What is D-dimer, what is its norm during pregnancy and why is it determined?
In the female body during pregnancy there are many different processes, the purpose of which is to create the most favorable conditions for carrying a baby, for its normal growth and development, to ensure maximum safety of childbirth. All these processes are monitored and controlled by doctors through a variety of analyzes. One of them is a D-dimer study. What is this survey, what it shows and why it is done, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
Much during pregnancy depends on the proper functioning of the circulatory system. The volume of blood in the body of the future mother increases, because to provide all the necessary substances, nutrition, vitamins, you need two living organisms at once - mother and baby. On the umbilical cord through the placenta, the child receives the mother's blood, enriched with oxygen and nutrients, and back gives her blood, saturated with carbon dioxide and products of its metabolism.
This exchange will be complete only when the woman’s blood has the right consistency - it is not too thick and not too liquid.
Special blood cells - platelets - are responsible for the thickness of the blood and its ability to clot. Their task is to prevent bleeding and blood loss, to quickly "close" the injury site. This ability of platelets is extremely important in childbirth. If the blood did not have such an amazing ability, then the birth of the placenta after the baby would always be accompanied by severe massive bleeding, dangerous to the life of the woman.
Too thick blood can clog the blood vessels, so nature provides not only the process of thrombus formation, but also fibrinolysis - the dissolution of blood clots. An analysis of D-dimer can tell how these processes occur in the blood of a pregnant woman.
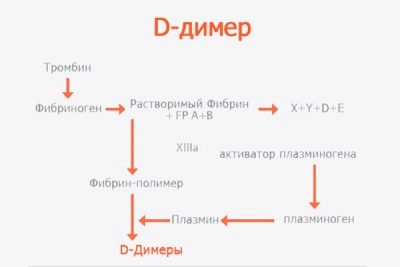
D-dimer is called a small piece of protein, which is formed during fibrinolysis. Blood clots are formed due to fibrin, which in the case of danger associated with bleeding (when injured, injured, in childbirth), acts a special enzyme - thrombin. As a result, blood cells begin to quickly communicate with each other in a clot, closing the wound and preventing blood loss. This is a protective mechanism that saves a person's life.
Once the danger has passed, there is no longer any need for the resulting blood clots. The body needs to get rid of them so that the vessels do not become blocked. For this, another protein comes into play - plasmin, it starts the process of fibrinolysis. Clots under its influence gradually dissolve, are destroyed, the vessels are cleaned, their patency is fully restored. And a part of the substance, which is formed after the disintegration of febrin, and is called the D-dimer.
What does the analysis show?
An analysis to determine the amount of D-dimer shows how both protective processes take place in the human body - the formation of blood clots and their subsequent dissolution. The body works normally when both processes are completely balanced. If there is a "bias" in one direction or another, the amount of the protein structure of D-dimer will necessarily “inform” about this by changes in its concentration.
Thus, the result of the analysis will allow the doctor to judge the blood clotting of a pregnant woman - the rate, increased thrombosis, which can lead to blockage of blood vessels and sad consequences, or low febrine activity, which reduces the ability of blood to clot and increases the likelihood of severe bleeding even with minor injuries.
The analysis appeared in the arsenal of physicians about 30 years ago. During this time, he proved to be excellent, since the accuracy of the research is estimated as high. Pregnant he is appointed several times during the period of carrying the baby, The analysis refers to the mandatory diagnostic measures recommended by the Ministry of Health. As with other tests, a woman has the right to refuse to undergo such a diagnosis, but it will not be very reasonable on her part, because the birth is ahead, and the condition of the blood is of great importance for their favorable outcome.
Indications for appointment
As already mentioned, the blood test for D-dimer is included in the list of mandatory laboratory tests for pregnant women. It is included in the list of blood clotting samples, which, in addition, include tests for determining the time of clot formation, samples for the content of fibrinogen, prothrombin, etc.
However, an unscheduled analysis for D-dimer can also be assigned to a woman if her attending doctor has reason to believe that the expectant mother has problems with blood circulation. Suspicious physicians may be suspicious for a number of characteristic symptoms:
If a pregnant woman complains of pain in her legs, which becomes stronger when walking and staying upright. The skin in the affected areas may have a paler color, legs may swell. In this case, the analysis is recommended to exclude such a dangerous phenomenon as deep vein thrombosis.
If the expectant mother began to cough with blood, she also complains of chest pain and shortness of breath. In this case, the analysis allows to find out if everything is in order with the vessels of the lungs.
If a pregnant woman looks pale, she has signs of cyanosis of the skin, she complains of strange pains in the heart, abdomen, bleeding gums, nausea and rare urination, as well as swelling of the hands and feet. Diagnosis of the D-dimer level in this situation is necessary to confirm or refute multiple vascular damage.
Frequent violations of blood pressure in combination with edema and symptoms of toxicosis - vomiting, nausea and the appearance of protein in the urine - this is also the basis for the appointment of an analysis of blood clotting.
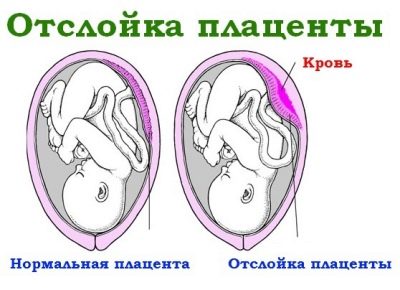
If the fetus will be exposed to the threat of hypoxia or the onset of hypoxia, then the woman will also be recommended to donate blood to D-dimer. Abnormal fluctuations in this protein formation may indicate placental abruption.
In combination with ultrasound the result will be the most accurate.
How is it done?
If the direction for analysis is received out of plan, then no special preparation for blood donation is required. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning, a woman should come to the treatment room on an empty stomach. If the coagulability complex is planned to be determined along with a number of other tests in a planned manner, it is desirable for the woman to carefully prepare for the procedure.
If there is no separate indication for determining the D-dimer protein, referral to this examination is on the list of diagnostic methods. In other words, a woman simultaneously gives blood for several tests. For example, a general analysis, biochemical analysis can be combined with a complex of coagulability, and RW combined with the diagnosis of HIV-accessories.
Planned campaign for blood donation should be anticipated a two-day diet, in which the woman is recommended to refuse fatty foods, from a large number of sweets and salt, spices.For 2-3 days you should, if possible, stop taking the medication, if the doctor does not object, and also reduce physical exertion. It is important to minimize stress and anxiety, because they trigger certain processes in the body with the participation of certain hormones and enzymes, all of which can “spoil” the clinical picture.
Standards of performance
Increased blood levels of D-dimer are characteristic of all pregnant women. The organism of the future mother begins to prepare in advance for the upcoming birth, and therefore the amount of protein increases in trimesters. The longer the gestation period, the greater the amount of the fibrin decay product can be detected in the blood of a woman.
Before deciphering the analysis, you should know that different laboratories use different methods for determining the protein structure, and therefore the numbers in the research form will vary greatly in different pregnant women. In addition, the ability of blood to clot - a rather individual indicator. That is why strict standards defined for all, as such, do not exist in nature. There are only recommendations for assessing the content of D-dimer in the blood of pregnant women.
For an adult somatically healthy woman, it is considered normal if the level of this indicator in her blood does not exceed 500 ng / milliliter. But this applies only to non-pregnant women.
In the “interesting position” the picture changes somewhat:
In the first trimester, the content of the protein component of D-dimer increases by about 1.5 times compared with its baseline level before the woman becomes pregnant.
In the second trimester, the level of D-dimer rises 2 times compared with the baseline characteristic of this woman before pregnancy.
In the third trimester, the level of the substance is tripled from the level before pregnancy.
Thus, it is only possible to know for sure the individual rate of D-dimer with proper planning of pregnancy, when the first blood test for clotting is done before conception. However, the survey before pregnancy, most women in Russia do not bother themselves, except for cases of infertility treatment, delivery of tests for IVF.
The rest come to the consultation after the delay of menstruation. And doctors have to analyze their blood for clotting, based on the maximum allowable rate of D-dimer for an adult. So there were generally accepted values for decoding:
Table of the maximum amount of D-dimer in the blood during pregnancy:
Some laboratories use protein product calculus. in micrograms per milliliter. Then the density of the substance in the blood of a pregnant woman for weeks looks like this:
Table of D-dimer values by week:
Obstetric term | The density of D-dimer, µg / ml |
4-13 week | 0,0 – 0,55 |
13-21 weeks | 0,20 – 1,40 |
21-29 week | 0,30 – 1,70 |
29-35 week | 0,30 – 3,00 |
35-41 week | 0,40 – 3,10 |
Norms and deviations from them are not independently estimated by the D-dimer index alone. To obtain the most accurate picture of the processes occurring in the blood, one should correlate the data on the density of D-dimer with the results of the coagulogram. If the doctor is not satisfied with the indicators of protein compounds in the blood, he will definitely prescribe a detailed coagulogram and, possibly, will give a referral to a hematologist for a consultation.
After IVF
Women who enter into the in vitro fertilization protocol, pass a lot of tests before transplanting and after embryo transfer. One study is necessarily determining the density of D-dimer.
Different clinics treat this analysis differently.
Somewhere doctors prescribe analysis twice, and somewhere they do it only once, when implantation after embryotransfer took place. Most often, blood is taken 5 days after embryo transfer. There is a widespread opinion even among specialists that the implantation process itself may cause a drop in the level of D-dimer in the blood.
It should be noted that 97% of women who decide to become mothers through IVF, this indicator in the blood is elevated. Therefore, it is not surprising that doctors “reinsure” and prescribe blood thinners after the embryos are inserted into the uterus.
The reasons for which D-dimer in the blood of such pregnant women grows more quickly are obvious - this is the implantation process itself, which is not easy given to the woman’s immune system, and the altered hormones, because in the IVF process a woman is necessarily receiving hormone therapy. The density of D-dimer can also be increased by diseases that for some reason have not been identified before.
After replanting, the D-dimer leap to a larger side may also occur due to the multiplicity, for with double or triple, this indicator grows at a different pace. The hormone estradiol also affects the level of protein, which, together with progesterone, is very important for the successful attachment of the embryo.
D-dimer rates after embryo transfer during IVF:
Obstetric term | The value of D-dimer, ng / ml |
4-13 week | No more than 280 |
3-21 weeks | No more than 700 |
21-29 week | No more than 850 |
29-35 week | No more than 1000 |
35-40 week | No more than 1550 |
Special attention is paid to patients with an alarming history. They can carry out blood tests in the dynamics. These include:
- women whose previous IVF attempts were unsuccessful;
- women whose close relatives have suffered a stroke or heart attack;
- women over 35;
- patients with identified blood pressure disorders and vascular problems;
- women who previously had a premature birth, non-developing pregnancies, miscarriages, habitual miscarriage.
Decryption
D-dimer is measured in several quantities - micrograms, nanograms, milliliters, µg FEU / ml (in micrograms fibrinogen-equivalent units per milliliter). And because it is important to check with the doctor by what standards does the laboratory in which blood tests will be performed. So it will be possible to more accurately imagine the result of the survey.
D-dimer alone cannot indicate a specific disease, but if it is significantly overestimated, then this will be the basis for a more thorough examination of the future mother. From the above tables it is clear that the indication of 1900 ng / ml at 7 weeks of gestation cannot be considered normal, as 1400 ng / ml in the first trimester.
If D-dimer slightly exceeds the norm, for example, up to 774 ng / ml at week 20, there should be no fear.
Deciphering the analysis should be handled by specialists; it is rather difficult for a woman to understand the complex biological processes of blood formation in a woman. In addition, in the case of deviations, therapeutic appointments will be required, and self-treatment is completely inappropriate here.
Individual factors cannot be excluded.. Not all women, the level of D-dimer grows with the same pattern. Sometimes it rises only in the third trimester, and it is understandable, because the organism is “mobilized” before the birth. Sometimes jumps occur only in the second trimester, and sometimes jumps do not occur at all.
Causes of deviations
As already mentioned, the diagnosis on the basis of such an analysis cannot be made. But doctors are alerted both by the low level of the protein compound D-dimer and the high one. Let's consider the most likely (but indirect!) Causes of changes in the density of this substance in the blood of a pregnant woman.
If elevated
A significant excess of blood levels of this protein fragment may indicate the presence of blood clots. These assumptions should be supported by other tests that show an increase in platelet count and a decrease in blood clotting time. High D-dimer in this case will be an “indicator”:
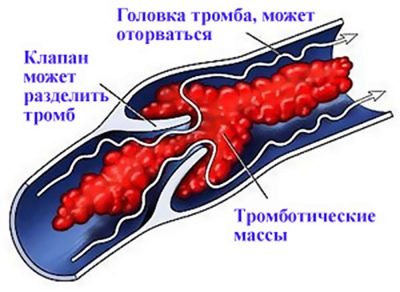
Thromboembolism is a deadly condition in which an existing blood clot comes off and clogs a blood vessel. The consequences can be different, up to the rapid death of a person.
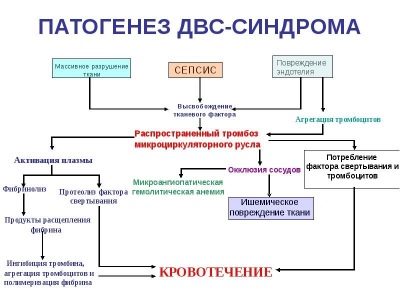
Syndrome DIC or disseminated intravascular coagulation - a disease in which the formation of blood clots is disturbed and small vessels clogged. This condition is massive, disrupting the functioning of almost all organs and systems.
At the same time, abnormal changes occur in the respiratory and urinary systems, in the digestive organs, blood appears in the urine.
If the level of D-dimer is exceeded, but only slightly, the doctor may suspect other diseases and conditions:
- the effects of recent injuries (especially cuts, burns, open fractures, if any of the expectant mother);
- residual effects after surgery;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in which it becomes possible destruction of the vascular walls;
- oncological tumors;
- liver disease.
There are reasons for the growth of D-dimer, peculiar only to women in the "interesting position":
- multiple pregnancies (twins or triplets);
- partial placental abruption;
- severe toxemia with vomiting;
- diabetes mellitus, including gestational diabetes.
Thus, with the results of coagulogram A woman will be referred for consultation to a cardiologist, oncologist, nephrologist, and general practitioner. But this happens infrequently, because a slight excess for pregnant women is a variant of the norm. In general, additional measures of diagnosis are required with a sharp jump in the density of the substance and the deterioration of the pregnant woman. If a woman has a slight increase in D-dimer, but her state of health doesn’t cause concern, she doesn’t complain about anything, she didn’t have injuries, then the doctor can evaluate it as a variant of the norm.
If there are complaints, and the problem with thickening of the blood is confirmed by related experts and additional tests, the pregnant woman can prescribe treatment with anticoagulants that thin the blood. The specific drug and its strict dosage is determined by the doctor. An abundant drinking regimen is prescribed to the woman, this also contributes to blood thinning. Thick blood creates problems with the transportation of nutrients from the mother to the fetus.
If lowered
If you look closely at the tables presented above, you can understand that it is difficult to imagine a reduced level of protein substance, because only the upper limits of the norms are indicated, and the lower ones are not indicated. therefore values from 0 and slightly higher are considered reduced by default.
If your result is exactly the same, you can breathe with relief, because there are no blood clots in the body. But it's not that simple. If a woman neglected the rules of blood donation and came to the treatment room after a hearty breakfast, the results can be false negative - if the blood is taken too early - before the clot broke up, or too late - after D-dimer was removed from the body.
Therefore, there is a reason to retake the analysis in a few days.
Low D-dimer indicates a decrease in platelet count and an increase in blood clotting time. This condition is very dangerous for a pregnant woman, because in labor she can lose a lot of blood. In addition, the risk of internal bleeding increases, which poses a mortal threat to both the woman and her child.
If you find such a problem woman necessarily sent for consultation to a specialist - hematologist, he studies in more detail the properties of the blood of the future mother and makes decisions about treatment. For therapy in this case, often use drugs-coagulants, which increase the viscosity of the blood.
For a baby in the mother's womb, liquid blood is not dangerous, it does not affect its growth and development, the main danger still exists for a woman. The reasons for conditional liquefaction (and it is considered conditional!), Most often such:
- hereditary blood disorders;
- oncological diseases, especially malignant tumors of the liver;
- low levels of hemoglobin in the blood;
- vitamin K deficiency;
- malnutrition.
It should be noted that problems with the reduction of D-dimer during pregnancy occur extremely rarely - usually these are isolated cases for hundreds of thousands of expectant mothers.
Prevention
Specific prevention of problems with blood clotting during pregnancy does not exist. Doctors recommend that you adhere to the correct daily routine, in which the woman will not experience strong physical exertion, will be enough time to sleep. It is important to saturate the diet with vitamins, especially vitamins C, B and K. Do not neglect the intake of folic acid.
It is precisely because of metabolic disorders of folic acid that increased thrombosis often occurs, its lack leads to an increased vascular injury, which increases the level of D-dimer in the blood. Diseases of the thyroid gland and kidney increase the likelihood of impaired hemostasis, and therefore such pregnant women should visit the doctor more often, not to abandon the planned and additional diagnostic measures.
How the increase in D-dimer in IVF affects, see below.