What is a coagulogram during pregnancy, what standards exist and how to decipher the results of the analysis?
It depends on how quickly the blood can coagulate if the pregnant woman is bleeding. If the blood has an excessive ability to clot, it is fraught with thrombosis. Both of these conditions can significantly complicate the process of carrying a child and the upcoming delivery. To assess the risks, doctors prescribe a coagulogram for expectant mothers - a special analysis. How it is carried out, what it shows and how to decipher it, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
The coagulogram has the second name - hemostasiogram. This is a blood test that allows you to establish at what speed, how quickly the blood coagulates and the processes of hemostasis occur. This analysis is mandatory and is done three times during pregnancy. The first time it is done at registration, to evaluate the predictions of complications during pregnancy.
The coagulogram is repeated in the second trimester, at about 22-24 weeks. A hemostasiogram is necessarily assigned shortly before delivery or elective caesarean section, so that doctors can predict blood loss, at least approximately, prepare more carefully and, if necessary, involve hematologists in labor.
The essence of hemostasis is that when the vessels are damaged by the action of special plasma proteins - enzymes - the process of creating a thrombus starts, which tightly closes the place of a possible “leakage”. After the restoration of the integrity of the endothelium in the thrombus is no longer necessary, the vessel needs to get rid of it. The hemostasis at this stage ensures the dissolution of the thrombus and the cleansing of the vessel.
So these processes look normal, but sometimes there are disturbances in the fragile hemostasis system, and such analysis as a coagulogram can tell a lot about them.
All the nuances of coagulation and anticoagulation systems and mechanisms are shown in the study, which is considered to be one of the most “laborious” and complex in laboratory practice. It requires great accuracy from the laboratory assistant and does not tolerate connivance and inattention.
The life of a person depends on the results and their correct decoding, and in the case of pregnant women, two lives at once.
A bleeding disorder can be a big trouble. So, liquid blood (this is what people call bad coagulability, its insufficiency) can cause placental detachment, the occurrence of bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth. It is dangerous in the postpartum period. Thick blood (meaning an increase in hemostasis) can lead to the formation of blood clots, which often causes fetal hypoxia.
Thrombus is one of the most common causes of maternal mortality - death occurs in minutes with pulmonary embolism. A bleeding disorder is also dangerous for the likelihood of premature birth or miscarriage.
Who is appointed?
As already mentioned, all pregnant women must donate blood for a coagulogram three times during pregnancy. However, there are such categories of future mothers who will have to take this analysis much more often. These include women with the following complications:
- rhesus conflict pregnancy;
- woman's tendency to varicose veins;
- various liver diseases in the future mother;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- several miscarriages in history, habitual miscarriage;
- pathology of the placenta;
- multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets);
- revealed violations of blood clotting factors.
In all these cases, the coagulogram is carried out according to the basic scheme. There is also an extended analysis - an unfolded hemostasiogram, which is carried out on special indications for women who suffer from high blood pressure, preeclampsia with edema in both the first and third trimesters.
A pregnant woman will be prescribed an advanced analysis even if she bears double or triplets, and also has a predisposition to blood and vascular diseases.
How to take an analysis?
Preparing for a coagulogram is to follow a diet. For a couple of days it is undesirable to eat spicy and salty, as well as fatty foods. 10-12 hours before blood donation it is not recommended to eat at all, it is allowed only to drink pure non-carbonated water. A day before the analysis, coffee, strong tea, fruit drinks, compotes and any carbonated drinks should be avoided. You should not drink too much liquid, from this indicators may be lowered.
Also, to prepare for the study, you should protect yourself from stress and emotional outbursts. It has long been proven that the nervous factor has a significant impact on the results of coagulogram.
Blood is taken from a vein in the morning. The analysis period is about 1 day. Depending on the workload of the laboratory, the maximum analysis time is 2 days.
Decryption
As a result of the analysis, several major key indicators that influence clotting factors in pregnant women.
- APTT. This abbreviation is shortly called activated partial thromboplastin time - the length of time required for the formation of a blood clot. In women who are expecting a child, APTTV is always slightly reduced compared to non-pregnant women and men. If the APTT is increased relative to the norm, this indicates that the blood coagulates slowly and there is a chance of bleeding. If the APTT is reduced relative to the norm, they speak of "thick" blood and the associated likelihood of blood clots.
- Fibrinogen. It is a protein that is produced by the liver. It is necessary for the formation of a blood clot, because when exposed to certain enzymes it creates the very fibrin filaments with which the injured site is tightened. Without fibrinogen, blood clots would be impossible. In all pregnant women, with an increase in gestation, a physiological increase in fibrinogen concentration is observed. So the pregnant woman's body is preparing for the upcoming birth.
- Tv Behind this abbreviation lies the time needed for clotting, thrombin time. In pregnant women, even perfectly healthy ones, the period of thrombus formation may increase, especially in the first half of pregnancy. This indicator is often broken relative to the norm in women suffering from liver diseases.
- VA. This indicator stands for lupus anticoagulant. This refers to an indicator that evaluates the formation of antibodies. The norm is the complete absence of lupus anticoagulant in the blood of the future mother. If VA is still present, it may indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease, preeclampsia, and thrombosis.
- CT This is the platelet count. It is these blood plates-cells that take the most active and active part in the process of blood clotting. High platelet count always indicates a clotting disorder, as well as a decrease in the concentration of these cells in the blood.
- D-dimer. It is a protein substance that is formed as a result of the disintegration of blood clots and the cleaning of the vessel - fibrinolysis.By the amount of the residual substance, it is possible to judge how balanced the second part of hemostasis is - the dissolution and elimination of blood clots. In all pregnant women, D-dimer is somewhat elevated, but a significant increase in its concentration in the blood of the expectant mother is a very disturbing phenomenon, characteristic of diabetes, preeclampsia, and kidney disease.
- Prothrombin. This plasma protein, which directly affects the process of blood clotting. The definition of prothrombin is considered the most important indicator of coagulogram. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the concentration of prothrombin may decrease slightly.
- RFMK. This refers to soluble fibrin-monomeric complexes, intermediate products of disintegration of a clot as a result of its dissolution (fibrinolysis). At increase of an indicator susceptibility to thrombosis, recent injuries connected with blood loss, operations are suspected. FEMC also increases with preeclampsia, preeclampsia, and renal failure.
- AT-3. This is another protein, antithrombin-3. Its task is to make the coagulability process slower, not to allow quick coagulation. It serves as a regulator. As with most other indicators, it is estimated that AT-3 levels are exceeded or reduced relative to the norm. The increase indicates the risk of thrombosis, and the decrease indicates that the expectant mother has too “thin” blood.
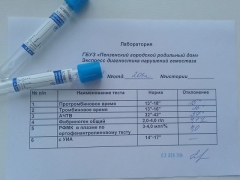
Coagulogram norms during pregnancy in the table by trimester:
Seeking indicator | First Trimester Norm | Second Trimester Norm | Norm in the third trimester |
Fibrinogen | 2-4 g / l | 3-5 g / l | 3-6 g / l |
APTTV | 17-20 sec | 17-20 sec | 17-20 sec |
Thrombin time (TV) | 18-25 seconds | 18-25 seconds | 18-25 seconds |
VA (lupus coagulant) | Not found | Not found | Not found |
Platelets | 120 - 415Х10 billion / l | 120 - 415Х10 billion / l | 120 - 415Х10 billion / l |
D-dimer | Up to 750 ng / ml | Up to 1000 ng / ml | Up to 1500 ng / ml |
Antithrombin -3 | 70-74% – 115-116% | 70-74% – 115-116% | 70-74% – 115-116% |
Prothrombin | 78-142% | 78-142% | 78-142% |
Causes of deviations
If the coagulogram gave unsatisfactory results, the woman has an increased or low ability to coagulate, this is not a reason for panic, but only the basis for a more detailed examination. If in one of the trimesters, according to the results of the analysis, there are significant deviations, the doctor may suggest the development of diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother, the presence of preeclampsia in the late period or severe toxicosis in the early period, as well as pathology of the kidneys and liver. It is on the identification of these causes that additional examination will be directed.
One of the most important indicators, in addition to the APTT, is the determination of lupus anticoagulant. If it is detected, the doctor examines the version of the autoimmune disease in the expectant mother. VA in the blood appears in rheumatoid arthritis, in disorders of cerebral circulation due to ischemic stroke, due to systemic lupus erythematosus.
In pregnancy, the appearance of lupus anticoagulant can talk about such problems as placental abruption, placental infarction, fetal death of the baby, as well as the formation of blood clots.
The increase in febrinogen in the blood can speak about diseases of the kidneys, heart, the presence of malignant tumors and inflammatory processes of different origin. Reduction of fibrinogen often indicates the presence of DIC, liver ailments. Antithrombin-3 is also increased in inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, liver and in the future mother's deficiency in vitamin K. Antithrombin is reduced due to DIC, coronary heart disease, and thrombosis.
Deviations in the coagulogram may also be caused by violation of the rules for testing. If a woman has not warned the lab technician that she is taking any medications, especially coagulant or anticoagulant drugs, in the case of donating blood to a full stomach or with a strong restriction of herself in the liquid before analysis, deviations in her hemostasiogram will be explained only by this.
To eliminate errors, the analysis after receiving unsatisfactory results is recommended to repeat.
In each case, it is required to assess the ratio of all indicators of the coagulogram, in order to assign an individual list of analyzes to the woman. Most often, a pregnant woman is given a referral for a biochemical blood test to determine the sugar content, and she should also give her urine to determine if everything is in order with the kidneys.
Sometimes it is required to perform an additional ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, to receive consultations from a cardiologist, general practitioner, and a hematologist, and only after this treatment can be prescribed.
What are dangerous deviations?
Despite the fact that treatment does not always require serious medication, and sometimes it is quite enough to comply with the correct adequate drinking regimen, special recommendations for nutrition and lifestyle, do not underestimate the bleeding disorders, especially during pregnancy. Refusal of treatment and examination, unwillingness of the future mother to pay due attention to this problem, unwillingness to consult a doctor - can lead to quite dangerous and even lethal consequences.
The most dangerous of them is the occurrence of DIC (syndrome of intravascular decomposition of coagulation). When hypercoagulable in a woman’s body, many small blood clots are formed that can clog the blood vessels. Such clots contribute to the disruption of blood supply between the mother and her child, the baby begins to receive significantly less nutrients and oxygen, and hypoxia can develop - oxygen starvation.
During hypocoagulation, blood clots do not live long and quickly disintegrate, a woman has worse blood coagulation and even minor wounds and scratches can lead to heavy bleeding. It is especially dangerous in the birth process, at the time of birth of the placenta, when the bleeding is most intense. During coagulation, blood does not clot at all.. The prognosis for this pathology is the least favorable - in most cases it is not possible to save the child, because there is a lot of uterine bleeding, and the fetus dies.
To reduce the risks of carrying a child It is desirable to make a coagulogram for a woman at the planning stage of pregnancy. This will help in a timely manner to identify possible pathologies that a woman who dreams of motherhood does not even realize to undergo treatment and become pregnant with more favorable prognoses for bearing and giving birth to a healthy baby. Also, do not give up coagulation during pregnancy.
After all, the fact that a woman never suffered from diseases of the liver and kidneys, did not complain of her heart, does not mean at all that everything is fine with her blood clotting factors.
See the following video for the importance of this analysis.