What is a non-invasive prenatal DNA test and why is it done during pregnancy?
The modern level of development of medicine allows a woman to find out if her baby is healthy when he is still in the womb. This question is central to all future parents, and sometimes it is so acute that in the prenatal diagnosis there is an urgent need. In all doubtful cases, women are referred for invasive studies.
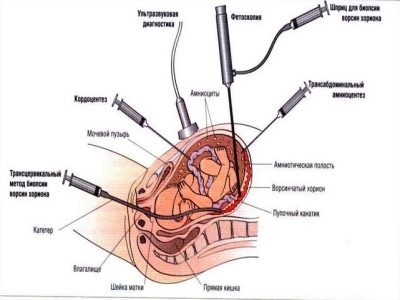
They are traumatic, the woman is very nervous, because all of them (and cordocentesis, amniocentesis, and other methods) are connected with the puncture of the uterus wall and the long needle taking of the genetic material of the fetus for analysis. Today there is a worthy alternative to this procedure - a non-invasive prenatal test. What it is and how it is carried out, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
Non-invasive prenatal DNA test (abbreviated as NIPT) is a relatively new method for examining pregnant women. In Russia, it appeared about five years ago, before such surveys were conducted only in the United States and Europe. Until that time, there were no alternatives for pregnant women — everyone who had increased risks of having a child with chromosomal pathologies, was sent for a consultation to genetics, and then to one of the invasive diagnostic methods.
Before a puncture for taking the genetic material of a fetus or an amniotic fluid sample, the chorionic villi are informed to the woman that the procedure itself is not harmless - it can lead to infection of the fetal membranes, water flow, death of the baby, to a premature miscarriage. Fear of puncture and fear of losing a child usually fade before the prospect of having a baby with Down syndrome or another gross anomaly, and women meekly go for a dangerous diagnosis.
Now to find out the key questions about the health of the crumbs can be without a puncture, without unnecessary stress, and most importantly, without putting the life of a tiny creature in the womb at no risk.
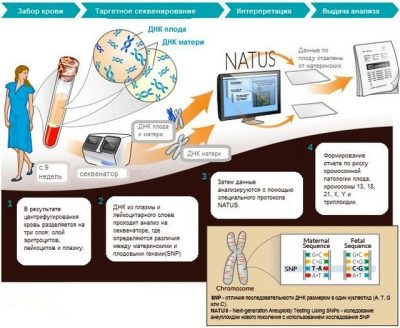
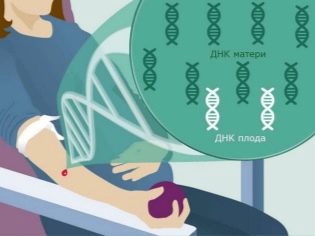
Non-invasive method allows you to make an analysis of genetic abnormalities in the fetus in the blood of the mother. During pregnancy from the 9th week of pregnancy, fetal blood cells penetrate into the blood of a woman in a small amount. They are isolated from the total mass, DNA is detected, and detailed genetic analysis is performed.
This method gives an accurate answer to the question of whether the child is healthy. Do not confuse non-invasive prenatal diagnosis with screening (NIPS - non-invasive prenatal screening). Mandatory tests that a woman undergoes in the first and second trimester, can only establish the likelihood of a baby's congenital chromosomal abnormalities, trisomy and aneuploidy, but in no way give a definite answer, that is, no diagnosis can be made based on the results of screening studies.
NIPT is one of the most accurate studies in obstetrics. True, pregnant women have a rather vague idea about it, if there is one at all. Gynecologists are not in a hurry to inform their patients about the new product. The reason for silence may lie in the fact that Such testing is carried out only on a fee basis, and public sector doctors are prohibited from imposing paid services on patients.
Risk groups
The need to conduct a study of the genetic health of the unborn child may occur even in healthy moms and dads, if both parents or one of them is in the so-called risk group on genetic pathologies. Of course, the issue of child health cares for any pregnant woman, and any child can do NIPT at will, for this it is not necessary to have a referral from a geneticist or special reasons. But there are categories of future mothers who are most desirable for such testing.
If the basic mandatory screening showed a woman a high risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, or other chromosomal abnormalities, non-invasive methods will be a worthy alternative to traumatic invasive ways to establish the truth. If the result is negative, the woman can not worry and not agree to any invasive methods.
In the case of a positive test result and if a woman wants to leave the “special” child, you also do not need to go through anything else. But if the spouses decide to abort pregnancy, invasive puncture still have to do, because The newest method of prenatal research is not a basis for abortion or artificial labor for a long term according to medical indications.
Non-invasive test is desirable to make women who have a previous pregnancy ended with the birth of a child with chromosomal abnormalities, miscarriage in the early period, fading at any time. With age, women age and ovules, their reproductive quality deteriorates, and therefore the risk of having children with genetic abnormalities is higher, the higher the age of the pregnant woman. All women over 35 who are going to have a baby, it is advisable to do such a test.
Invasive diagnostics can sometimes not be carried out if a woman has a threat of miscarriage - any traumatic effect on the muscles of the uterus can lead to abortion. In this case, doctors may refuse amniocentesis or biopsy of chorionic villi. The non-invasive DNA test will come to the rescue.
For women who are not sure of paternity, as well as for women who are in a closely related marriage, the test is not just desirable but necessary. It would not be superfluous to be examined if there were cases of birth of children with genetic problems from both the man and the woman.
It is worth making a similar diagnosis even when a mom or dad has a history of even treated alcohol or drug addiction - long-term bad habits lead to mutations of certain genes, deterioration of the quality of eggs and spermatozoa, which often leads to the development of violations of the chromosome set of the child.
Contraindications
Testing is not performed for women whose gestation period is less than 9 obstetric weeks. In the female blood before this date, the fetal blood cells are not detected, the material for DNA testing cannot be obtained.
If a woman is pregnant with twins, the test can be done, but in case of multiple pregnancies, triplets will not be diagnosed, it will be too difficult to identify the DNA of each fruit.
Such a diagnosis does little to help couples who were forced to resort to the help of a surrogate mother. By the blood of a woman who is not a true biological mother, it will not be possible to accurately identify the baby's DNA. If the pregnancy is due to IVF using a donor egg, testing is also not possible.
A woman will be denied non-invasive DNA testing and if she recently underwent a bone marrow transplant, she received a blood transfusion. All the rest will be analyzed.
Conducting research and preparation for it
From pregnant does not require any training. It is necessary to decide in which medical genetic center or clinic to undergo a diagnosis, make an appointment and come to the appointed time.For the study take the most common blood test from a vein (no more than 20 ml). The blood of a woman is placed in a special centrifuge, her mother's blood cells and children are divided. The sequencing method allows two genomes to be identified. One undoubtedly belongs to the mother, the other to the fetus. Then one of the prenatal tests is carried out (we will tell about several types below), the algorithms with mathematical precision allow us to calculate the probability of a particular pathology not just in percents, but in tenths and hundredths of a percent.
This whole laborious process usually takes 10 to 14 days. Some types of tests make longer and women report results for 3 weeks. Can the test fail? Theoretically, of course, it can, because people make it, and the human factor is very unpredictable. But in this case, a pregnant woman will be called for a second blood collection. In case the invasive diagnosis fails, a repeated puncture is performed, and this is much harder and more dangerous.
results
Testing determines the likelihood of a child's Down syndrome, Turner, Edwards and Patau. Some types of NIPTs can determine Klinefelter's syndrome, all without exception are very likely to detect possible existing pathologies of the sex chromosomes.
If a woman bears one child, the list of anomalies for which the biomaterial will be investigated is wider. With double the conclusion will include only Down syndrome, Edwards and Patau, and more precisely, the likelihood that one or two children have such anomalies.
Additionally, a non-invasive prenatal DNA test with great accuracy determines the sex of the child, as well as its Rh factor and blood type, which can be very important in case of a risk of hemolytic disease of the fetus, which develops due to immune rejection by the body of the Rh-negative pregnant child with a positive rhesus factor blood.
Different test systems have different reliability, but it differs very slightly - no more than 1%. On average, the accuracy of the result of a prenatal non-invasive test is about 98-99%. Note that this is not 100%, but not the 70% that “gives” the general screening in the antenatal clinic.
The interpretation of the results will not cause questions to the woman and her family members. If the child is healthy, the risks will be estimated at 0.1 - 1%. Reviews of doctors about this study are quite positive, the probability of obtaining false-positive or false-negative results is negligible.
Advantages and disadvantages
Prenatal test provides a unique opportunity to identify the probable anomalies in the development of the baby, a record early. In the analysis of the blood of the mother determine the DNA of the fetus from a period of 9-10 weeks. There is no mandatory screening at this time. Therefore, testing provides an opportunity to obtain information about the state of the baby even before undergoing screening studies of the first trimester. Some women who have taken the test and are convinced that the child is healthy will refuse to be screened in consultation with a clear conscience.
A new word in the prenatal genetic diagnosis is the ability to determine the sex of a child in such an early period, which no modern ultrasound can do. At the same time, the accuracy of determining the sex will be 99%, and no one will give more than 80% on ultrasound.
Calm during pregnancy, the certainty that everything is fine with the baby, the future mother needs. After all, because of the experiences can develop a variety of pregnancy complications. Prenatal tests give such calm and confidence.
The disadvantage can only be considered the high cost of the survey. Different types of tests in different clinics will cost at least 25 thousand rubles. On average across Russia, the NIPT is in the range of 25-60 thousand rubles. Finding a clinic where such an analysis will be done is also not easy. So far, such diagnostics is carried out only at genetic centers and family planning centers that have their own genetic laboratory.Such centers are not in every city, and therefore, perhaps, a woman will have to go to a neighboring city or even a region to do such an analysis.
In searching for clinics, it is important not to “run into” scammers. To pass the examination, it is best to choose the leading clinics of Russia, which have a large network of branches by region, for example, Genomed, Genetico, Genoanalyst, Eco-Clinic.
Kinds
There are about a dozen different tests and algorithms for detecting signs of genetic pathologies. They are distinguished not only by their names, but also by the spectrum of the problems they identify. In some tests, the range of considered syndromes and anomalies is wider, others determine only the standard minimum set of chromosomal disorders. Accuracy, as already mentioned, is about the same.
The Panorama test (“Panorama”) is not the most budget-friendly option, its cost starts at 34 thousand rubles, but this test makes it possible to find out the health status of children conceived with IVF, its accuracy with regard to the analysis of this pregnancy is slightly higher other NIPT.
Prenetix is considered more affordable and not less accurate, in any case, in case of singleton pregnancy. Its minimum price in 2018 is 23 thousand rubles. There are also tests such as Veracity and DOT test. They also show highly accurate results.
Reviews
There are not so many reviews about prenatal non-invasive diagnostics, because such tests have not yet become widely known. However, those women who submitted such an analysis claim that the results turned out to be accurate, and in the end it was not at all sorry for the money spent on research.
For information on what a non-invasive prenatal DNA test is and why it is done, see the next video.