Betadine for children
Betadine is one of the popular antiseptic agents used in surgery, gynecology, pediatrics and other areas of medicine. At what age can you use this medicine in children and what features of the application is important for parents to know?
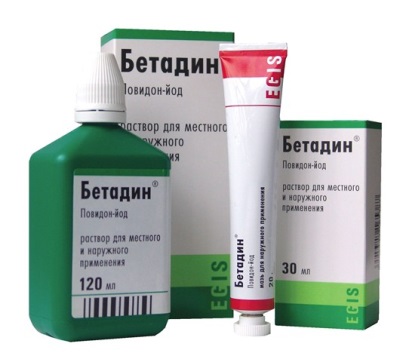
Release form
In the pharmacy assortment you can find this Betadine:
- The solution used for external processing. This brown transparent liquid contains 10% of the active substance. The solution is poured into bottles of polyethylene of different volume - 30 ml, 120 ml and 1000 ml.
- Ointment for external use. It is represented by a homogeneous mass of brown color, which has an unexpressed smell of iodine. One tube contains 20 g of ointment with a 10% active ingredient content.
- Vaginal candles. They have a dark brown color, elongated shape and homogeneous structure. One pack contains 7 or 14 suppositories.
Composition
- The main ingredient of any form of Betadine is called Povidone-Iodine. In 1 ml of solution and 1 gram of ointment it is contained in a dose of 100 mg. In one suppository, such a substance is contained in an amount of 200 mg.
- Water, glycerol, Na hydroxide solution and disodium hydrogen phosphate are added to the liquid form. In addition, citric acid and nonoxynol 9 act as auxiliary components of the solution.
- In addition to povidone-iodine, purified water and sodium bicarbonate, 4 types of macrogol have been added to the Betadine ointment (400, 1000, 1500 and 4000).
- In candles, macrogol 1000 is an additional component.
Operating principle
Betadine is referred to as antiseptic agents used topically and externally. Iodine, which is released from such a drug upon contact with the mucous membrane or the surface of the skin, combines with microbial proteins, as a result of which the bacteria die within 15-60 seconds after treatment.
The drug has a bactericidal effect against many gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. It also affects fungi, protozoa and viruses. Only mycobacterium tuberculosis has resistance to it.
The principles of Betadine's action are very well shown in this video:
Indications
Betadine in solution is used with a different purpose:
- Such a preparation is used to treat the patient's skin during surgical treatment, both before the operation and after the intervention.
- Betadine is used for various medical procedures, for example, with injections, punctures or biopsy. This solution smears the skin around the probe, catheter or drainage.
- Surgeons and other medical professionals apply this medicine on their hands before various procedures.
- Betadine is advised to handle the hands of people who care for infected patients.
- Such a drug is also in demand for the treatment of patient care items.
- The tool is used topically for infection of the nasopharynx (dripping into the nose), as well as the oral cavity (mucous is treated for stomatitis, used for gargling).
- Betadine successfully used for various skin infections. It helps with viral lesions (for example, with chickenpox), with fungal infections and purulent skin lesions.
- Treatment with Betadine prescribed for trophic ulcers, as well as for bedsores.
Betadine in the form of ointment is required for purulent dermatitis, wounds, burns, trophic ulcers and other skin problems.
Betadine suppositories are prescribed for vaginosis, candidiasis, vaginitis and Trichomonas infection, as well as for diagnostic or surgical manipulation of the vagina.
At what age is it allowed to take?
Instructions for use of the ointment or solution prohibits Betadine treatment in children in the neonatal period.
The use of the drug in the first 4 weeks of life is permissible only when absolutely necessary and only after tests that determine the state of the thyroid gland.
Children older than a month can use these forms of medicine safely, and in candles it is prescribed to girls over 8 years old.
Contraindications
Treatment with Betadine is prohibited:
- In renal failure.
- When adenoma of the thyroid gland.
- When hypersensitivity to iodine.
- When hyperthyroidism.
- With dermatitis herpetiformis.
Side effects
If the patient has a hypersensitivity to iodine, the treatment with Betadine will cause him to have hyperemia, itching and other local symptoms, after which the drug should be immediately canceled. To make sure there is no iodine intolerance, the first use of the medicine should be trial - in small quantities on a small area of skin.
If Betadine is used in large quantities, treating a large area of skin or mucous membrane, iodine from the drug will be absorbed, which can impair thyroid function. The same side effect can be observed with very long medication use.
Instructions for use and dosage
Liquid Betadine is used according to such recommendations:
- To treat the skin with Betadine solution, it is not required to be diluted. For treatment of mucous membranes, drains, burn surfaces and in some other cases, the preparation is diluted to a concentration of from 0.1% to 5%.
- Heat liquid Betadine can not.
- The medicine should not fall into the eyes.
- If Betadine, when treating wounds, comes into contact with blood, this will reduce its bactericidal effect.
- The drug should not be used for bites of animals or insects.
- The surface treated with Betadine turns brown due to the film that forms, from which iodine is released. When it disappears, the effect of the drug ends. If necessary, such a film can be easily removed with water.
Ointment Betadine gently lubricate the damaged skin. This dosage form is applied in a thin layer from 2 to 3 times during the day. If required, you can cover the treated surface with an occlusive dressing. Ointment should not get on the mucous eye, and the skin after lubrication, as in the treatment solution, acquires a brown tint, which is easy to remove by washing with plain water.
Candle Betadine need to moisten with water and gently enter into the vagina (especially carefully used this form in virgins). The medicine is used overnight for 7-14 days.
Overdose
An unnecessarily large dose of the drug leads to acute iodine intoxication, which manifests itself as:
- Metallic taste in the mouth.
- Increased salivation.
- Pains in the mouth.
- Heartburn.
- Irritation and swelling of the eyes.
- Skin reactions.
- Digestive problems.
With a very strong poisoning, laryngeal edema, deterioration of the kidneys and blood circulation, as well as pulmonary edema are possible. For treatment, the doctor prescribes symptomatic therapy.
Interaction with other drugs
Liquid Betadine can not be mixed with any disinfectants and antiseptic drugs, especially if they contain enzymes, mercury or alkali. The same restriction is provided for ointment.
Terms of sale
Buying any form of drug at a pharmacy is available without a prescription.The average price of 30 ml of solution is 160-170 rubles, ointment tubes - 240-250 rubles, and packages of 7 suppositories - 350-400 rubles.
Storage conditions and shelf life
For storage, you should choose an unlit, dry place where there is no access for a small child. The liquid form should be stored at room temperature (below + 30 ° C), the optimum temperature range for storing ointment is + 15 + 25 ° C, and for storing candles - + 5 + 15 ° C. The shelf life of the solution and ointment is 3 years, in suppositories - 5 years.
Reviews
On the use of Betadine as an antiseptic, most parents respond positively. Moms praise such a tool for high efficiency and no side effects. Negative symptoms after using this medication are extremely rare.
Analogs
If you need to replace Betadine with another medicine, you can use drugs with the same active ingredient, for example:
- 10% solution Povidone-iodine.
- 10% solution Aquazan.
- Vaginal suppository iodoxide or iodosept.
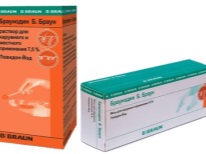
- 7.5% solution Braunodin B. Braun.
- Spray or vaginal suppositories Iodovidone.
- 10% solution of iodine ka.