Suspension "Zinnat" for children: instructions for use
For bacterial infections, doctors prescribe effective antibiotics for children. Especially popular are drugs in liquid form, because the suspension and dispense for kids is easier, and it is easier to swallow the child. One of the effective antibacterial agents in this form is Zinnat. When it is worth giving it to a child, can it adversely affect the health of children and how is such a medicine properly dispensed?
Release form
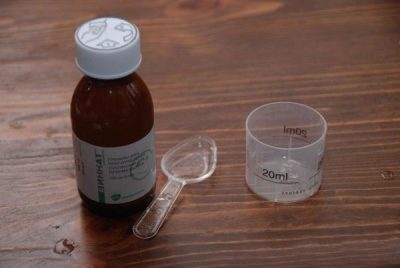
The Zinnat suspension is prepared from granules placed in a vial in the amount of 1.25 g. A measuring cup and a dosing spoon are applied to the glass bottle inside which the medicine is located.
The granules themselves look like grains with different sizes and irregular shapes, up to 3 millimeters in size. They have a white color, so after adding water, a white suspension is obtained, which may have a light yellow tint and there is a characteristic smell of fruit.
The medicine is also produced in tablets that cannot be broken. They are prescribed only to children who can swallow this form of medicine.
Composition
The main component of the suspension is cefuroxime in the form of axetil. This antibiotic for every 5 milliliters of the drug contains 125 mg. To make the medicine sweet, sucrose and sweeteners such as aspartame and acesulfame potassium have been added to it. For the smell in the preparation there is a tutti-frutti flavoring. In addition, granules include xanthan gum, stearic acid and povidone K30.
Operating principle
The drug is representative of cephalosporin antibiotics and belongs to the second generation. It has activity against a sufficiently large number of pathogens, including microbes that produce beta-lactamase, so this suspension can be administered with resistance to ampicillin or amoxicillin.
Zinnat has a bactericidal effect on microbes, acting on the process of synthesis of the walls of bacterial cells.
The medicine destroys:
- Intestinal sticks.
- Hemophilic sticks.
- Gonococci
- Klebsiella.
- Proteus.
- Providences.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Epidermal Staphylococcus.
- Pyogenic streptococci.
- Pneumococci.
- Streptococcus group B.
- Peptostreptokokki.
- Peptococci
- Gram-negative and gram-positive bacilli, including bacteroids and fuzobakterii.
- Borrelia
The drug is inactive against pseudomonads, listeria, legionella, enterococci, citro and enterobacter and some other microbes. The drug may not work on certain strains of clostridia, staphylococci or Proteus, so before treatment it is advisable to conduct a test that will determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to cefuroxime.
Indications
Suspension is prescribed for bacterial infections caused by a pathogen that is sensitive to cefuroxime:
- When tonsillitis, otitis, pharyngitis and other diseases affecting the upper respiratory tract.
- When urethritis, cystitis or bacterial infection of the kidneys.
- With pyoderma, boils and other skin lesions.
- With gonorrhea.
- With Lyme disease.
- With bacterial bronchitis or pneumonia.
At what age is it allowed to take?
Zinnat in a liquid form is prescribed to babies who are 3 months old. The use of medication in newborns is not recommended.The tablet form can be used over the age of 3 years if the child does not protest against the tablets and can safely swallow them.
Contraindications
Suspension Zinnat should not be used in the treatment of children in whom:
- There is intolerance to cephalosporins.
- Phenylketonuria was detected.
Increased attention to the doctor in the appointment of such a drug requires the detection of kidney pathology of the child and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially if high doses are used. Since the suspension includes sucrose, this should be taken into account when treating children with diabetes.
Side effects
Therapy with Zinnat suspension can cause a child:
- Allergic reaction. The most frequent manifestation of it is a rash on the skin, a little less - itching or hives. In rare cases, the occurrence of drug fever.
- Candidiasis. This side effect is associated with the suppression of not only harmful, but also beneficial microorganisms that hinder the development of Candida fungi.
- Stool thinning, soreness in the stomach, or nausea. Rarely, the suspension provokes vomiting or the development of colitis.
- Changes in blood counts. Most often, an increased number of eosinophils is detected, a little less - leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Occasionally, the child's body reacts to the drug hemolytic anemia.
- Headache or dizziness.
- Liver damage, which often manifest a temporary increase in enzyme activity, but can be represented by cholestatic jaundice or hepatitis.
Instructions for use and dosage
To dilute the granules with water, you need to use a measuring cup, typing boiled water in it to the mark corresponding to 37 ml. Shake the granules to make them more crisp, pour the water inside the bottle and close it with a lid. After turning the bottle over, shake it for about 15 seconds, then turn it back to its normal position and shake again.
The child can be given medication undiluted or dilute the required amount of suspension with a small amount of milk or fruit juice just before use. Hot liquid or food with the drug should not be mixed.
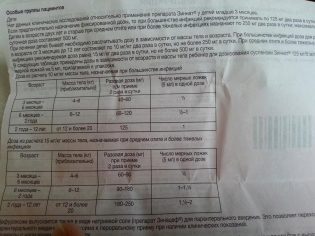
For many children, the doctor prescribes Zinnat in a fixed dosage, which for most infections is 125 mg twice a day. Over the age of 2 years with severe infections, a single dose may increase to 250 mg, which corresponds to a daily dosage of 500 mg.
In some cases, pediatricians calculate the dosage of suspension by weight of a small patient. A single dose of the drug under the age of 12 years is 10 mg per kilogram of body weight of the child, and for severe infections - 15 mg / kg. Having determined the right amount of the active substance, it is given to children twice a day.
For example, a child at the age of 1 year weighs 12 kg, then a single dose of Zinnat for him will be 120 mg (one scoop), and with average otitis or another infection with a severe course, 180 mg (1.5 scoops) should be given.
Overdose
Drinking too much of a suspension can cause nervous excitement and convulsions. Treatment of children with an overdose is usually symptomatic, and in severe cases dialysis is prescribed.
Interaction with other drugs
- Zinnat should not be combined with drugs whose action is aimed at reducing the acidity of juices in the stomach, as this affects the bioavailability and absorbability of cefuroxime.
- If prescribed suspension together with "loopback" diuretics, this will lead to a decrease in the removal of the drug through the kidneys and increase its concentration in the blood.
- Combined use with aminoglycosides increases the risk of toxic effects of cefuroxime on the kidneys.
Terms of sale
To buy Zinnat in granules at the pharmacy, you must first obtain a prescription from your doctor. The average price of one bottle of this medication is 260-270 rubles.
Storage conditions
Granules in a closed bottle can be stored at home at temperatures below +30 degrees for the entire shelf life of this form of medicine for 2 years. When the suspension is already prepared, it should be kept in the refrigerator (the storage temperature of such a drug is from +2 to +8 degrees) for no longer than 10 days. It is important that the bottle be inaccessible to a small child.
Reviews
Most of the feedback from parents on the use of Zinnat suspension in their children is positive. Moms confirm the high efficacy of such an antibiotic for otitis, pharyngitis, furunculosis, pyelonephritis and other infections. Children usually do not protest against his taste, and for dosing mothers often use a syringe from Nurofen or another drug in suspension. As for the negative reviews, then they most often complain of side effects, for example, on the part of the digestive system.
Analogs
Instead of Zinnat, it is possible to use other drugs containing cefuroxime. These include Zinatsef, Axetin, Cefurus, Cefuroxime, Axosef, Cefurabol, Xorim, Cefurozin and other drugs. All of them are represented by injectable form and only a few are available in tablets. If analogue is required Zinnata in suspension, the doctor may prescribe other cephalosporins or penicillin antibiotics, for example, Suprax, Pancef, Augmentin, Hikontsil, Amosin or Ecoclav.
In the following video, a popular children's doctor Komarovsky tells in detail about antibiotics, for what they are needed and in what cases they should be used.