfactory, but requires careful monitoring in the postpartum period. |
|
4/5 or 5/6 |
The baby is in a state below average, but there is a tendency to improve it. Crumbs should be carefully observed during the first week of life. |
|
4/4 or 3/4 |
The child’s condition is poor. He needs the help of obstetricians and more careful observation in the first weeks after birth. Typically, such assessments require a third survey in the tenth minute of life. |
|
2/3 or 3/3 |
The child is in critical condition. In most cases, he should perform emergency resuscitation. |
|
1/2 or 2/2 |
There is a threat to the life of the baby, therefore, resuscitation is required. |
|
0.1, 0/2 or 1/1 |
Baby's life is at stake. Need urgent resuscitation and detailed examination of the crumbs. |
Forecast
Telling parents about the value of the Apgar scale, it should be noted that the sum of points does not always show the real picture of the health of the crumbs. Do not forget that the points are given by a person (even though he is a health worker), based on his subjective opinion and experience.
Such an assessment also can not be called a diagnosis. This is only an auxiliary method for the pediatrician and obstetrician, with which the vitality of the baby is determined in a matter of seconds.
High figures for Apgar do not need to be proud, and low should not be a reason for additional alarm. The main objective of this method is to help doctors promptly assist the infant.
The difference between 4-5 points and 8-9 points is big enough, but if the baby gets 7 or 8 points, this should not upset the mother, because the 9/9 indicator does not mean that the baby is healthier and stronger than the baby with a rating of 8 / 8 or 7/7. This may mean that the peanut with 9 points shouted more strongly, and his reflexes were more pronounced, and the baby with 8 points could have a bluish color of the skin due to protracted labor.
The Apgar figures only serve as a signal to the obstetric staff, indicating what activities the baby needs in the delivery room and in the postpartum ward. After a general examination, all newborns are also examined by other examinations (blood test, urinalysis, ultrasound scan, and other tests), as a result of which tactics are determined for further medical follow-up of the crumbs.
In any case, the Apgar score below 5 means that the newborn needs the attention of the medical staff much more than the baby with a score of 7 or higher. However, if in the first minute the crumb received 4-5 points, and in the fifth, his condition can be estimated at 7 or 8 points, then the baby is transferred to the category of children who do not need close medical supervision.
Note that babies after cesarean often get higher marks for Apgar, because the natural way of birth is more difficult for the crumbs and often accompanied by hypoxia. For this reason, Caesarians often receive grades 8 and 9.
As for multiple pregnancies, Apgar is generally low for twins and twins. In most cases, such tots are born earlier, and in premature babies developmental indicators are worse than infants born in time.
Apgar has a low score for birth injuries, for example, if it results in severe spastic tetraparesis. The consequences of such injuries are different, but it is difficult to say for sure that the child will be disabled in the first minutes after birth. Putting a small score of low, the baby is given the necessary help and prescribed treatment.
Reviews
Doctors believe the Apgar method is very important, because on this scale, you can quickly determine whether the baby needs reanimation in the first minutes after birth. Using the Apgar scale, according to obstetricians, it helps not to get confused and to immediately navigate in further tactics of action. This is especially important for beginners who have little experience.
Pediatricians who observe the child after discharge from the hospital, also speak positively of the Apgar scale. During the first inspection of a toddler, they always look at the extract and pay attention to the points, taking into account the condition of the baby during childbirth.
As for parents, some study the information about staying in the maternity hospital and know about the Apgar scale, so they don’t worry because of grades 7 or 8. Others encounter such numbers after delivery and may perceive them incorrectly. For example, some mothers are upset that the indicator is only 8, not all 10 points. Someone associates Apgar scores with the mental abilities of the crumbs, which is completely wrong.
There are mothers who are worried that the score does not change, for example, 7/7 or 8/8, considering that the second amount should certainly be higher (perceiving this as an improvement in the condition of the baby). To avoid unnecessary worries, you should learn more about the Apgar scale during pregnancy.