What to do with low platelet levels during pregnancy?
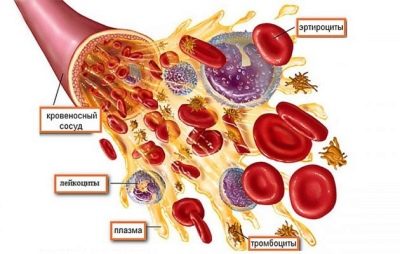
The number of platelets in the blood of the expectant mother is of great importance for pregnancy and childbirth. These blood cells are involved in blood clotting, preventing large blood loss, and also help wounds heal faster. An insufficient number of such platelets can be dangerous for the mother and the baby. In this material we will tell you what to do if the blood test showed low platelets.
How is the level determined
To establish the level of platelets in the blood allows a general analysis, which does not require a woman to absolutely no prior training. A general blood test is done several times over the term of the baby. Doctors have the ability to track changes in the composition of the blood in dynamics.
For women who are not pregnant, and for men 180-360 * 10 ^ 9 cells per liter of platelets are considered normal. While carrying a baby, the norms are somewhat different. The number of platelets in a pregnant woman is reduced compared with non-pregnant adults, and this is a reasonable explanation.
By the middle of pregnancy, the amount of blood in the body of the expectant mother increases, and therefore the concentration of individual cells, in particular platelets, decreases.
Normal for a woman carrying a baby is considered the number of platelets from 140 to 340 thousand / μl with aggregation from 40 to 60%. The number of blood plates decreases in the blood gradually, the lowest value falls on the third trimester. But nature wisely decreed that by reducing the number of cells that are involved in coagulation, it increased their ability to aggregate. This is a kind of preparation for an important event - childbirth, because they are always accompanied by bleeding in one degree or another.
Norm platelets in the blood of pregnant women - a table of average values:
Periods of gestation | Platelet Concentration (Min-Max Level) |
1 term | 170-340 thousand / μl |
2 term | 160-330 thousand / mcl |
3 term | 140-320 thousand / μl |
The reduction of platelets above the norm is called thrombocytopenia. It is always associated either with insufficient production of blood platelets, or with a decrease in their ability to aggregate and participate in the most important biochemical processes occurring in the body.
Reasons for the decline
The reasons for which the number of platelets in the blood decreases, are diverse. In order for the doctor to understand what exactly led to such a clinical picture, additional research will be needed. For this woman is prescribed blood donation for biochemistry, as well as for infections, including hepatitis and HIV status.
In order to understand whether everything is in order with the function of these blood plates, a complex analysis of blood clotting will be prescribed, which will show not only the platelet count, but their quality, determine the blood coagulation rate, show whether there are enough enzymes and proteins involved in the factors coagulability.
The following diseases and conditions most often lead to thrombocytopenia:
- Allergy. With any inadequate response of the body to the allergen, the composition of the blood changes. Platelet count may be reduced.
- Autoimmune processes.Quite often, the reason lies in the fact that a woman's body produces special antibodies that destroy platelets. A decline in this case is inevitable.
- Lack of nutrition and lack of vitamins. An unbalanced, poor or unhealthy diet affects the composition of the blood, while quantitative formulas can vary considerably in one direction or another. Most often, reduced platelets during pregnancy are observed with a deficiency of vitamin B 12 and folic acid.
- HIV infection. In a state of immunodeficiency, the number of platelets is sharply reduced. Even if the first HIV test was negative (and it is done to all pregnant women when registering), there is no guarantee that the second test will also be negative. The incubation period of the disease is long, and the infection could have occurred after registration.
- Thyroid problems. If this gland produces an insufficient or excessive amount of hormones, this also affects the composition of the blood.
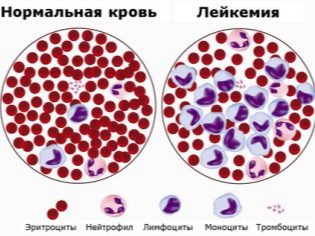
- Blood disorders. Some ailments, such as leukemia, are accompanied by a significant decrease in the number of platelets. A woman will need a consultation from a hematologist and an additional examination in order for this reason to be confirmed or refuted.
- Oncology. Recently, the number of pregnant women in whom malignant tumors are detected for the first time in the process of carrying a child has increased. In any oncologic process, the platelet count drops. The decline is more pronounced and is rapidly observed in malignant processes affecting the bone marrow.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases and acute ills. Infectious diseases, as well as the existing pathologies of the internal organs during childbearing are undesirable also because they affect the composition of the maternal blood, leading to thrombocytopenia, anisocytosis (growth) of platelets.
- Medication. Acceptance of some drugs, such as antihistamines, antibiotics, painkillers, can cause a decrease in the concentration in the blood of the expectant mother of platelets.
Symptoms
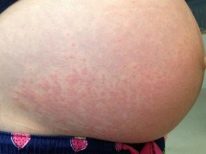
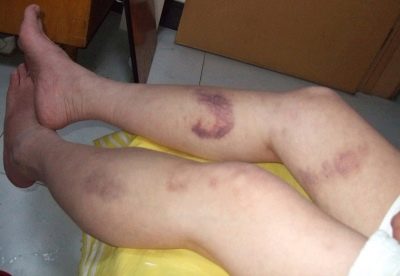
The decrease in platelets makes the blood more "liquid". Thrombocytopenia is referred to in this way in the people. This condition has characteristic symptoms and signs that are hard to ignore. So, a woman with a lack of platelets, completely spontaneously appear bruises on the body. To do this, it is absolutely not necessary to use force, sometimes a light touch on the hand of the future mother is enough to have a large and deep bruise on it in a couple of hours.
A bleeding disorder is manifested not only spontaneous hematomas, but also difficulties in injuries and burns.
Even a shallow wound can bleed for a long time, it can be difficult to stop the blood.
A woman whose platelets have "fallen" is characterized bleeding gums. This is especially noticeable during brushing. Expectant mothers may often have nosebleeds.
Often, thrombocytopenia during pregnancy is manifested by the appearance sukrovichny pink discharge from the genitals. The mucous membranes, including the vagina, are exposed to the hormone progesterone and other pregnancy hormones, they become more friable. Decreased platelets and a bleeding disorder make the membranes even more vulnerable.
Danger
Usually, even a marked deficiency of platelets is not perceived by a woman as a serious disease requiring immediate medical attention. Her condition is generally not a concern.and this is the main danger of thrombocytopenia. An unsuspecting future mother can develop severe internal bleeding at any time, any wounds and injuries are deadly to her because of the probability of losing too much blood.
The most dangerous are childbirth. Blood loss with them is inevitable, the largest amount of it is lost at the time of birth of the placenta.
In a woman with normal coagulability, the surface of the uterine wall, from which the “childish place” departs, is thrombated rather quickly. If the blood plates are not enough, it threatens with massive bleeding, which will be very difficult to cope with even for a brigade of physicians who are ready for everything.
While carrying a child, the “liquid” blood of the mother does not cause the child any particular problems. It does not interfere with its development, does not interfere with the normal growth and circulation of blood in the mother-placenta-fetus system. but even a slight detachment of the placenta can lead to the death of the baby and is a danger to the life of his mother. In addition, a woman with thrombocytopenia has risks of dangerous hemorrhages - in the lungs, in the brain, with all the negative consequences resulting from this until death.
Treatment
The first thing to do when detecting low platelets is to consult with your doctor and undergo additional examinations. Tactics and treatment regimen depend on the true cause of the phenomenon. Traditionally, thrombocytopenia is used prednisonehowever, this steroid hormone has a lot of side effects, and during pregnancy, treatment is markedly different from standard therapy.
If the prichn, for which platelets were reduced, lies in an infectious disease, it should be treated. If we are talking about SARS or the influenza virus, then the composition of the blood is normalized after the woman finally recovers, without any therapy at all.
The treatment will not be needed even if the number of blood plates has decreased due to the medications that the expectant mother has taken. It is enough just to stop taking these medications, and the blood will return to normal.
If the state of platelet deficiency is associated with disorders of the thyroid gland, kidneys, then the woman is referred for consultation to a nephrologist or endocrinologist. Together with the gynecologist, these specialists will have to plan a treatment regimen for the main disease.
Special medications that have the ability to increase blood clotting are rarely prescribed, since they are not intended in principle for use during pregnancy. If the reduction of blood platelets is critical, then the woman is hospitalized and coagulants are injected into the hospital under the supervision of a doctor. This is especially true when there are only a few days left before delivery.
And at home and in the hospital women are recommended to take vitamin complexes. She should also be more attentive to her diet. Products that increase blood clotting are bananas, apples, chicken and quail eggs, meat and fish, fresh greens.
With a slight lack of platelets, changing the rules of nutrition is more than enough to correct the composition of the blood.
The most difficult treatment to be women with autoimmune thrombocytopenia. They are prescribed hormonal drugs (glucocorticosteroids) in a hospital setting. In some cases, if the condition of the pregnant woman is threatening, donor blood transfusions may be performed. This helps at least temporarily increase the number of blood platelets and increase the body's defense.
In hormone treatment, they most often start with Dexamethasone, gradually moving from therapeutic to prophylactic doses, until the platelet count returns to normal or approaches the current norm.
If hormone therapy cannot raise the number of blood plates, human immunoglobulin injections are prescribed. Future mother is waiting for several injections for pregnancy, in each course - only 1 shot.
In the most severe cases, when proper nutrition and hormones are powerless, a woman can undergo a laparoscopic spleen surgery for health reasons, because it is in this organ that most of the platelets die.The puncture is done small, splenectomy itself is performed under general anesthesia.
The dosage of drugs for drug sleep is calculated by an experienced anesthesiologist. The prognosis of such an operation during pregnancy is positive.
How to increase platelets at home, see the following video.