Norm platelets in the blood during pregnancy, the causes of deviations
The level of platelets during pregnancy is of no small importance. Blood tests determine the number of these blood plates in order to timely diagnose various problems with the future mother, which can be potentially dangerous for the health of the woman and for her baby.
What should be the rate of platelets in the period of gestation and what can say deviations, we describe in this article.
What it is?
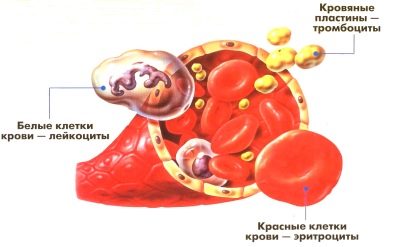
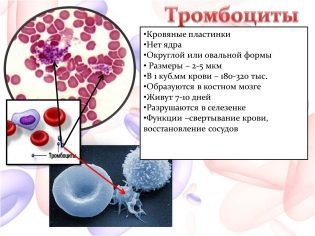
Platelets are not accidentally called blood plates. They literally with their own calves close the space through which the body can lose a large amount of blood when injured.
A few decades ago it was believed that on this platelet function can be considered exhausted. However, modern doctors and scientists have found that, in addition to the creation of a blood clot, platelets contribute to the healing and repair of tissues after injury, injury or surgery. To do this, they emit special substances into damaged tissues called growth factors.
Platelets are involved in the process of blood coagulation, as part of the primary tube, which closes the wound. In addition, their surface accelerates plasma coagulation processes.
Additionally, platelets take on the role of immunity aides. They contribute to the immune defense, interacting with specific cells of the immune system - antibodies.
A lack of platelets in the blood, as well as an excess, are conditions that are dangerous to a person’s life. At the same time, not only the number of blood platelets, but also their functionality plays a big role. Sometimes, with a normal number of cells with reduced function, insufficient aggregation is observed, and blood clotting is disturbed.
Analysis
Separate analysis of platelet content pregnant women are not prescribed. Their number is well defined in the general blood test, which is given repeatedly during the carrying of the baby. Preparation for this analysis is not required, it is not necessary to pass it on an empty stomach.
In identifying problems with platelets, a woman may be assigned additional tests to help answer the question of which of the cellular functions are insufficient or excessive.
These can be complex blood tests for clotting, coagulogram.
Norms for pregnant women
The blood of an adult healthy person contains about 180-360 * 10 ^ 9 cells per liter of platelets. However, during pregnancy, their number is understandable and reasonably decreases - the amount of circulating blood in the expectant mother increases, and therefore the concentration of blood plates decreases.
In the third trimester the number of platelets in the blood of the expectant mother reaches its minimum. At the same time, the ability of plates to communicate with each other and participate in aggregation increases. Thus, the pregnant woman's body is preparing for the upcoming birth, because the most important thing is to prevent severe bleeding in the process of giving birth to a new person.
For a pregnant woman, the average amount of platelets is 140 to 340 thousand / μl with aggregation of 40 to 60%.
The normal concentration of platelets during pregnancy - table:
Gestation period | Average platelet count (acceptable range) |
1 term | 170-340 thousand / μl |
2 term | 160-330 thousand / mcl |
3 term | 140-320 thousand / μl |
The number of platelets at 12 weeks of pregnancy, exceeding 180-190 thousand / μl, is considered as a high content of blood plates, and indicators below 110-125 at 34-36 weeks of pregnancy are regarded as an insufficient number of platelets.
Possible violations - causes
The composition of blood is not a constant, its quantitative and qualitative composition directly depends on a variety of causes and factors, both external and internal. Therefore, an increase or decrease in platelets in the blood of the future mother is not regarded as an independent disease, but is seen as a bright symptom requiring a more detailed investigation - why this happened and how to fix it.
An increase in platelets leads to a phenomenon that people have "thick blood". This is fraught with the emergence and separation of blood clots and the possible death of the mother. The fruit does not receive beneficial substances, because the blood flow in the mother's body is slowed down.
Low platelet count creates a risk of bleeding, which will be very difficult to stop. It is especially dangerous in childbirth, at the time of birth of the placenta.
Increased content
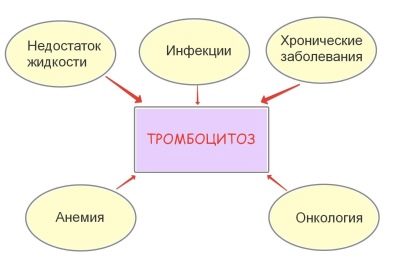
An increased level of blood platelets is considered if their number exceeds 380-400 thousand / μl. In medicine, this phenomenon is called thrombocytosis.
Many future mothers may wonder why at the upper threshold of 320-340 thousand / μl thrombocytosis is diagnosed only closer to 400 thousand / μl. Everything is very simple - Doctors leave free “corridor”, which may be due to individual physiological characteristics, because the body of each pregnant woman prepares for childbirth with its own "nuances". Therefore, the value of platelets in 370 thousand / μl at 36 weeks of pregnancy will not be considered as thrombocytosis and need any treatment.
Thrombocytosis in expectant mothers is often associated with toxemia. Nausea and vomiting, which often accompany the first trimester, and sometimes return in the third, lead to loss of body fluids, which in turn immediately affects the composition of the blood - it thickens, the number of platelets in it increases.
If there is no toxicosis and vomiting, and a woman still has high platelets, This may be due to a large number of reasons:
- Lack of fluid. Some of the expectant mothers are so afraid of edema, which limit fluid intake to a critical point. The same reasons can cause an increase in platelets in a pregnant woman in the summer, when it is hot outside and sweating is increased.
- Infections. Viral and bacterial diseases also cause the rise of platelets in the blood. Thrombocytosis can also be a fungal infection.
- Chronic diseases. During pregnancy, the load on all organs and systems increases. If a woman has chronic diseases, then their exacerbation is possible. It will also cause the rise of platelets, which are very sensitive to any changes in the body.
- Anemia. The lack of hemoglobin in the blood during pregnancy is not so rare. But platelet count is primarily affected by anemia associated with iron deficiency.
- Oncological diseases. Elevated levels of platelets often accompany malignant tumors and processes, especially in the hematopoietic system.
- Medicines The increase in the number of platelets is influenced by diuretics or hormones that could be used by the expectant mother.
A woman may not experience any symptoms of thrombocytosis, however, in some cases, symptoms such as spontaneous hematoma - even with a light touch, a woman may have bruises.Sometimes a small vascular rash can appear on the skin, it is very similar in character to a small “star” meningococcal rash.
To guess about the problems with the blood of a woman can for such fairly universal symptoms as bleeding gums. There may be nosebleeds. Elevated platelets can cause changes in blood pressure, tingling and numbness in the tips of the fingers, pallor of the skin, shortness of breath, headaches.
Reduced content
Low platelet count is a decrease in their number below 140 thousand / µl. 120-122 thousand / μl - this is moderate thrombocytopenia. If there is a fall below 110 thousand / μl - this is pronounced throbocytopenia.
In the early period it is dangerous by miscarriage, and in the later period - by massive internal or external bleeding.
The reasons that can cause a decrease in platelets are also diverse:
- Allergic reaction. Any allergy causes a whole cascade of reactions in the body if a woman has an allergic tendency. Lowering blood platelets is just one of the changes in the composition of the blood. Eosinophil levels will help doctors establish the truth. With allergies, it is also elevated.
- Avitaminosis. Lack of vitamins and essential minerals in the future mother's body, lack of nutrition can also be the cause of thrombocytopenia. Especially often the reduction of platelets develops against the background of a lack of folic acid and vitamin B 12.
- Endocrine disorders. Hormonal imbalances can cause many complications during pregnancy. Especially often the drop in platelets develops against the background of a lack or excess of thyroid hormones.
- Blood clotting disorders. The number of blood platelets may decrease due to some deviations in various clotting factors. Thus, the lack of the enzyme thrombin leads to an excess of platelets, and an excess of fibrinogen - to their lack.
- Problems with the bone marrow. The composition of the blood changes due to bone marrow hypoplasia or oncological diseases that affect the bone marrow.
- Medicines More "liquid" blood becomes due to the intake of antibiotics and diuretics, as well as from antihistamines and painkillers.
Laboratory tests confirm thrombocytopenia, but an attentive woman can guess about her herself on a number of characteristic symptoms, among which the main criterion is a bleeding disorder.
At the slightest cut woman it's hard enough to stop the blood, she often has bruises, the origin of which the expectant mother herself cannot recall, as well as nosebleeds.
Women in an “interesting position” with a lack of platelets in the blood may experience weak blood supply of “daub” from the genitals, which many mistakenly mistaken for threatening abortion. It can last for several days, or it can remain unchanged for weeks, accompanying almost the entire pregnancy, if the expectant mother is not provided with medical assistance aimed at eliminating the cause.
Treatment
With high platelets
Doctors recommend treating thrombocytosis in the hospital, because a woman can be prescribed medications - angiagreganty and anticoagulants, which are poorly combined with fetus bearing.
Dosages are selected on an individual basis; in a hospital, doctors have the opportunity to provide all possible risks.
With a slight excess in the drugs is not necessary, it is quite enough just to change the diet of the future mother.
On the table, women with elevated platelets must necessarily have products that have a beneficial effect on blood viscosity, reducing it. These are vegetable oil, fish oil, tomato juice, onions, cranberries, green apple, green vegetables, buckwheat porridge, kefir and cottage cheese, fish caviar and seafood.
Hyperagregation needs in the correct drinking regime. During the day a woman needs to drink at least 2 liters of liquid. Allow clean drinking water, green tea, homemade fruit drinks from the berries.
Before you take such a regimen as a rule, you should always consult with your doctor, because with preeclampsia and a tendency to swelling, you should be careful with the liquid. In this case, the doctor prescribes an individual drinking regimen, and the amount of fluid required per day may differ from the average values.
Folk remedies for pregnant women is better not to use, despite the fact that they help to quite effectively thin the blood. At home, a very difficult task is to correctly calculate the dosage of medicinal plants.
Even the most innocent herbs and inflorescences with non-compliance with the dosage and ignorance of their side effects can adversely affect the condition of the fetus and the woman herself.
With a lack of platelets
With a slight decrease, especially if it is due to a previous infection, for example, influenza or ARVI, treatment is not required. Usually the platelet count is normalized after the woman finally recovers. In the same way they cope with thrombocytopenia caused by medicines, they simply cancel the drugs that cause such an effect.
Problems with the internal organs - the kidneys or the thyroid gland - should be solved by narrowly specialized doctors. Consultation with a nephrologist and endocrinologist is necessary for a womanso that she is prescribed the correct treatment.
If a biochemical blood test confirms that the reason for the drop in the number of blood platelets lies in the lack of certain vitamins, the expectant mother will be prescribed vitamin complexes.
Coagulant preparations that cause blood thickening should also be used preferably only in a hospital under the supervision of a physician. Usually such a need arises in the last trimester of pregnancy, when a woman should be prepared for childbirth or a cesarean section.
In other cases, it is enough to adjust the lifestyle of the pregnant woman and change her diet. Daily menu should be included. bananas, apples, chicken eggs, meat and fish, greens and beans.
With significant thrombocytopenia, in which the body itself produces antibodies against platelets, a woman is hospitalized. She is shown taking corticosteroid hormones, medicamentally suppressing immunity, and also replacing blood transfusions if the level of blood platelets drops below a critical point at which there is a serious danger to life. Helping such a pregnancy helps the gynecologist hematologist.
For more information about the level of platelets in the blood and the reasons for its fluctuations, see the following video.