Biochemical blood test during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the woman repeatedly donates blood for biochemical analysis. What this type of diagnosis can tell and what are the norms of indicators for expectant mothers, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
This method of laboratory diagnosis, as a biochemical blood test, is very common in medicine. And this is not without reason - the results of the study provide an opportunity to get the most complete picture of the future mother's health status, about the slightest changes in the work of her internal organs.
During pregnancy, a large load falls on the heart, liver, kidneys, and endocrine system. Control over their activities is an important component of dispensary registration.
In addition, the results of the analysis allow you to judge how the processes of metabolism - carbohydrate and salt metabolism, is there enough for a woman of important vitamins and minerals. They are needed not only for her, but also for the normal growth and development of the baby, since he receives everything he needs with his mother's blood.
In the blood of a pregnant woman, the biochemistry method determines the concentration of sugar and urea, creatinine and total protein, cholesterol, and a wide variety of proteins and lipids, which, in relation to normal values, may indicate a developing pathology of internal organs, inflammation or an allergic reaction.
Analysis is optional, it is only recommended by the Ministry of Health of Russia for the examination of pregnant women. Every woman is theoretically entitled to refuse such a diagnosis. But this should not be done, because the violations detected in time allow doctors to quickly respond and begin treatment, save lives and health of both the woman and her baby.
It took medicine and science several decades to find out the chemical and biological components of all the processes occurring inside the future mother, and also to find out what is considered normal for pregnant women and what is pathological for pregnant women.
Biochemical analysis of blood in pregnant women is a separate story, since the indicators in their blood differ significantly from those in the blood of non-pregnant women and men.
How to pass
Having received a referral to a biochemical blood test, the expectant mother is usually not puzzled by the question of how to do this research correctly. This is a big mistake, because many factors can affect the results of biochemistry.
As a result, the doctor will receive an inaccurate laboratory report. By mistake, a woman can begin to treat a disease that she doesn’t actually have. But it is much worse if the treatment of a disease that does exist, but which is not reflected in the results of laboratory diagnostics, does not begin.
The analysis must be preceded by a certain preparation. Before you go to the treatment room or laboratory, it is desirable for a woman for a couple of days limit the consumption of fatty foods, strong tea and coffee, spices, as well as to abandon the abundance of sweets and minimize salt intake.
Surrender analysis exclusively on an empty stomach since this is the only way the picture of biochemical processes in the body will be the most truthful. However, do not starve for a long time, the long absence of food also distorts the result.The optimal time interval from the last meal to the test is 6-8 hours.
If you take any drugs, dietary supplements, you should definitely inform your doctor, if the situation allows, for a couple of days it is better to stop taking drugs and dietary supplements.
If a woman goes in for sports, and even during pregnancy does not limit herself in physical exertion, you should temporarily reduce them, also a few days before donating blood. Loads activate and slow down certain processes in our body.that causes fluctuations in values in one direction or another, a distortion of the real picture is possible.
Under severe stress on an unfavorable psychological background, a woman’s chemical composition of the blood also changes due to certain hormones, such as cortisol. therefore balance must be maintainedand if this is not possible, then transfer the analysis to a later time, when the “passions subside”.
Blood is taken from the cubital vein. If it is impossible to make a puncture in this place, then physicians can take venous blood samples for examination from any other vein. It will not affect the results.
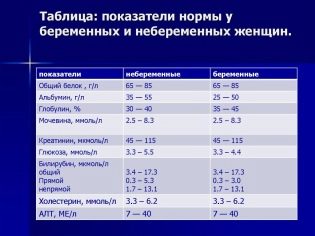
Table of norms of indicators for pregnant women
Results are compared with the following table:
Definable indicator | Normal value for the first trimester | Normal value for the second trimester | Normal value for the third trimester |
Total protein | 63-83 g / l | 63-83 g / l | 63-83 g / l |
Albumen | 32-50 g / l | 28-55.7 g / l | 25.6-66.0 g / l |
Urea | 2.5-7.1 mmol / liter | 2.5-7.1 mmol / liter | 2.5-6.2 mmol / liter |
Cholesterol (cholesterol) | 6.16-13.7 mmol / liter | 6.16 -13.7 mmol / liter | 6.16 -13.7 mmol / liter |
Globulin | 28-112 g / l | 28-112 g / l | 28-112 g / l |
Sugar (glucose) | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter |
Creatinine | 32-70 μmol / liter | 32-50 μmol / liter | 32-47 μmol / liter |
Diastase | 25-125 u / l | 25-125 u / l | 25-125 u / l |
ALT | Not more than 32 U / L | Not more than 31 U / L | Not more than 31 U / L |
AST | Not more than 31 U / L | Not more than 30 u / l | Not more than 30 u / l |
GGT | Not more than 36 u / ml | Not more than 36 u / ml | Not more than 36 u / ml |
Total bilirubin | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter |
Direct bilirubin | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter |
Indirect bilirubin | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter |
Alkaline phosphatase | 40-150 u | 40-190 u | 40-240 u |
Iron | 8.93-30.4 μmol / liter | 8.93-30.4 μmol / liter | 7.2-25.9 microns / liter |
Sodium | 135-155 mmol / liter | 135-145 mmol / liter | 135-155 mmol / liter |
Chlorine | 98-107 mmol / liter | 98-107 mmol / liter | 98-107 mmol / liter |
Potassium | 3.4-5.3 mmol / liter | 3.4-5.5 mmol / liter | 3.4-5.3 mmol / liter |
Phosphorus | 1.0-1.57 mmol / liter | 1.0-1.40 mmol / liter | 0.87-1.47 mmol / liter |
Magnesium | 0.85-2 mmol / liter | 0.85-1.7 mmol / liter | 0.85-1.4 mmol / liter |
Decoding and causes of deviations
Deciphering the analysis, of course, should be done by doctors. However, pregnant women are also interested in what the accumulation of numbers means as a result of their analysis, and most doctors simply do not have time to clarify each incomprehensible point. So let's decode your biochemical analysis together.
Total protein
This is an indicator that indicates the amount of protein in the serum. An insufficient level of total protein may indicate that the nutrition of a pregnant woman is inadequate, that she is undernourished, eats little meat and dairy products, and is depleted.
Throughout pregnancy, the level of this indicator is kept at the same level; normally there should not be sudden changes.
This indicator does not depend on the duration of pregnancy. The increased level of total protein is a reason for a detailed analysis of the so-called "liver function tests" - other indicators of biochemical research, which we will discuss below.
Excess normal protein is an indirect sign of liver disease.
Albumen
This is a protein, an important component of blood plasma. His main job is to circulate blood and carry important substances. Albumin transports hormones and vitamins, bilirubin, cholesterol and all those medications that we take when we are sick. Molecules of this plasma protein carefully stored amino acids, without which our body can not work normally.
Elevated albumin occurs in pregnant women who experience dehydration.Reduced - in future mothers with chronic kidney disease, in female vegetarians, because they do not receive the required amount of protein foods, as well as in patients with diseases of the digestive system and recently suffered injuries.
In general, albumin is slightly reduced in all pregnant women compared to non-pregnant women.
Urea
It is a byproduct of protein metabolism. Urea helps the human body to get rid of excess harmful and toxic ammonia, which is also formed in the process of protein metabolism. Urea is produced by the liver, excreted by the kidneys.. Therefore, the excess of urea in the norm can show problems with the kidneys, impaired excretion functions.
An increase in this indicator may also indicate that a woman is nervous, eats too much protein food, completely eliminated salt from the diet. An increase in urea in the first trimester may indicate toxicosis associated with vomiting.
For a specific degree of excess, the doctor makes a conclusion about the degree of kidney damage and prognosis. An insufficient level of urea sometimes indicates a violation of the activity of the liver. In trimester 3, a decline occurs for natural, physiological reasons and is not considered a deviation.
Cholesterol
It is a natural fatty alcohol, an organic compound that can be found in the cells of all living things. Despite the fact that this substance is scolded and denounced by manufacturers of low-fat products and medicines, it has significant benefits - cholesterol ensures the stability of cell membranes, it participates in the synthesis of vitamin D, corticosteroids, bile acids.
Elevated cholesterol is often a sign of liver disease, diabetes, kidney failure, and diseases of the pancreas and thyroid glands. The decrease in the substance according to the results of the analysis may indicate chronic ailments of the respiratory tract, anemia in the expectant mother, as well as an existing or recent infection.
Globulins
This is the total value of all blood proteins in the form of globules - globules. Their number indicates how protein processes take place, how many proteins circulate in the blood of a pregnant woman. A sufficient number of them is a guarantee that A sufficient amount of hormones and vitamins are transported in the blood.
During pregnancy, the number of globulins of all types and fractions decreases in all women. Lowering the same over the standards established for future mothers can speak about various metabolic disorders, nutritional deficiencies.
The elevation of globulins of certain fractions indicates inflammation in the body.
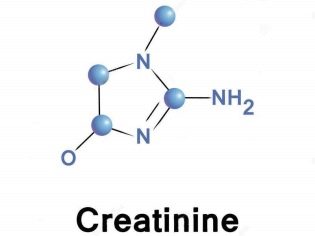
Creatinine
It is a product that remains in the blood as a result of energy processes in muscle and other tissues. The substance itself does not say anything, it is measured and evaluated only with urea. Thus, creatinine fluctuations on the background of increased urea are always evidence of poor kidney function.
Diastase
It is an enzyme that helps the body break down carbohydrates and extract glucose, which is necessary for the life of all organs and systems, which gives energy for their work. A significant excess of the values of diastase indicates a malfunction of the pancreas, its inflammation or cancer education.
The increased level of the enzyme may also be due to a lack of kidney function, which normally removes diastase from the body. Also Diastase indicators are important if you suspect diabetes in a pregnant woman.
Reduced diastase may indicate a cancer in the pancreas, cystic fibrosis.
ALT and AST
These are enzymes: ALT is responsible for the normal functioning of the liver, AST is responsible for the functioning of the heart. The elevated level of these enzymes may indicate problems with these organs.
Bilirubin
This is a breakdown product of hemoglobin. Elevated bilirubin may be due to liver problems, intoxication from a number of drugs.The growth of direct bilirubin often indicates the presence of infectious diseases in women - syphilis or hepatitis. Also, increased bilirubin in the body of a pregnant woman can respond to a parasitic disease or vitamin B12 deficiency.
In the third trimester, the level of bilirubin may rise slightly, this is due to the pressure of the uterus that has grown on neighboring organs, as a result of which bile flow is disturbed. It is not considered a disease bilirubin values return to normal several days after delivery.
Reduction of bilirubin can talk about anemia, because if the pigment that forms during the breakdown of hemoglobin is small, then the hemoglobin itself is clearly not enough.
Minerals
These include iron, chlorine, potassium, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. All of them are direct participants in mineral metabolism and are very necessary not only for the mother, but also for the child in her womb. With each element in the case of deviations from the norms are dealt with separately.
A lack of iron, for example, speaks of anemia, and an excess of calcium - a violation of the kidneys. The amount of minerals is considered together with other indicators of the analysis.
Video on decoding standards and indicators of biochemical analysis of blood in pregnancy, see below.