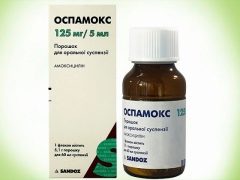
Ospamox for children: instructions for use
Ospamox is a group of penicillins and is in demand in the treatment of both adults and young patients. This antibiotic is a product of the well-known company Sandoz and is presented in several forms, which allows you to choose a drug for children of different ages. Due to the wide range of effects and mostly well tolerated, such an antibacterial agent is often prescribed for children with various infections.
Release form and composition
The most popular form of “Spamox” in childhood is powder, from which a suspension is made at the beginning of treatment. It is sold in glass bottles, to which is attached a measuring spoon and paper instruction. This powder has a white or yellowish-white color and a fruity odor. After mixing with water, it forms a bittersweet white or yellowish-white liquid that smells like fruit.
Depending on the content of the active substance, which amoxicillin acts in (Ospamox) (it is in powder in the form of trihydrate), there are three dosages of the suspension - 125, 250 and 500 mg per one milliliter of the finished (diluted with water) medicine. The dosage of amoxicillin affects the amount of powder in the vial, which can range from 5.1 to 20 grams. But the auxiliary ingredients of such drugs are the same and are represented by aspartame, talc, sodium benzoate, orange, lemon, and other compounds.
In addition to the powder, Ospamox is also produced in the form of dispersible tablets. They also contain amoxicillin trihydrate as an active ingredient. If you count it on amoxicillinthen the dosage in one tablet is 500, 750 or 1000 mg. Inactive ingredients, regardless of the amount of amoxicillin, are microcrystalline cellulose, aspartame, mannitol, maltodextrin, flavoring agents, and other compounds.
The tablets themselves are distinguished by oblong convex shape and white color, sometimes with a yellow tinge. On both sides, they have a risk that allows such Ospamox to be divided into halves. The drug is sold packaged in blisters of 6, 7, 8, or 10 tablets, and one package can contain from 12 to 100 tablets.
Abroad, instead of the powder "Ospamox" you can buy granules. After adding water, they become a sweet suspension containing 125 or 250 mg of the active ingredient in 5 milliliters. The difference of this form from the powder is only the composition of auxiliary substances. In addition, in other countries, there is such a solid form of "Ospamox", as tablets in the shell. They are available in dosages of 500 and 1000 mg of amoxicillin per tablet.
Operating principle
The active substance "Ospamox" has a bactericidal effect on many types of bacteria. The drug disrupts the formation of cell walls, which is why microbes die. The medicine can destroy:
- listeria;
- haemophilus sticks;
- corynebacteria;
- enterococci;
- streptococci;
- E. coli;
- gonococci;
- protea;
- salmonella;
- clostridia and many other microorganisms.
Many staphylococci, Klebsiella, enterobacteria, pseudomonads, chlamydia, bacteroids and some other pathogens are insensitive to the action of Ospamox. This antibiotic does not work on viral particles.
Indications
Children "Ospamox" is most often prescribed for infection of the respiratory tract, for example, if the bacteria affect the throat (for tonsillitis) or the ear (for acute otitis), as well as for pneumonia and bronchitis. In addition, the drug can be used for infections of the digestive tract, skin, subcutaneous tissue and urinary organs. Another reason for the appointment of "Ospamox" is endocarditis or its prevention.
From what age is prescribed?
For the use of "Ospamox" in children, there is no age limit. The drug can be prescribed for both infants and older patients, including adolescents and adults.
Contraindications
Treatment with Ospamox is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to amoxicillin and allergy to other penicillin preparations. Also, the suspension or tablets should not be given in case of intolerance to any inactive component of such drugs. In addition, the drug is not recommended for viral infections, leukemia and infectious mononucleosis, as well as for allergies to cephalosporin antibiotics and drugs of the carbapenems group.
Side effects
During treatment with Ospamox, negative symptoms of the digestive system can occur, for example, loss of appetite, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, nausea, or the development of dysbiosis. Also, taking the drug can cause skin redness, itching and other signs of an allergic reaction. More rarely, the drug provokes anemia, fever, kidney damage and other negative phenomena. If they occur, you should immediately cancel the antibiotic and consult a doctor.
Instructions for use
To dilute the powder with water properly, you need to pour the liquid inside the bottle to the mark on the bottle. Dilution is best done not immediately with the entire volume of water, but in two stages - first pour water about 1 cm below the mark and shake up the powder, then let the foam settle and add liquid to the mark, then shake the medication again. Agitation is recommended for each subsequent use of liquid "Ospamox".
When using tablets that dissolve, they can be easily swallowed or chewed with water, but they can also be diluted in 20 ml of liquid to form a sweet syrup, or dissolved in 100 ml of water to form a suspension.
Dosage medication for patients younger than 12 years old and weighing less than 40 kg is calculated by body weight. Per 1 kilogram of child's weight often take from 25 to 50 mg of amoxicillin (maximum - up to 60 mg for severe infections). The daily dose calculated in this way is divided into 2-3 doses. Adolescents over 12 years old are given 750-3000 mg per day in a dose (a specialist determines a more accurate dosage), dividing this amount of Ospamox into several doses.
How long to give Ospamox to a child should be determined by the attending physician. Most often, they continue to take a few more days after the symptoms of the infection subside. Stop giving the medicine before the prescribed period of the doctor is not worth it, because it can provoke the development of resistance in bacteria.
Overdose
If you exceed the dose of Ospamox, it can cause vomiting, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and other digestive disorders. To eliminate them, you need to give the patient "Activated carbonOr other symptomatic remedies.
Drug interaction
"Ospamox" is not recommended for use with many other drugs, among which are anticoagulants, cardiac glycosides and aminoglycoside antibiotics. If the child is already taking any medications, you need to tell your pediatrician before starting treatment.
Terms of sale and storage
To purchase any form of Ospamox at a pharmacy, you must first take a prescription from your doctor.Shelf life of the powder in a sealed bottle - 3 years, after dilution with water - 14 days. Shelf life of dispersible tablets is also 3 years, but this form of the drug is not stored in water diluted form. You can keep the medicine in any form at home at room temperature, taking care that a small child cannot get it.
Reviews
About the treatment of children "Ospamox" speak mostly positively. This medicine is called effective and convenient to use, even in small children, but in some babies it still provoked unpleasant side effects. Some moms call the price of medication affordable and others overpriced.
Analogs
If you need to replace "Ospamox" antibiotic with the same active ingredient, you can use "Flemoxine Solutab», «Amoxicillin"," Ecobol ","Amosin"Or" Hikontsil ". Such amoxicillin-based drugs are available in soluble tablets, capsules, powder, and other forms, so you can choose the right medicine for both babies and schoolchildren.
In addition, the replacement of "Ospamox" can be drugs, which include amoxicillin supplemented with clavulanic acid. These include antibiotics "Panklav", ""Amoxiclav"," Augmentin "and others. Their spectrum of antimicrobial effects is wider, since clavulanic acid protects amoxicillin from destruction by enzymes.
For information on how to prepare Ospamox suspension, see the next video.