Antibiotics for laryngitis in children
Children's laryngitis, regardless of the type and form, needs serious treatment. As a rule, it is complex and includes inhalations and physiotherapy, as well as taking additional medical preparations of expectorant, antihistamine or anti-inflammatory action. But are antibiotics needed for treating laryngitis in children? Many generations of doctors argue about this. Let's look at this issue in detail.
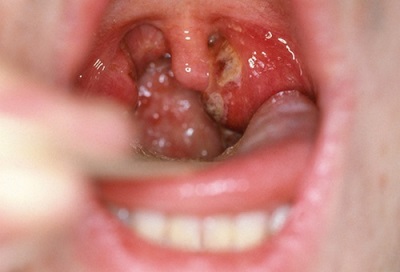
In order to determine therapy and prescribe antibiotics, if required, the doctor must know which microorganisms are the causative agents of the disease. To do this, take a smear from the larynx.
Laryngitis can be caused by various reasons, which ultimately determine the appropriateness of prescribing antibiotics for laryngitis (laryngeal damage) or laryngotracheitis (damage to the larynx and trachea).
These diseases can have different origins:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Viruses
- Mechanical effects on the larynx and vocal cords.
Most often, laryngitis is caused by viruses (adenovirus, rhinovirus, etc.). In this case, the symptoms of the disease will be different from other forms of laryngitis. To the overall picture of the disease will add a high temperature, which rises rapidly, and muscle pain. Such laryngitis with antibiotics does not make any sense to treat. After all, antibiotics effectively destroy bacteria and some fungi, but they cannot cope with viruses.

However, if the disease is of bacterial origin, antibiotics will be the basis of its treatment.
Features of the course of laryngitis in children
Laryngitis in children is significantly different from the disease in adults, which means that the treatment in children will be different. The fact is that in children under 10 years old, all the mucous membranes in the body are very loose, and in the larynx is no exception. Therefore, in the case of a peanut laryngitis, there is an additional risk of getting complications of laryngitis, among which the most dangerous and unpleasant is “false croup”.
It is also called podskladochnom laryngitis, and, unfortunately, this complication occurs in medical practice quite often. The mucous membrane of the larynx in the region of the vocal cords becomes a continuous edema. The child is experiencing extremely difficult breathing, he begins to experience hypoxia, the skin first turns pale, and then completely blue. In this case, only the ambulance can help.
Laryngitis treatment with antibiotics
For children with laryngitis or laryngotracheitis, doctors try to prescribe antibiotics as a last resort. The origin of the disease is often not established. The fact is that in most polyclinics there are no bacteriological laboratories, and if there is, then it will take about 10-14 days to wait for the result of the analysis. The usual practice in the treatment of laryngitis - costing physiotherapy, while taking antiviral drugs. Sometimes the doctor approves local antiseptics in the form of a spray to irrigate the throat, for example, "Miramistin».
If a secondary bacterial infection has joined the primary viral infection, then the doctor will definitely raise the issue of prescribing antibiotics.
When antibiotics are prescribed for laryngitis
There are forms and stages of laryngitis in which the question of the appropriateness of antibiotic therapy does not arise.
In these cases, antibiotics are always prescribed:
- If bacterial origin of laryngitis is confirmed by analyzes,
- If a child has lungitis purulent or purulent mucous sputum,
- If purulent film appears on the larynx during laryngitis,
- If viral laryngitis is over with complications,
- If the laryngitis in a child is protracted,
- In chronic laryngitis with fairly frequent exacerbations.
Antibiotics for laryngitis in children
Usually in children with laryngitis and laryngotracheitis, penicillin group antibiotics are used, macrolides and azalides are quite effective. If the disease is severe, antibiotics of the cephalosporin family will help.
Name of antibacterial drug | Indications for use | Antibiotic Dosage | Antibiotic release form | Contraindications |
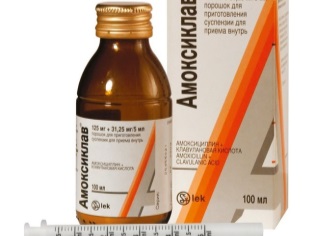
Acute laryngitis, chronic laryngitis, laryngitis prolonged | Babies from 3 months to 1 year-half tsp of suspension three times a day. Children up to 7 years old - 1 tsp. Suspension 3 times a day. Adolescents up to 14 years old - 2 tsp. Of drug three times a day. | Pills, Powder for suspensions, powder for injection. | Mononucleosis, lymphocytic leukemia, cholestatic jaundice and hepatitis, liver failure. | |
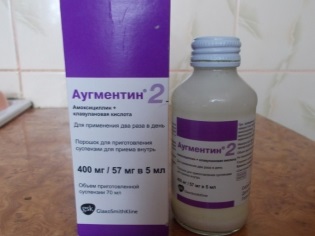
Augmentin | Laryngitis and laryngotracheitis | For children up to 3 months, the dose of the suspension is calculated individually. Children from 12 years old are given a suspension at the rate of 20-40 mg per 1 kg of body weight. | Tablets, suspension, powders for injection | Phenylketonuria. Children under the age of 12 are prohibited from giving a tablet form of the antibiotic. |
Laryngitis, laryngotracheitis | Children from 3 months to 2 years old - a daily dose of about 30 mg (in 2 doses). Children from 2 to 7 years old — daily dose of about 30 mg. (in 3 doses). Children from 7 to 12 years old - 62.5 mg per day (in 3 doses every 8 hours). | Pills | Renal failure, disorders of the liver, lymphocytic leukemia, infectious mononucleosis. | |
"Aksetin" | Laryngitis in acute and prolonged form | Children older than 3 years, 30-100 mg per 1 kg of body weight of the child 3-4 times a day. The optimal daily dose is 60 mg per kilogram of the child’s body weight. Newborns and children up to 3 years old - 30 mg per 1 kg of weight per day in 2-3 doses. | Injection Powders | General depletion of the body, Chronic renal failure, prematurity in newborns, Diseases of the stomach and intestines. |
Laryngitis and laryngitis | The dosage of the drug for children over 12 years old - 0.5 gr. every 12 hours. The dosage for children under 12 years of age is calculated by the doctor individually for each patient. | Dry matter for the preparation of injections | Pathology of the liver and kidneys, intolerance of cephalosporins. | |
«Cefixime» | Laryngitis acute, chronic, prolonged | Children over 12 years old are prescribed 400 mg. drug 1 time per day, children from 6 months to 12 years, the dosage must be calculated by the doctor on an individual basis. | Tablets and powders for self-preparation of the suspension | The state of porphyria, the age of death up to 6 months. |
Laryngitis, laryngotracheitis | Children are prescribed 5-10 mg of the drug for each kilogram of the patient's body weight 1 time per day. | Tablets, capsules | Increased intolerance to macrolides, liver failure. | |
"Clarithomycin" | Laryngotracheitis, laryngitis | Daily dose - 7.5 mg per 1 kg of patient weight. The maximum daily dose is 500 mg. | Tablets, capsules | Severe liver failure, hepatitis, porphyria. |
In addition, a child with laryngitis can receive antibiotics during inhalation. In this way, it is possible to “deliver” the antibacterial drug directly to the affected area. This speeds up the treatment, reduces the risk of dysbiosis.
The following medications are used for inhalation:
- «Bioparox - a drug based on herbal antibiotic Fusafungin. In pharmacies sold in the form of aerosols with interchangeable nozzles. It can be injected through the mouth or through the nose. In the treatment of laryngitis, it is preferable to choose the first method. Inhalation with "Bioparox" should not practice more than 7 days.
- Fluimucil - This is a mucolytic drug that can be bought in the form of powders or solution for inhalation. The dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor individually, depending on the complexity of the patient's condition. The course of inhalation with laryngitis usually lasts from 5 to 10 days, with chronic laryngitis with the permission of the doctor, it can last up to six months.
- "Gentamicin" (in ampoules for the nebulizer). For one inhalation, children over 12 years old require 20 mg of the drug, the procedure is repeated 1-2 times a day. Children from 2 to 12 years old can take no more than 10 mg of the drug per inhalation. Dilute antibiotic should be saline in the ratio of 1 to 6.
The main condition - inhalation with antibiotics should be carried out if you have an inhaler at home. Folk ways to breathe over boiling water, boiled potatoes - in the treatment of laryngitis can be a disservice, and the inflammatory process will only worsen.
General rules for taking antibiotics for laryngitis
- If, after 3 days of taking antibiotics, there is no improvement, the doctor should change the drug.
- It is impossible to stop taking antibiotics when an improvement occurs. It is necessary to complete the entire prescribed course.
- The child should take antibiotics for laryngitis for at least 5 days, but not more than 14. Because in 2 weeks the bacteria will develop their own immunity against the drug. The course duration is determined only by a doctor.
- With high fever laryngitis, it is permissible to take febrifuges with antibiotics. What - the doctor will prompt.
- When treating laryngitis with antibiotics, it is important to remember about the prevention of dysbacteriosis and abundant drinking to remove toxins from the child’s body. You can drink tea, broth hips, chamomile.
- If antibiotics are present in the treatment of laryngitis in the form of tablets or suspensions for oral administration and in parallel in solutions for inhalation, ask your doctor about the compatibility and interaction of two different drugs.

Read more about antibioticsWhen and how they are used, see the next video. Comment gives the popular children's doctor Komarovsky.