What to do with uterus tone in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy?
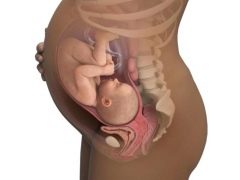
In the final third trimester of pregnancy, women often encounter such a phenomenon as an increased tone of the uterine muscles. The uterus in the last three months of bearing a large fetus, it takes up almost all the space in the abdominal cavity, and therefore its stress, which was sometimes indistinguishable in the early stages, is now perfectly felt by the woman, and is easily diagnosed by an obstetrician at the palpation.
Whether hypertonus is dangerous in the later periods, this article will tell.
What it is?
Hypertonus is the condition of increased excitability of the myometrium (middle layer of the uterus). The smooth musculature of the female reproductive organ after conception is maintained in a relaxed state by the hormone progesterone. Due to this, it becomes more elastic, loose, which makes it possible for it to grow freely. The soft uterus ensures the normal functioning of the placenta, whereas the tension in the areas of the myometrium can negatively affect the state of the uteroplacental blood flow, with the result that the baby may receive less nutrients and oxygen.
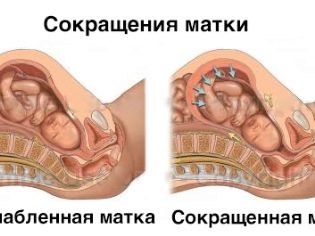
The uterus tone in the third trimester can be both physiological, natural, and pathological. In the first case, it is a question of such a mysterious and insufficiently studied phenomenon, as the struggles of Braxton-Hicks, or the false ones. In the second case, the tension is long, unhealthy, threatening the woman with the onset of preterm labor.
Obstetricians have long noticed that the tone in the third trimester is most common in expectant mothers who have not reached the age of 19, as well as in women who become pregnant after 35 years.
In the former, the uterus is not sufficiently mature and ready for childbirth, the latter have an impressive obstetric history, in which there is a place for both abortions and difficult births, and infectious and inflammatory gynecological diseases.
Pathological hypertonus
Most often, the pathological hypertonus develops due to hormonal progesterone deficiency. The level of this hormone must be quite high throughout the entire gestation period. Only in the last weeks its concentration begins to decline gradually, yielding the dominant right to estrogen and oxytocin. This is what becomes the biochemical basis for the onset of labor.
Among other reasons that can lead to the development of increased uterine tone in the later periods, include the following situations:
- the woman is very nervous, is experiencing chronic stress, is in a state of depression;
- the future mother has bad habits (smoking, drinking, caffeine addiction);
- pregnancy proceeds against the background of endometriosis or with existing uterine myoma;
- the future mother has thyroid disease;
- In the first trimester or the first half of the second trimester, the woman had the flu, a viral infection.
Pathological hypertonus has two degrees.
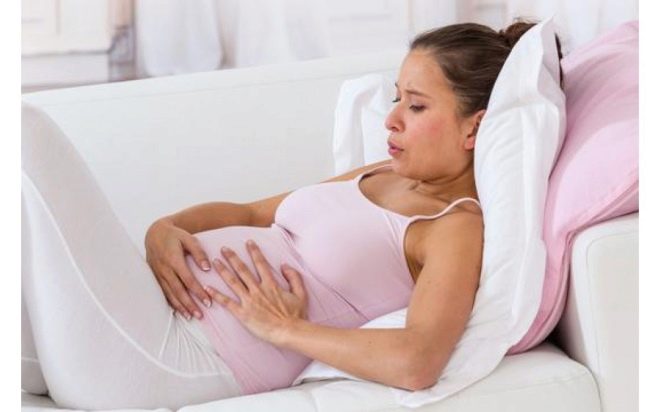
- First - the occurrence of tension on the back of the reproductive female organ. Such a tone is less dangerous, especially if contractile activity is not observed in the area of attachment of the placenta. In the early stages, women usually do not feel this kind of hypertonus.But in the third trimester, the first-degree tone is manifested by pulling sensations in the lumbar region with spreading to the sacrum.
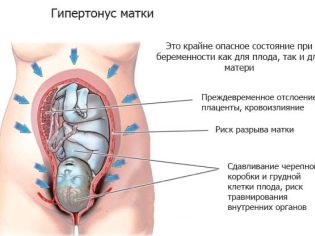
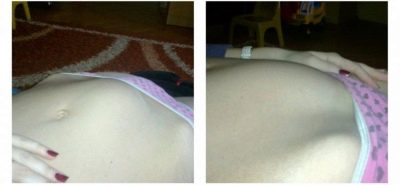
- Second degree hypertonus - The tone of the anterior wall of the reproductive organ or the entire myometrium. It feels like breaking pain in the lower abdomen, tension in the abdomen, its “petrification”. The pathology is easily visible even to the woman herself - the abdomen rises higher, becomes dense, hard, urination becomes more frequent, women often experience false urges to defecate, but it does not occur.
Hypertonus in the later stages is dangerous not only by the probability of premature birth. In a state of tension, the uterus vessels are disturbed, which leads to fetal hypoxia, and sometimes to its death. The probability of placental abruption is not excluded.
It is impossible to ignore the violation, the woman needs to provide qualified assistance and special treatment.
Treatment
With a pathological tone of a woman bed or half bed mode is recommended. If the first degree, then you can allow treatment at home. With the second degree with severe symptoms, and sometimes brownish or blood discharge from the vagina, hospitalization is recommended.
It is important for a woman to reduce physical activity, calm down and stop being nervous.
For the treatment using drugs - antispasmodics. "No-Shpa" helps not only to reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus, but also helps to prepare the cervix for the upcoming labor.
If the gestation period has reached 34 weeks, progesterone preparations may be used for treatment in case of detected progesterone deficiency. After 34 weeks, reduction of progesterone in the body is considered normal, and they are trying to refuse drugs based on it, so as not to lead to hormonal failure.
Often, late tonus develops against the background of a magnesium deficiency. Therefore, pregnant women are shown taking magnesium and injections of "Magnesia" intramuscularly. For the normalization of the emotional background, sedative preparations of plant origin can be recommended, for example, motherwort tincture.
If an obvious psychogenic factor is identified, a psychotherapist and a psychologist should work with a woman. The sooner the source of chronic stress is eliminated, the more likely it is that the tone will decrease.
With the development of pathological hypertonus for up to 34 obstetric weeks, doctors may prescribe a woman tocolytic drugs (Ginipral, Salgim other). They allow you to gain time to start introducing betamethasone-based drugs to the pregnant woman, which will help your baby’s lungs to ripen in an accelerated mode. So the crumbs are prepared for the birth of prematurely. If he is born with a small amount of surfactant in the alveoli of the lungs, then the development of distress syndrome, acute respiratory failure is possible.
Training bouts
False contractions occur in the third trimester, not all women. They are felt as short-term tension of the uterine muscles. The uterus tenses for no apparent reason, stays in that position for a few seconds or minutes, and then relaxes. The next episode of tension can be repeated completely spontaneously - and in a few hours, and in a few days. There is no systematic approach in such fights, which distinguishes them from generic ones.
Some women the first such contractions appear at the 20th week of pregnancy, but for the majority - only in the third trimester of pregnancy. As the gestation period increases, the intensity of the training bouts may increase. Moreover, their complete absence is also an absolute norm.
Brexton-Hicks contractions do not affect the fetus, do not harm its development, do not approximate the moment of commencement of labor, have no effect on the condition of the cervix, do not lead to its disclosure, do not increase the likelihood of premature birth and therefore should not scare a woman.They are considered a manifestation of the preparatory activity of the uterus before the difficult process of labor.
There is also a theory that false contractions are the result of disturbances in the work of the female nervous system. During pregnancy, uterine tissue grows, and in the third trimester, the amount of nerve fibers in the uterus naturally begins to decrease - this is part of the prenatal preparation of the female body. Partially the occurrence of nerve impulses, straining the uterus, may be associated with this process.
How to make it easier?
Symptoms of training bouts in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy help to relieve a warm shower, change of body position, adequate physical activity, taking an antispasmodic pillif agreed with your doctor, a cup of warm herbal tea and a positive attitude. Sometimes it's enough just to lie down and breathe correctly.as it was taught in the courses of future mothers, and the tension of the uterus goes away. Useful yoga, walking in the fresh air.
False contractions do not need treatment, but if they appear frequently and cause marked inconvenience and anxiety, the woman should definitely report them to her obstetrician-gynecologist at a planned reception in the antenatal clinic.