Antibiotic Ear Drops
Ears in children hurt quite often. No, perhaps, not a single child who has ever suffered from earache. More often than others, children under three years of age are subject to inflammation of the hearing organs.
Due to the age-related features of the structure of the Eustachian tube, microbes more easily penetrate from the nasopharynx into the auditory canals.
Ear pain is always an unpleasant, painful condition, which can also be dangerous if the baby does not receive the necessary help in time.
The ears are close to the brain, and the undertreated or burdened otitis is quite capable of causing meningitis or encephalitis.
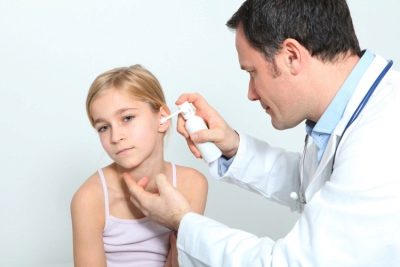
It is easy to notice the ear pain in a child, even if the crumb does not yet know how to speak and is not able to tell about his sensations. The baby becomes capricious, it may increase body temperature, when pressing on the trestle near the auditory orifice, the pain increases, it can release fluid from the ear, sometimes with impurities of pus.
Why does a child's ears hurt?
The causes of ear pain may be several:
- Sulfuric plug formation.
- Foreign body in the auditory pathways.
- Inflammation caused by fungi.
- Residual inflammation after infectious diseases (influenza, measles, scarlet fever)
- Bacterial inflammation (otitis external, medium and internal).
Indications
Determine what exactly was the cause of the inflammatory process in the ears, can only ENT on a personal examination. The fact is that before prescribing drugs, the doctor will need to make sure that the eardrum has not suffered. After all, most of the drops in the ears will have no effect if the membrane is broken.
After determining the diagnosis, the doctor is likely to raise the issue of prescribing antibiotics. With a number of forms and degrees of severity otitis antibiotics prescribed in tablets, suspensions, often in injections. Especially often antibiotics are prescribed for purulent otitis.
The doctor may prescribe local antibiotics either as an independent agent or in combination with another treatment. Antimicrobial drugs in this form have long proven themselves in the fight against otitis media only from the best side. They immediately fall into the focus of inflammation, bypassing the stomach and intestines. This means that the risk of dysbacteriosis or other side effects associated with taking antibiotics is significantly reduced.
A quick hit into the zone of inflammation, a quick action leads to the fact that the pain passes more quickly, and the inflammation decreases after the first day of taking the drops.
Drops with antibiotics try to appoint very carefully, only as needed. They will not take any action against otic inflammation caused by viruses (flu or ARVI). There is also no sense to drip antimicrobials in the event that the pain in the ear is caused by a sulfur plug, a foreign object entering the ear canal.
However, if the ears ache after water enters the pool, or as a complication after the flu, then it is probably a bacterial infection, and here drops with antibiotics will come in handy.
Ear Antibiotics
"Polydex Drops". Two fairly powerful antibiotics in these complex drops are a great way to get rid of otitis of the outer ear. And if the nasal version of the drug - spray - is allowed only for children after 2.5 years, then ear drops can be used at any age.Contraindications, however, are the same: kidney disease and hypertension.
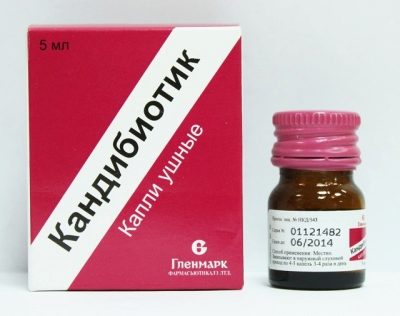
«Candiotics». Antimicrobial and hormonal drops with antifungal effects, which can be used for otitis children for children from 6 years. These drops are popular among parents and children because they have an excellent combination of “efficiency - price”.
«Anauran». Drops with antibiotic and analgesic lidocaine. They relieve the baby of the pain syndrome and destroy a large range of microbes. Do not drip the medicine continuously for more than seven days.
«Otofa». Antimicrobial drops with rifamycin are prescribed for various forms of otitis. The medicine can be given even to newborns, however, strictly observing the dosage and frequency of administration prescribed by the doctor.
«Levomycetin». Alcohol solution of a known antibiotic perfectly helps the child to cope with purulent otitis. However, you should not bury the medicine without a doctor's prescription, it has side effects, in addition, such drops are contraindicated in children with kidney and liver diseases.
"Sofradex". Antimicrobial solution of framycetin is used with great caution in the treatment of ear inflammation in children under 4 years of age.
When instilled into the ears, you must first clean the auricle from sulfur, accumulated pus, and separable liquid.
"Normaks". These drops are available in bottles of 5 ml. and are an effective treatment for all types of otitis, whether external or internal otitis. In addition, these drops are suitable for processing the ear canals after removing foreign objects from them. If the channel is injured, the doctor will appoint a course of digging "Normaksom." The minus of the drug is that it has a minimal anesthetic effect.
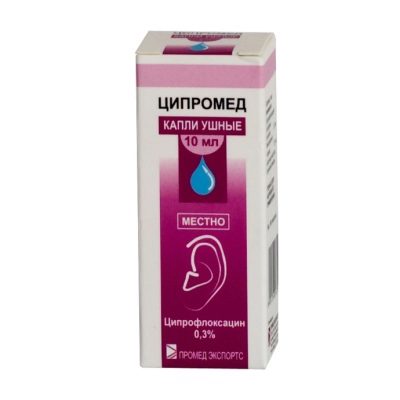
«Cypromed». Drops with antimicrobial action, which are "aimed" not only at the causative agent of ear inflammation, but also at the healing of the eardrum, already affected by the inflammatory process. The drug is contraindicated in children under 1 year.
Other drops
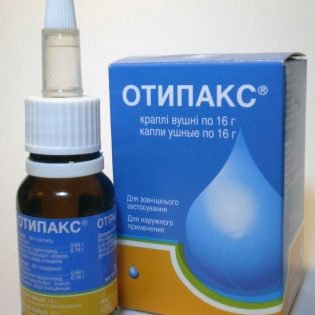
In addition to children's ear drops with an antibiotic, other medicines in the form of drops are used to treat ear pain and the inflammatory process. it anti-inflammatory drugs («Otipaks», «Otinum"), Which are also widely used for otitis media. They, according to parents and doctors, are good and fairly cheap.
Drops can be "complicated." Combined drugs include antihistamines, antifungal, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, hormonal.
How to drip
- Before instillation, thoroughly clean the auricle and the visible part of the ear canal from sulfur and purulent secretions. This may help hydrogen peroxide. If you drip it into the ear canal, it will quickly dissolve the "deposits" of sulfur, to which it is otherwise impossible to reach. It perfectly cleans the ear and has a slight warming effect of boric alcohol.
- To clean the ear in young children, it is better not to use cotton buds. The fact is that the baby can jerk sharply and damage the eardrum with a stick. Better use wadded turunda.
- When instillation of drops with antibiotics, strictly follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor. If after several steps it becomes much easier for the child, you should not interrupt the course or reduce the dose at your discretion. Bring the treatment to the end.
- Drops with the introduction should be slightly above room temperature. To achieve this, it is sufficient 15-20 minutes to hold the bottle in your hand, warm it, and only then inject the drops with a pipette into the sore ear.
- Drops injected into the sore ear can and with the help of turunda. A small cotton roll, rolled up between the fingers, is soaked with medicine and injected into the auditory canal.
- It is necessary to bury the drops in the ear of the child in the prone position, with the ear up. If the baby is agile and restless, close the entrance to the auditory canal with a cotton swab, but do not push it too deep.
- It is better to store the opened bottle of medicine in the refrigerator.
Dr. Komarovsky told in his program about how to properly treat otitis media: