Antibiotics for cough for children
I have met more than once parents who begin to treat any sneeze and cough from their offspring indiscriminately with antibiotics. As a rule, arguments about the feasibility of such a serious treatment have little effect on them, and as a result, it is these kids who are “healed” by loving mothers who, as a rule, are more often ill with their peers, and in general their physical development leaves much to be desired.
Is it necessary to treat children's cough with antibiotics
The answer to this question each time in each case will be different.
Children's cough can also be of a bacterial nature, i.e. can be caused by pathogenic bacteria, and viral origin.
Microorganisms - pests begin to multiply successfully under favorable conditions for themselves:
- The child's immunity is reduced, for example, the presence of a viral infection in full swing or a recent illness.
- The child is supercooled.
The use of antibiotics for the treatment of a child in some cases is justified, but not always a necessity.
In order to clearly understand the situations in which antibiotics are needed, parents need to learn to “recognize the enemy by sight.” If the fever has risen rapidly (39 and above), a runny nose and cough have appeared, the head ache and almost all the muscles are viral infections (ARI, ARVI, flu).
Antibiotics cannot cope with viruses in principle, and therefore taking antibacterial drugs with such a cough does not cure, but cripples the baby more - after all, the full set of side effects from the antibiotic, as well as unpleasant consequences (thrush, diarrhea, vomiting) are guaranteed.
Antibiotics are also not recommended if the cough is caused by an allergic reaction, including if it is a cough that appeared after taking an antibiotic course.
Antibiotics are not needed and will not help if the cough is caused by mechanical damage to the respiratory system.
If the symptoms manifest themselves gradually, slowly, the temperature in the region of 38 degrees has been holding for more than three days, the child has noticeable shortness of breath, signs of intoxication, lethargy and drowsiness - this is a bacterial disease.
In this case, the cough may be of a different nature:
- Dry cough
- Moist cough
If a child’s cough does not go away for more than three weeks, it is considered to be protracted. And if the baby has been coughing for three months, it is a chronic cough.
Cough itself is not a disease at all, but a separate symptom of a whole range of diseases. Therefore, to treat only cough with antibiotics - it makes no sense.
Cough as a protective function of the body (and this is an unconditioned reflex) can persist long after recovery, it usually always passes the most recent. However, if he keeps in the absence of other complaints and symptoms for 2.5-3 weeks, it is worthwhile to show the child to the doctor. Perhaps the baby will need antibiotic treatment.
When do you need antibiotics when you cough?
When coughing, the doctor prescribes antibiotics if the baby has one of the following diagnoses:
- Pneumonia. When pneumonia cough usually long, almost constant, wet, hacking.
- Angina. In this disease, the cough may be dry or wet.
- Bronchitis. In this case, the baby may be plagued by a dry, suffocating cough or a wet, prolonged.
- Tracheitis (purulent). At first, when the child is ill, there is a dry cough, mostly at night. After a few days, it becomes wet with sputum mixed with pus.
- Pleurisy. In this disease, the child’s cough is dry and unproductive.
- Tuberculosis. In tuberculosis, cough is different and depends on the stage and form of the disease. When the miliary form - it is dry, but with abundant sputum. In the destructive form - deaf and painful.
- Whooping cough. This disease is usually accompanied by debilitating long-lasting cough convulsive nature. Often there is the so-called "barking" cough or ("seal barking").
What antibiotics can be prescribed by the doctor when coughing
It is best if the doctor receives the results of bacteriological examination of sputum and smear from the larynx and nose of the child before choosing a drug. Then the specialist will surely know which bacteria have caused the disease, and which antibiotic against them "put in the line of fire." But the analysis of such a plan is not done everywhere, and lab technicians take a long time to report on the results - from 10 to 14 days. These two weeks, as we understand, have neither a sick child, nor his concerned parents, nor a doctor. Therefore, doctors try to prescribe for children when they cough. broad-spectrum antibiotics new generation.
For the treatment of cough, monotherapy is usually chosen - that is, use one, usually relatively weak, antibiotic. If within 4-5 days of improvement does not come, the doctor will change the drug to a more potent and effective. A stronger antibiotic (for example, from the group of cephalosporins) will be prescribed by the doctor even if the child has recently been treated with antibiotics of weaker action (for example, penicillin).
For babies from birth to 3-4 years old, an antibiotic will be recommended in the form of a suspension, which people mistakenly call "syrup" or in drops. Children from 5 to 10 years old can take the medicine in pills, and adolescents can take the medicine prescribed by the doctor in capsules.
For all ages with severe disease, antibiotics can be prescribed in the form of injections - intramuscular or intravenous injections.
The list of antibiotics most commonly prescribed for children when they cough:
Antibiotic name | What treats? | What form to take? | At what age is it recommended to take? | What are the contraindications? |
Acute, obstructive form of bronchitis Pneumonia Tracheitis Angina | Capsules of 250 and 500 mg. Suspension granules Powder for injection | Newborn, including premature, and everything else. | Bronchial asthma Pollinosis Liver failure Dysbacteriosis Lymphocytic leukemia | |
Acute, chronic bronchitis Pneumonia Angina | Dispersible dissolving tablets 125 and 250 mg each | Children 0 and up | Tendency to local allergies - itching, rash | |
Augmentin | Acute, chronic bronchitis Pneumonia Bronchopneumonia | Tablets and powders for suspension. | Children 3 months and older | Jaundice and disorders of the liver (in history). Kidney disease. Phenylketonuria |
Acute, obstructive form of bronchitis Pneumonia Tracheitis Pharyngitis | Tablets of 250 and 500 mg. Powder for suspension Powder for injection | Children from birth and older | Bronchial asthma Atopic dermatitis Liver and kidney disease | |
«Ecoclav» | All forms of bronchitis Pneumonia Angina | Pills Powder for suspension | Children from birth and older | Diseases of the kidneys and liver Infectious mononucleosis |
"Cefuroxime" | Bronchitis Pneumonia Pleurisy Pharyngitis | 500mg tablets. Powder for injection | Children from birth and older | Hypersensitivity to cephaloporins |
Bronchitis Pneumonia Pleurisy | Powder for injection | Children from 2.5 years and older | Increased individual sensitivity to cephalosporins | |
"Cefuroxime - axetil" | Pleurisy Bronchitis Pneumonia Pharyngitis | Powder for injection 500mg tablets | Children from birth and older | Individual intolerance to the drug |
«Suprax» | Acute bronchitis and chronic Angina Pharyngitis | 200 and 400 mg capsules Granules for suspension | Children older than 6 months | Kidney disease |
«Sumamed» | Acute and chronic bronchitis Pneumonia | Tablets 125 and 500 mg. 250mg capsules. Powder for injection Powder for suspension | Children older than 6 months | Diseases of the kidneys and liver |
Angina Pharyngitis Pneumonia Chronical bronchitis Whooping cough | 400mg tablets. Suspension granules | Children from birth and older | Severe liver disease | |
All forms of bronchitis Pneumonia Pharyngitis Whooping cough | 250mg tablets. Capsules of 250 and 500 mg. | Children of all ages | Impaired liver and kidney function | |
"Rulid" | Bronchitis Pneumonia Acute pharyngitis | Pills | Children of all ages | Severe pathology of the liver and kidneys |
All forms of bronchitis, Angina Pharyngitis Pneumonia | Tablets of 250 and 500 mg. Capsules of 250 and 500 mg. | Children from 12 years and older | Diseases of the kidneys and liver |
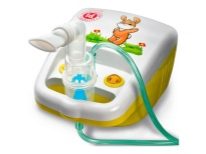
Antibiotics for inhalation
Quite effective treatment of children's cough is inhaled with antibiotics. With this method of drug intake, the negative impact of strong antibacterial drugs on the child's body is significantly reduced. Antibiotics, which are delivered “exactly to the address” where they are most needed - in the respiratory tract - cope with bacteria faster, have less effect on the intestinal microflora and stomach, and therefore dysbiosis, if it occurs, will not be so pronounced. In this case, the disease will be able to win more.
If the child’s cough is not caused by tuberculosis or a very severe form of pneumonia, the doctor may agree to inhaler treatment. Provided that you have a nebulizer at home. Inhalation with antibiotics "grandmother's" ways (over steam, boiled potatoes or decoction of herbs), adding an antibiotic there, is not worth it. This will not bring the desired result and may be fraught with burns of the respiratory system.
A special device - an inhaler with ultrasound or a directed air flow, if it is a compressor nebulizer, turns a medicinal solution into an aerosol with non-heated microscopic particles of a medical preparation. The child will be able to inhale this air mixture through a tube or a special mask. For babies, the option of a mask inhaler is optimal, for older children - with a tube. For antibiotic treatment, it is better to choose a compressor inhaler. Ultrasound is more suitable for phytotherapy and spraying antitussive agents.
Mild cough can be cured by inhalation with saline (0.9%). The course of inhalation with healing mineral water (Essentuki and Borjomi) will also help effectively.
If a child with a severe cough makes a serious diagnosis, then simultaneously with the main antibiotic treatment (in the form of tablets, suspensions or injections), the doctor may prescribe inhalations with mucolytics that dilute the sputum and remove it from the body as soon as possible. As such means may be prescribed. solution for inhalation "Ambrobene"Solution for nebulizers" Lasolvan ", solution for inhalation" Ambrogeksal ".
If it is decided to treat the child’s cough with antibiotics with an inhaler, parents should familiarize themselves with the names of drugs that can be prescribed.
Dioxidine
This antibacterial drug that quickly and fairly effectively destroys staphylococci, streptococci, and also pyogenic bacteria. For inhalation, it is available in the form of a special solution.
Recently "Dioxidine"Children tried not to prescribe due to the fact that the drug is considered quite" heavy "for a growing organism. However, in 2013, this antibiotic began to be used for inhalation.So, if the doctor prescribed your baby inhalation with "Dioxidine" do not panic! Such inhalations are recommended for children from 2 years. In young children, inhaling the drug can cause swelling and burns to the mucous membranes.
This is one of the most inexpensive drugs. A solution of 0.5% should be diluted with saline in a ratio of 1: 2. A solution of 1% is diluted for inhalation with a saline solution in a ratio of 1: 4. The solution, ready for use, should be stored in a refrigerator for no more than 10-11 hours.
Children under 6 years of age must not exceed 1 minute. Children up to 12 years old can breathe in couples for no more than 2 minutes. It is better to adhere to the scheme of double daily use at intervals of 12 hours. Apply "Dioxedin" in the treatment of cough in a child should be exclusively prescribed by a doctor!
Ceftriaxone
This antibiotic is considered very powerful. In the form of a solution for inhalation, it is not for sale, it is necessary to use bottles with a dry mixture for injections. Bottle of 1 ml. diluted with 5 ml of water for injection. The resulting solution should be very thoroughly stirred, shaken, so that there is no sediment on the bottom.
Remember that inhale the aerosol from this solution through a nebulizer can be no more than 5 minutes. The younger the child, the less time he will need for the procedure.
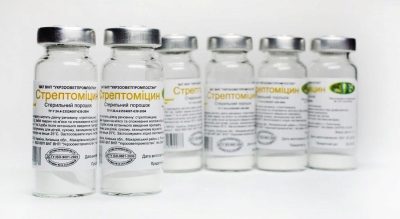
Streptomycin
Inhalation with this antibiotic, an aminoglycoside, is good for children with bronchitis, whooping cough, and pneumonia. True, not recommended for very young patients. For dilution of the solution taken vials of dry matter of 0.5 g or 1 g.
The contents of the vial must be dissolved in water for injection at a ratio of 4 ml of liquid per 1 g of the preparation. Prepare the solution immediately before use.
There are a few simple but important rules that must be followed when coughing antibiotics for a child.
- If the child was prescribed inhalations with antibiotics, and besides them, inhalations with mucolytic or anti-inflammatory drugs, then the procedures should be done in a strict sequence - first mucolytics, then anti-inflammatory drugs and last - antibiotics. Mixing drugs of different groups in the same inhaler is strictly prohibited!
- Inhalation of a child can be no earlier than 1 hour after a meal.
- After inhalation for an hour and a half you cannot drink expectorants and gargle.
- Try to provide the child with peace and quiet so that during the procedure nothing distracts and scares him.
- The duration of treatment should be determined only by a doctor! Even if the child has become easier, and the cough has decreased, inhalation can not be stopped.
Dr. Komarovsky tells in detail about IB inhalation:
General rules and principles of antibiotics for children with cough
- An antibiotic in any form should be taken at regular intervals between one-off procedures. If the drug is prescribed twice a day - take it in 12 hours, if 3 times a day - in 8 hours.
- If your baby has been prescribed antibiotics when coughing, take care of a constant influx of fresh, sufficiently moistened air into the room. This will help the child recover faster.
- The effectiveness of the antibiotic in the treatment of cough should be assessed 72 hours after the start of its reception. If you do not see any improvement in the condition of the baby, this drug is most likely not suitable for you. Do not cancel the drug yourself, the doctor should do it with a replacement with another antibacterial drug.
- The duration of antibiotics should be observed with high accuracy. Usually, the course of treatment with antibacterial drugs ranges from 5 days, and may be the maximum - 14 days.
- To avoid negative effects on the intestinal microflora during antibiotic treatment, ask your doctor to prescribe you prebiotics and probiotics to prevent dysbiosis.
- Carefully read the instructions to the drug.Some medicines should be taken before meals, and some - after. These requirements must also be strictly observed.
- Keep track of the expiration date of drugs. Overdue antibiotics cause a crushing blow to the baby’s liver and kidneys, and can lead to very sad consequences.
What to do if no antibiotics are prescribed for coughing
If the pediatrician considers that you do not need antibiotics when you cough, and the baby is able to cope with the problem, you can alleviate his condition through various methods.
However, listening to the advice of neighbors and moms from the women's forums, be careful! Not all methods are good. For example, gargling with salt and soda does not do any harm, but lubricating the throat with lugol solution is a long-obsolete method that modern pediatricians try not to prescribe.
The famous doctor Yevgeny Komarovsky believes that the huge doses of iodine that a child receives when treating his throat with lugol solution can cause incredible damage to his thyroid gland and cause iodine poisoning.
The opinion of Dr. Komarovsky on the treatment of children's cough can be found here:
The popular method of treating sea buckthorn cough oil, in which this means lubricates the throat and oral cavity, is fully justified, since sea buckthorn is an excellent natural "antibiotic" and quite effectively destroys microorganisms on mucous membranes. But experts warmly advise treating the chest with salt with great caution - warming is contraindicated in case of some diseases of the respiratory system accompanied by coughing. In addition, physiotherapy methods can not be carried out in children with a strong cough on the background of high temperature.
An abundant warm drink is the very thing that a coughing baby needs. Old centuries-old tea with raspberries, milk with soda, warm honey water with lemon is the best tool at hand to facilitate the release of sputum.
Some interesting facts about children's cough, noticed by pediatricians:
- Between the ages of 10 and 11 years, cough is more common in boys than in girls.
- In toddlers, cough is often behavioral, i.e. so the body and mind of a completely healthy child adapt to new stressful conditions — a visit to the kindergarten.
- According to the observations of pediatricians, most often an allergic cough is observed in children in whose apartments the birds live. Not cats, not dogs, but birds.
- After coughing, the vocal cords come to tone and the voice becomes more resonant, which is why people, when making public speeches, cough up before speaking.
For details on when it is worth giving antibiotics to a child, see Dr. Komarovsky’s program.