Concussion in a child: symptoms and treatment
Moving and inquisitive children are often injured. Falls from a swing, a trampoline, from a bicycle, from a chair - this is not even so much an incident as a childish way of knowing the world around. Therefore, brain concussion is a widespread diagnosis in childhood. All parents should know its symptoms. In this article, we will tell you what this type of injury is, how to correctly organize first aid and how to treat a baby.
About pathology
Among all existing craniocerebral injuries (TBI), brain concussion is generally regarded as the lightest. And all because the pathological processes in this most important part of the human body occur mainly at the cellular and subcellular levels. Neither the brain structure, nor its sections and zones are significantly affected. The essence of the injury is to strike the brain against the inner wall of the skull.
The brain is located in the center of the skull, between it and the cranial bones there is free space filled with cerebrospinal cerebral fluid. It protects and washes the brain. With a strong blow, a short-term inertial movement of the brain and its impact on the bones of the skull occur. After that, he returns to his place, anatomically suffers nothing. But between some parts of the brain there may be some inconsistency.
After a few days, the functions of the brain and central nervous system usually recover completely.
To understand how widespread concussion is in children of preschool and school age, you need to refer to the data of medical statistics. She says that with a variety of injuries between the ages of 1 year and up to 17 years, the average child will be treated for 13-15 times at the emergency room. About 65% of injuries occur in head injuries, of which more than 80% are cases of concussion. In case their form and degree are very light, most of them are not obvious to parents.
Less often than others, children under one year old get such a diagnosis. The bones of the skull are soft and mobile due to the presence of fontanelles, facilitating the passage through the birth canal. In addition, the amount of cerebral fluid in babies more significant. Therefore, it is rather difficult to get a concussion to a child before closing the fontanels and hardening them in the fall.
A child aged 2 to 5 years will not have tremors as often. Children of school age, from 6-7 to 12 years old, are the real champions in the number of strokes, falls and tremors. These children are very mobile, especially boys, and therefore fights, jumps, falls are almost a normal component of their daily life.
The reasons
Concussion most often occurs after a fall with a head. But a child can get such an injury without falling if he just gets hit on the skull. But shocks and falls are not the only causes of injury.
A child may well shake the brain if the axial load on the spine is broken - when jumping from a great height, when landing on the ass, with a concomitant spinal injury.
The one-year-old child very often falls on the ass, because this part of the body in young children always outweighs, and the vestibular apparatus and the coordination of position in space are not yet sufficiently developed. It is not the drop itself that is to blame for such a concussion, but the reflex head of the reflex, which is accompanied by all people.
It is at the moment of vskidyvaniya head the brain inertia shifts towards the cranial bone. Thus, it becomes clear the danger of jumping on a trampoline, a sharp acceleration or a sharp slowdown on a circular carousel, on a “roller coaster”. Sudden braking during a traffic accident and the corresponding sharp head protruding at this moment are also common causes of brain concussion in children.
It is rather difficult to understand what happens in this case, especially since scientists and physicians have not yet understood the specific reasons for the occurrence of subsequent violations. Presumably, the impact of the body of the brain on the cranial wall causes a temporary change in the functions of the brain - the metabolic processes in the neurons are disturbed.
The key word here is temporary. Since the coherence and interaction of the brain, due to the compensatory mechanisms of the human body, quickly restored.
Classification
Concussion is differentiated by the degree and severity of the condition. The key diagnostic criteria are loss of consciousness and amnesia (complete or partial loss of memory for the incident itself and the circumstances of the injury, or for the events that followed the coming to life).
- first degree SMG - a slight concussion that was not accompanied by fainting, the child remembers everything that happened to him;
- second degree SMG - a moderate concussion, in which there could be no loss of consciousness, and there could be a brief syncope, but the child is confused; the child does not remember all the circumstances of the injury and cannot clearly tell what happened to him;
- third degree SMG - This is a severe concussion, which was accompanied by a fainting state, the child’s memory is significantly impaired, there is a retrograde or other form of amnesia, the consciousness is confused.
Concussion is characterized by a large variability of manifestations, which will determine the final assessment of the degree of traumatic injury. Even a mild injury can lead to severe symptoms, and a severe blow with loss of consciousness during the recovery process can be evaluated by the doctor as a moderate or mild concussion if severe symptoms are absent.
You should talk in more detail about how parents can detect and recognize a concussion.
Symptoms and signs
Concussion refers to a closed cranial injury, and therefore it may not be accompanied by any external signs on the scalp. Yes, and the fact of loss of consciousness does not always reach the parents, especially if the fall did not happen before their eyes. Loss can last from several seconds to several tens of minutes. Therefore, to understand immediately after injury, whether there is a concussion, it will be quite difficult.
Careful observation of the state of the child will help mom and dad to understand what is really happening. An injury of this type, like SMG, is manifested by a whole list of possible signs. It is not necessary that the child a few hours after the impact or fall all these signs appear, but a few of them, with the presence of a concussion, will necessarily show up:
- the child's mood changes - he becomes sluggish, inactive, headaches can appear;
- the child has nausea and vomiting (most often single);
- the child complains of dizziness, the appearance of "stars" or "flies" in front of his eyes and tinnitus;
- general sweating increases, even if the room is completely cool, and a child has a minimum of clothes;
- an older child will be able to formulate a symptom such as soreness when the eyeballs move;
- there may be some divergence of the eyeballs in relation to each other, one pupil may be larger than the other, may show small nystagmus (trembling);
- appetite is disturbed (the child does not want to eat);
- sleep is disturbed (either the child is constantly sleeping, or almost can not sleep at all);
- nosebleeds may occur, even if the nose was not injured.
Body temperature is usually normal or slightly elevated (up to 37.0-37.5 degrees). Arterial blood pressure is unstable: if the pressure is measured several times in an hour, then the indicators will differ significantly from each other. In severe cases, there may be a violation of coordination of movements, the development of seizures.
The hardest thing to understand is whether there is a concussion in an infant. Such children cannot describe their feelings in words, and parents will have to be very careful to see the first signs of injury. In both babies and large children, the signs and clinical symptoms of tremors usually develop within a day after a traumatic fall or stroke.
Observation of infants during the day should be the most intent. The fact is that infants and children under three years of age rarely faint when receiving TBI. Usually, their concussion proceeds more smoothly, gently, and it is rather difficult to understand the signs of clouding of consciousness in children, as well as to detect signs of amnesia.
Most often, when shaking, babies first cry long and hysterically, and then fall asleep. After waking up, parents can pay attention to the fact that the baby refuses to eat, he is sluggish, he has neurological signs - abundant regurgitation, arching the back, he does not sleep well, sleeps restlessly.
If signs are not detected within a day or two, then with a high degree of probability there is no concussion in the child. After a few days, usually the existing signs begin to diminish and disappear completely as the functionality of the brain recovers. Only headaches and emotional instability can last longer.
First aid
A child needs a doctor if his parents suspect a concussion. The concussion itself is not as dangerous as its possible consequences. Therefore, the injured child must be shown to the doctor. You do not need to take the child to the emergency room, it is more correct to call an Ambulance and create the right conditions for the victim, while waiting for the medical team to arrive.
If the child has struck and fainted, place a small pillow or a roll-up towel under his feet. The second is the same towel to put under the head. Turn the child on the right side and let sniff ammonia. In the absence of breathing, give the child artificial respiration, and as soon as the child comes to himself, do not give him to drink and eat, do not give any medicine and do not allow to rise and talk.
If there was no loss of consciousness and the parents have already discovered additional symptoms, it is important to call the ambulance immediately after the characteristic symptoms described above are detected.
The algorithm of actions will be similar: the child should be in a horizontal position with raised legs and head. If there is nausea and vomiting, parents should avoid standing on their backs: an attack of vomiting can cause asphyxiation - the child may choke on vomit. The safest body position is on the side.
Try to entertain a child of preschool and school age right up until the arrival of the doctor - he should not fall asleep. The dream will “spoil” the clinical picture and will not allow the doctor to objectively evaluate all neurological disorders caused by trauma. A small child can be allowed to fall asleep.
Since there is a risk of convulsions during shaking, parents should bend the baby's limbs at an angle of 90 degrees: put their hands on the diaphragm, and bend their legs at the knee joint. This will avoid additional injury to the limbs in the event that seizures do begin.
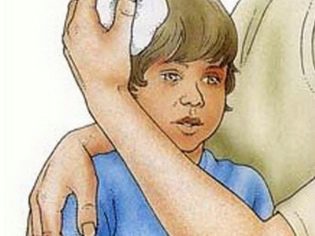
In anticipation of the doctor, handle the place of impact on the head (if any). A bump and swelling need some ice wrapped in a towel or cloth. The wound and abrasion must be treated with hydrogen peroxide. After that, ice is also applied to the edges of the wound in a towel or napkin, but avoid exposure to cold directly at the incision site.
Whatever the symptoms of a particular child, avoid giving him any medications, medications, pills, make injections, drink plenty of water, even if the child asks to drink.
How to diagnose?
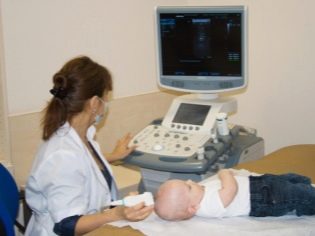
To diagnose a condition in children such as concussion of the brain, the visiting doctor can, after collecting the most complete information about the circumstances of the injury, assessing the totality of symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis, babies up to two years old are prescribed neurosonography - an ultrasound of the brain, which is carried out by a sensor through a spring. This diagnosis is harmless, harmless, painless, allowing you to know exactly whether the baby has signs of concussion.
An injured of any age must be examined by a neurologist. This specialist can identify various disorders of the nervous system - asymmetry of reflexes, nystagmus, different pupils' reaction to light stimulation. Quite often, schoolchildren have a jerking of the muscles of the chin, if you tickle your thumb.
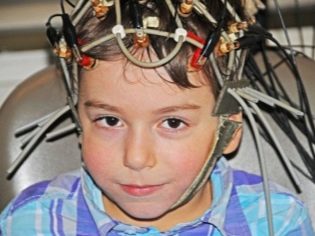
Children older than 2 years old, who are no longer able to perform neurosonography, are prescribed skull x-rays, which allows the doctor to identify possible fractures and bone fractures, because quite often other cranial injuries are “masked” at the initial stages. Electroencephalography allows to exclude a contusion of the brain, the formation of hematomas that are dangerous to the life and health of the child. You also need to be examined by an oculist, who by means of an ophthalmoscopy can check the condition of the fundus.
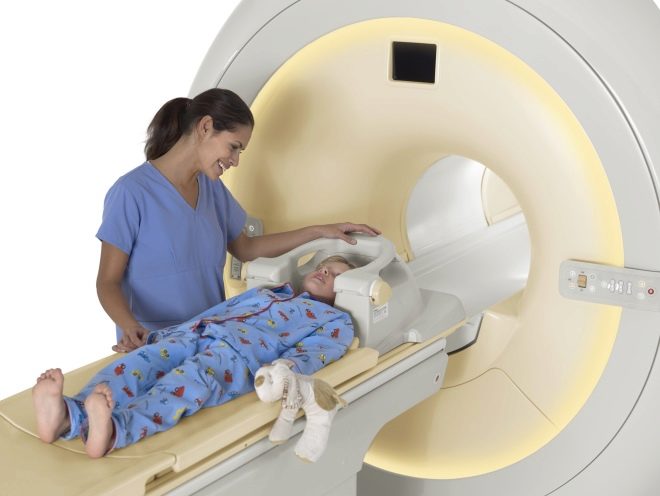
Comprehensive data on possible concussion can be obtained by performing a CT scan or MRI scan. The results of these studies do not show abnormalities and abnormalities in brain tissues and departments in brain concussion. If pathological changes are found, the diagnosis is changed to another, for example, a brain contusion, and treatment is prescribed, which corresponds to the clinical picture.
How to treat?
Children, regardless of the degree of concussion during the first 2-3 days hospitalization is recommended. In a hospital setting, doctors will be able to observe a child with a more attentive professional eye. If the baby has only a concussion, it will be possible to treat it at home - the baby will be allowed to go home, when doubts about possible other injuries to the skull and brain will be dispelled and the danger is ruled out.
The main thing in treating concussion of the brain is rest and normal, prolonged healthy sleep. Since it is precisely with sleep for several days after the injury that problems arise, children are prescribed sedatives and strong hypnotics, for example, Phenobarbital in the age dose. During the first days of the child is shown strict bed rest. At home, parents should exclude long-term watching TV programs and cartoons, playing at a computer, tablet, phone. It is generally better to abandon gadgets at least until the symptoms of neurological disorders disappear. A child of school age should exclude reading books, as well as listening to music in headphones.
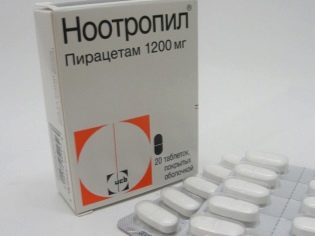
There is no universal cure for concussion, and therefore doctors do not prescribe medicines to everyone and not always.With mild concussion, only nootropic drugs can be recommended (“Pantogam" or "Nootropil") To improve blood circulation in the brain and more quickly restore neuronal metabolism.
The remaining drugs are recommended by the doctor depending on the symptoms present:
- with headache painkillers may be recommended to help relieve seizures;
- with nausea and vomiting - antiemetics;
- with diarrhea - antidiarrheal drugs;
- if the child had convulsions The doctor may prescribe a course of anticonvulsants.
Quite popular in the treatment of motherwort extract, Ginkgo Biloba, Valerian and Fenozepam. The doctor will build on the patient's age, on the strength of the symptoms. In case of concussion of the third degree, vascular therapy is shown in the hospital - the child will receive vasodilator drugs in combination with nootropic drugs.
In most cases, even without the use of medicines, the symptoms disappear for 5-7 days. But correct treatment and following all the recommendations of the doctor can reduce the likelihood of long-term effects on the health of the baby.
During treatment, the child is shown a diet that excludes fatty and fried, salty. Useful vitamin drinks, fruit drinks and fruit drinks, especially with a diuretic effect. Meals should be complete, varied, rich in vitamins. Complex preparations of vitamin-mineral composition are also prescribed during the recovery period after a head injury.
About a month later, a neurologist assesses the condition of the child. While maintaining certain neurological disorders, massage and physiotherapy procedures are prescribed by course treatment.
Possible consequences
In most cases, the concussion of a child passes without long-term consequences. Repeated concussions are dangerous: they significantly increase the likelihood of developing post-traumatic encephalopathy, in which the motor functions of the legs are disturbed (the child begins to noticeably “spank” with one foot or limbs begin to move at different tempos).
Such long-term effects can then manifest a temporary loss of balance that occurs suddenly, with bouts of dizziness. Children who at an early age suffered more than one concussion are more susceptible to infectious diseases.
Often, even a few years after the injury, the child begins to show signs of neurosis, depressive disorder, and phobic disorders can torment him.
Concussion, if its consequences were significant, if the injury was repeated several times, can lead to the development of regular headaches, convulsions, memory loss, disturbance of the processes of memorization and assimilation of new information. It is harder for such children to study, they get tired quickly, they do not sleep well.
In one out of ten children, a few days after injury, post-commotion syndrome may develop, manifested by dizziness, severe headaches, fears and sudden anxiety, insomnia. This syndrome is difficult to treat, and the constant use of analgesics for headache can cause persistent drug addiction in a child.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
Pediatrician and TV presenter Yevgeny Komarovsky urges parents not to panic and not to engage in overdiagnosis. If the child has hit, cried, slept, and after that behaves normally, do not call the doctor and expose the kid to the stress of diagnosis - there is no concussion.
Even if signs of a violation are detected, panic will not add benefits to anyone. You need to call a doctor, but do not turn the incident into a tragedy - in most cases, concussion is not dangerous.
Observing parents for a child during the first time after injury is of great importance - no one knows the character and behavior of the child better than the mother.That is why it is mother who can more quickly understand that there is something wrong with a child than a dozen of the most highly qualified, but alien for a baby, doctors.
Treatment, if prescribed, should be carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations of the doctor, there is no place for amateur performances and experiments with folk remedies. And to prevent recurrences will help injury prevention measures, which parents, after suffering a baby shake willy-nilly, will have to pay special attention.
Useful tips and tricks
Some special prevention, of course, does not exist, but a few simple tips will help avoid both primary and secondary cranial trauma:
- bed in the bathroom on the floor and on the bottom of the bath non-slip mats;
- make sure that the house does not have puddles or oil spilled on the floor;
- teach your child to quietly climb and descend the stairs;
- watch the baby’s games on the playground more closely;
- avoid trampolines and unreliable swings;
- purchase a helmet and kit for roller skating, running races and bicycles for your child;
- teach your child to sort things out in words, not to get into fights.
Forecasts
In 95% of cases, the doctors' forecasts are favorable: treatment and adherence to the regimen during the recovery period help to restore the functions of the brain and central nervous system in full. A slight sensitivity to bright light and loud, harsh sounds may persist for a year or even one and a half years after a concussion, but this is considered a normal variant.
In the case of re-injury, the prognosis is less favorable, but if the child's concussion is recorded 3-4 times, the risks of subsequent disability are estimated at about 10-15%.
Reviews
According to parents, the symptoms of tremors are much wider than medical sources describe. For some children, diarrhea was the first sign, for some, a panic fear of darkness or bright light. Usually, mothers do not have enough patience to watch the child for a long time after falling and hitting his head, because fears for the child's life are stronger.
Doctors, according to reviews of mothers, usually recommend week-long hospitalization. After the treatment, which can last for 2 weeks and a few months, the child should have follow-up at the neurologist for 2–3 years. If there are no complications, they are removed from the register.
According to the moms, the most difficult thing is to make the child lie quietly in bed for several days. Small restless and bored teens quickly lose their patience and require a change of atmosphere or at least body position.
For babies, mothers are advised to use a finger theater, fairy tales, and for teenagers, listening to audiobooks without headphones at rest with eyes closed.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky on concussion in a child, see the following video.