What to do with uterus tone in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy?
Normally, the muscles of the uterus during the whole pregnancy remain relaxed, calm, and only with the onset of labor, a physiological tone appears that accompanies each labor contraction. The appearance of the tonus in the process of carrying a baby may be associated with training contractions, but the tone in this case is short, not affecting the condition of the fetus. If hypertonus is detected in the second trimester of pregnancy as a long-term condition, this cannot be considered the norm.
What it is?
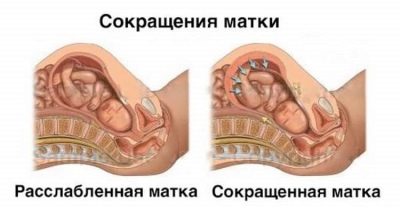
Tonus or hypertonus is called the increased excitability of smooth muscles of the uterus. Calm and relaxed three layers of uterine walls - a pledge of normal gestation of the fetus until delivery. Then, under the action of oxytocin, the myometrium begins to contract during cervical dilatation - this is labor contractions.
Second trimester tonus too early for labor. Therefore, the condition attributed to the pathological. The exception is false contractions that can occur in nulliparous after 20 weeks of gestation. They appear short-term infrequent voltage of the uterus, which persists from a few seconds to several minutes, after which the uterus relaxes.
Increased uterine tone is mainly associated with hormonal changes or any adverse psychological, emotional, psycho-physiological factors.
Most often women who have not reached the age of 18–19 years old and women older than 34 years old complain about the tone of the uterus during pregnancy. Early pregnancy at a too young age proceeds against the background of the underdevelopment of the sexual sphere and the insufficient readiness of the reproductive organ to bear the child. Pregnancy at the age of 34 years has its own characteristics, and women often approach this age with several abortions in history, the presence of infectious or inflammatory diseases in the present or past, in a personal medical history.
We will understand whether the tone is dangerous in the second trimester. It is no less dangerous than the first, because it represents a real threat to the life and health of the child, it can cause the development of oxygen starvation, late miscarriage in the 2nd trimester, as well as a trigger for preterm birth. There is evidence that prolonged and severe hypertonus increases the likelihood of stillbirth, fetal death.
How does it arise and why does it develop?
From the very beginning of pregnancy, the hormone progesterone is produced in a woman’s body in high concentrations. Its main task is to soften the uterus myometrium and keep it in a relaxed state. In most cases, hypertonus occurs with a reduced level of progesterone, its insufficient amount.
A reduced level of progesterone increases the sensitivity of uterine receptors, its contractile ability increases. A critical lack of pregnancy hormone leads to miscarriages, severe fetal hypoxia and death.
The uncritical decline is also felt by the female body, and the female reproductive organ responds first to the lack of a substance important for the safe course of pregnancy - an increased tone occurs.
Studies have shown that hypertonus most often develops in the second trimester in women with hyperandrogenism - increased production of male sex hormones in the female body. And also the tone is found in women with a high content of the hormone prolactin, this condition is called hyperprolactinemia.
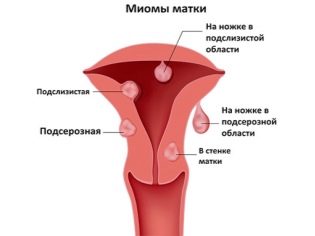
The primary cause of high tonus of myometrium can be any hormone-dependent disease, which the expectant mother could have long before the onset of pregnancy. Such diseases include uterine fibroids, endometriosis.
Myometrium can react with voltage in the second trimester to the rapid growth of the uterus and fetus, as well as in the event that a woman has previously had inflammatory gynecological ailments. Muscle tone may be impaired due to disorders in the central nervous system, which regulates the tone of all muscles in the body, including the smooth muscles of the female reproductive organ. Due to failures in the central nervous system, an increased uterine tone usually develops in pregnant women who are carrying twins or triplets, suffer from high hydration or carry large fetuses. In this case, the muscles of the uterus are over-stretched, and the central nervous system often cannot adequately regulate the state of muscle tissue.
As well as hypertonicity in the second trimester are subject to:
- women with thyroid abnormalities;
- future mothers who had viral infections in the first trimester;
- working at night, in hazardous work, suffering from sleep deprivation, often nervous women;
- experiencing prolonged chronic stress, experiencing for any reason, impressionable women prone to depression;
- suffering from bad habits.
Symptoms and signs
Any part of the myometrium may be strained. The tone of the uterus does not mean that it is all tense. Therefore, at the place of stress, two degrees of uterine hypertonus are distinguished. The first degree is the tension only of the back wall of the organ, and women usually do not feel this tone. It can only be installed by specialists during ultrasound diagnostics.
By the end of the second trimester, the increased tone of the female reproductive organ of the first degree can be felt by weak stretches in the lumbar region, the pain is not acute and is mainly given to the back, to the sacrum. There are no other manifestations.
Second-degree hypertonus is the tension of the anterior part of the myometrium, and usually this tone is richer in signs and symptoms: a woman may experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, they are very similar to pain during menstruation. Sometimes the pain extends to the perineum, and the external genitalia. A woman begins to go to the bathroom more often because of "little need."
The abdomen becomes more rigid, it is located slightly above the normal position in a healthy pregnancy. It is not difficult for an experienced obstetrician to determine the hypertonicity of the uterus through the anterior abdominal wall during routine examination.
The lower segment of the uterus strains extremely rarely. Usually this is observed only in women who have suffered previous injuries to the cervix.
Diagnostics issues
Detection of increased uterine tone in the second trimester of pregnancy is a very alarming symptom, which should not be underestimated by the physician or patient. If the gestation period has not reached 22 weeks, the doctor will suspect the threat of late miscarriage, and after 22 weeks he will warn the patient about the high risk of premature birth. The future prognosis for the mother and the fetus will depend on how quickly the tone is detected, as well as on the treatment performed.
The tone can be a find on the most ordinary examination, which in the middle of pregnancy a woman visits every two weeks. When feeling the abdomen (palpation), the doctor will necessarily pay attention to the altered form of the abdomen and its rigidity up to the so-called stone state.
A woman will have an ultrasound scan, this is necessary if you suspect hypertonia. This study will help to identify which part of the muscles of the uterus is prone to contraction and over-stimulation. It is very important to assess the tone of the uterus at the place of attachment of the placenta. If the site of tension is under it or near to it, then placental abruption is not excluded. On the ultrasound scanner monitor, hypertonus looks like a thickening of the walls of the uterus.
Correct action
In order to preserve pregnancy, when a hypertonus is detected, the expectant mother is recommended bed rest or bed rest. This means that you need to leave all the cases, take the sick-list from the obstetrician-gynecologist and just lie down at home. It is important to eliminate stress, lack of sleep, any physical activity, so as not to aggravate the situation. If the tone is small, the doctor will be able to resolve home treatment with the mandatory observance of all recommendations by the pregnant woman.
In cases of severe second-degree hypertonia, they may offer hospitalization in the second trimester in order to undergo inpatient treatment under the close supervision of doctors.
Do not rush to give up, because the life of the baby is more expensive than the current household chores, and at home it is not always possible to get rid of stress, especially if the cause of stress lies in the family.
Hospitalization is clearly shown for:
- the appearance of spotting blood from the genital tract on the background of second-degree hypertonus;
- the appearance of red blood from the genital tract (a likely sign of placental abruption);
- with severe symptoms and discomfort.
First of all, doctors will need to establish whether the expectant mother has enough progesterone. To understand this issue will help blood tests for hormones. If the concentration is insufficient, progesterone-based drugs will be prescribed - Duphaston, Utrogestan and others.
If a biochemical blood test of a pregnant woman shows a lack of magnesium in her body, she is prescribed magnesium preparations in tablets or capsules or injected Magnesia (magnesium sulfate) if the woman is treated in a gynecological hospital.
A woman is shown taking antispasmodic drugs - «No-shpa"," Papaverine ", both in the form of tablets, injections, and in the form of rectal suppositories (in relation to papaverine). Woman is prescribed and sedatives, which will help to quickly calm down and tidy up the emotional sphere - motherwort, valerian (at the discretion of the doctor). Chemical sedatives are excluded, only herbal sedatives are shown to a woman in the second trimester. "Cherry on the cake" in the treatment scheme is usually present multivitamins - in the second trimester, they are highly recommended.
If the state of serious hypertonus occurs before the 34th week of pregnancy (and this is the entire second trimester and half of the third), then the woman is recommended to administer drugs with tocolytic action - the means traditionally used to stop preterm labor. These include "Ginipral", "Fenoterol", "Salgim", "Indomethacin" and others). If the tone can not be reduced, doctors will try to do everything possible to maintain the pregnancy as long as possible.
It is tocolytics that will give the opportunity to win some time to begin introducing "Betamethasone" to a woman - a substance that accelerates the ripening of the lungs of the fetus. If it becomes clear that the birth will be premature, then such injections will increase the child's chances of survival after birth - without surfactant in the lungs, the baby will experience distress syndrome and the inability to take independent breaths.
Forecasts
Despite the description of the rather dire consequences of hypertonus, in practice, forecasts are usually evaluated as quite favorable.If medical care is provided in a timely manner, then in 99% of cases, it is possible to remove the increased excitability of the uterine muscles in time and prolong the pregnancy not only until the expected date of birth. Often, women who have suffered hypertonicity in the middle of pregnancy and who have received treatment can change the baby and give birth only at 42-43 weeks.
Experts believe that the pregnancy is extended “on nerves” - the more the woman worried about the safety of the pregnancy, the more chances she has for a psychogenic prolonged pregnancy.
If a woman refuses treatment and hospitalization of forecasts, no one will give, because nobody can predict how a woman’s central nervous system and uterine smooth muscles will behave.
There are cases when, due to the tone against the background of stress, only the elimination of the stress factor helps a woman. It is also possible that the tonus persists for a long time, which will increase the chances of fetal hypoxia, in which his brain can suffer, the work of the heart, intrauterine growth retardation may develop.
For more on the symptoms of uterine tone during pregnancy, see the following video.