What are the standards for blood tests during pregnancy and what are the causes of deviations?
Blood is a very informative environment that can tell a lot to experts about what is happening in the human body. Therefore, it is not surprising that during a responsible and important period of pregnancy, women are often given different directions for blood tests. What studies are conducted by expectant mothers, what are the norms of indicators for basic research and what are the reasons for deviations from these norms, we will tell in this material.
What blood tests does a pregnant woman give?
Studies of the composition of the blood are different. Some are taken from a vein, others require capillary blood from a finger. Studies are conducted by different laboratory methods, and the search field is different in each case.
A complete blood count, for example, can tell about its quantitative composition, and biochemical analysis reflects the essence of the processes occurring in the body. That is why it is impossible to collect blood in one tube in order to immediately carry out several tests, although some tests of laboratory assistants during blood sampling still manage to combine, for example, HIV and RW. Let's look at the main types of analysis in more detail.
Clinical (general)
The first time such a survey will be offered immediately, as soon as the expectant mother will be asked to register with the consultation. Then, in the course of carrying the baby, she will pass it on several more times - in the 2nd trimester, at 30 weeks when applying for maternity leave, as well as in the final pregnancy and on admission to the maternity hospital.
This method helps to calculate the number of the main components of the blood mass - blood cells, which are red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes. In addition, technicians determine the ESR - the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an important indicator of health - hemoglobin level.
This analysis allows you to identify anemia, as well as inflammatory processes and allergic reactions. The blood for the study is taken both from the finger and from the vein, this makes it possible to prescribe a diagnosis at the same time as some other tests - no additional blood sampling is required.
In addition to the basic composition of the blood, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, myelocytes and other parameters are determined in the sample.
Biochemical
This method of laboratory diagnostics, in contrast to the previous one, is aimed at determining organic and chemical compounds that may be characteristic of one or another reaction in the body. He gives a fairly accurate idea of how the internal organs and systems of the future mother work, whether there are metabolic or other problems. The load on all the organs of the expectant mother during the period of carrying the child increases significantly, and monitoring their condition is very important both for the doctor and for the woman herself.
A detailed analysis that examines several dozens of different indicators makes it possible to identify violations in time and provide a woman with timely and competent medical care.
Biochemical analysis allows you to set the blood sugar and cholesterol, various proteins, enzymes, metabolic products. Certain concentrations of them well characterize the state of individual organs and systems and the whole organism.
For a long time, doctors could not measure the norms that are specific to pregnant women, because the woman’s body works differently in the state of expectation of the child, other processes take place in it, which means that the general norms of blood biochemistry cannot be considered a measure. But now the average values are derived, and the accuracy of the analysis is quite high if properly prepared for the analysis.
Hormone
The study allows to determine the ratio and the number of substances that perform an important function - they are responsible for the normal development of the embryo, and then the fetus, for its preservation and growth.
Hormonal tests are not required they are assigned to expectant mothers as needed. Moreover, there is no single study on all hormones, the doctor can give direction only to those whose concentration causes questions to him.
Blood is taken from a vein, as is the case with biochemical analysis.
Hormones accompany all stages of carrying a child, and a change in their level can be detrimental to the effect - the baby will stop developing, miscarriage will occur, and the likelihood of congenital malformations will increase. The process of childbirth and lactation is also a sphere of influence of hormones, as well as the mood and well-being of the future mother.
Ladies in the “interesting position” can be prescribed tests for the determination of estriol and estradiol, testosterone and prolactin, thyroid hormones, as well as many other hormones that affect the course of pregnancy.
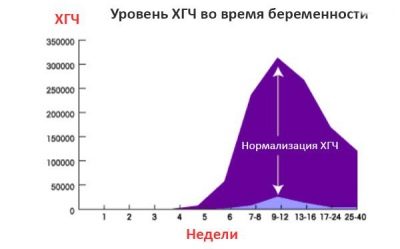
The most popular among pregnant women in the early stages are blood tests for the content of hCG and progesterone. It is these hormones "in response" for the preservation of the baby and its normal development.
Screening research
A special place in the list of blood tests is assigned to two screening examinations, which are held in the first and second trimester:
- In the first trimester, blood from a vein is taken from week 11 to week 14, the biochemical material is taken on the same day with ultrasound diagnostics, because only in the complex can the results be interpreted and the risk of a particular woman to give birth to a baby with Down syndrome can be calculated , Turner and Edwards diseases, gross abnormalities of the brain, spine and other terrible diagnoses.
In the course of this survey, the level of the hCG hormone (human chorionic gonadotropic human hormone), as well as a special protein, which is part of the blood plasma only during pregnancy - PAPP-A, is determined.
- In the second trimester, screening is prescribed for 16-19 weeks, ultrasound can be done later - up to 21 weeks inclusive. The test, which will be carried out in the laboratory, is called triple, because three indicators will be evaluated already - alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), hCG (a hormone already known to us) and the level of free estriol.
The task of these methods is to help identify the possible risks of the birth of babies with incurable gross and lethal pathologies, genetic abnormalities.
Blood for infection, for HIV status, for syphilis (RW)
These analyzes are considered mandatory. HIV and syphilis a woman should donate venous blood three times:
- upon delivery to the account (usually from 6 to 10 weeks);
- before making maternity leave at 30 weeks;
- during hospitalization in the maternity hospital.
On TORCH - infections, samples for research are taken once per pregnancy, usually at registration or a little later.
The number of blood samples for syphilis and HIV infection is not established by chance. This is due to the fact that the incubation of ailments is very long, the first result may be negative, but the following result is positive.That is why once every three months the data is rechecked.
TORCH - infections are a complex immunological study of blood for the detection of antibodies to such dangerous for pregnant diseases as toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes.
In the blood, it is possible to detect antibodies to them, if a woman has previously been ill with these ailments, as well as a special type of antibodies, if she is suffering from any of the infections at the moment.
Another mandatory test is blood for hepatitis C and B. The fact is that they can be infected not only sexually, but also everyday, and very often the symptoms are mild and resemble the common cold. Therefore, there is no guarantee that a woman does not suffer from one of hepatitis, until the appropriate laboratory examination has been done.
Hepatitis blood is donated twice - at registration of the dispensary registration and at the end of pregnancy at the exit to the decree. Sometimes the analysis is done and the third time - already in the parent house.
Determination of blood clotting
This analysis has a more complex, but more capacious name - coagulogram. It is done three times for the entire term of carrying a baby, if there are no grounds for additional examination. The task is to determine the ability of blood to coagulate quickly in order to prevent massive bleeding during childbirth. Special laboratory techniques allow you to set clotting time - APTT, as well as the amount of fibrinogen, platelets and prothrombin, lupus anticoagulant.
The coagulation and blood thinning are equally dangerous during pregnancy and during childbirth, and therefore coagulogram is considered a very important diagnostic step.
Description and norms
Many norms of indicators during pregnancy differ from those of non-pregnant women, men and children. That is why the blood test, regardless of its purpose and type, should be evaluated according to special tables and standards calculated exclusively for pregnant women.
A blood test - a table of norms during pregnancy
Rates and deviations:
Defined in the study indicator | Normal value in 1 trimester | Normal value in the 2 trimester | Normal value in 3 trimester |
Red blood cells | 3,5x10 ^ 12 - 5,6x10 ^ 12 units | 3,5x10 ^ 12 - 5,6x10 ^ 12 units | 3,5x10 ^ 12 - 5,6x10 ^ 12 units |
Hemoglobin | 112-160 g / liter | 108-144 g / liter | 100-140 g / liter |
Hematocrit | 31-49% | 31-49% | 31-49% |
Color index | 0.85-1.1 u | 0.85-1.1 u | 0.85-1.1 u |
Reticulocyte | 0,2-1,5% | 0,2-1,5% | 0,2-1,5% |
Platelets | 140x10 ^ 9 - 400x10 ^ 9 units / liter | 140x10 ^ 9 - 400x10 ^ 9 units / liter | 140x10 ^ 9 - 400x10 ^ 9 units / liter |
White blood cells | 4x10 ^ 9 - 9x10 ^ 9 units / liter | Not higher than 11x10 ^ 9 u / liter | Not higher than 15x10 ^ 9 u / liter |
Band neutrophils | 1-6% | 1-6% | 1-6% |
Segmented neutrophils | 40-78% | 40-78% | 40-78% |
Myelocytes | 0-3% | 0-3% | 0-3% |
Lymphocytes | 18-44% | 18-44% | 18-44% |
Monocytes | 1-11% | 1-11% | 1-11% |
Eosinophils | 0-5% | 0-5% | 0-5% |
ESR | Up to 60% (45 mm per hour) | Up to 60% (45 mm per hour) | Up to 60% (45 mm per hour) |
Biochemical blood test - a table of normal indicators for pregnant women
Rates and deviations:
Definable indicator | Normal value for the first trimester | Normal value for the second trimester | Normal value for the third trimester |
Total protein | 63-83 g / l | 63-83 g / l | 63-83 g / l |
Albumen | 32-50 g / l | 28-55.7 g / l | 25.6-66.0 g / l |
Urea | 2.5-7.1 mmol / liter | 2.5-7.1 mmol / liter | 2.5-6.2 mmol / liter |
Cholesterol (cholesterol) | 6.16-13.7 mmol / liter | 6.16 -13.7 mmol / liter | 6.16 -13.7 mmol / liter |
Globulin | 28-112 g / l | 28-112 g / l | 28-112 g / l |
Sugar (glucose) | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter | 3.5 - 5.83 mmol / liter |
Creatinine | 32-70 μmol / liter | 32-50 μmol / liter | 32-47 μmol / liter |
Diastase | 25-125 u / l | 25-125 u / l | 25-125 u / l |
ALT | Not more than 32 U / L | Not more than 31 U / L | Not more than 31 U / L |
AST | Not more than 31 U / L | Not more than 30 u / l | Not more than 30 u / l |
GGT | Not more than 36 u / ml | Not more than 36 u / ml | Not more than 36 u / ml |
Total bilirubin | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter | 3.4 -21.6 μmol / liter |
Direct bilirubin | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter | Not more than 7.9 μmol / liter |
Indirect bilirubin | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter | 3.4-13.7 μmol / liter |
Alkaline phosphatase | 40-150 u | 40-190 u | 40-240 u |
Iron | 8.93-30.4 μmol / liter | 8.93-30.4 μmol / liter | 7.2-25.9 microns / liter |
Sodium | 135-155 mmol / liter | 135-145 mmol / liter | 135-155 mmol / liter |
Chlorine | 98-107 mmol / liter | 98-107 mmol / liter | 98-107 mmol / liter |
Potassium | 3.4-5.3 mmol / liter | 3.4-5.5 mmol / liter | 3.4-5.3 mmol / liter |
Phosphorus | 1.0-1.57 mmol / liter | 1.0-1.40 mmol / liter | 0.87-1.47 mmol / liter |
Magnesium | 0.85-2 mmol / liter | 0.85-1.7 mmol / liter | 0.85-1.4 mmol / liter |
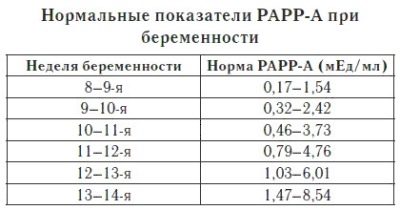
First Trimester Screening - Double Test
Rates and deviations:
Chorionic gonadotropin hCG | Protein PAPP-A |
0.5 - 2.0 MoM | 0.5 -2.0 MoM |
Second Trimester Screening - Triple Test (Week 16-19)
Rates and deviations:
HCG | AFP | Free estriol |
10 000-58 000 mU / ml or 0.5 - 2.0 MoM | 15-95 u / ml or 0.5-2.0 MoM | 15-16 weeks - 5.4-21 nmol / l; 17-18 weeks - 6.6-25 nmol / l; 19-20 weeks - 7.5-28 nmol / l. |
Coagulogram
Rates and deviations:
Defined in the study indicator | Normal value for pregnant women |
APTTV | 17-20 seconds |
Prothrombin level | 80-140% |
Platelet count | 131х 10 ^ 9 - 402 х10 ^ 9 units / liter |
Fibrinogen | Not more than 6.4 g / l |
Thrombin time | 9.5 - 18 seconds |
Antithrombin -3 | 70-120% |
Lupus anticoagulant | Not detected |
Causes of deviations from the norm
The fact that there are deviations does not always indicate a disease or a threat:
- You should always “make a discount” on laboratory errors and incorrect analysis.
- If a woman comes on a full stomach, having previously eaten something sweet and fat, if she is in a state of severe stress, is ill, takes some medication, all this must be brought to the attention of the doctor. The analysis, if time permits, will be postponed for other periods when circumstances are more favorable.
- For the single deviations that appeared in the analysis once and were not seen anymore, no one will put diagnoses.
Any deviation from existing standards is just the basis for a more thorough and meticulous additional diagnostic study. But waiting for more solid and reasonable conclusions for pregnant women is usually difficult. I want to know as soon as possible what the causes of certain deviations may be. Let's look at the most obvious ones.
Deviations in clinical analysis
The results of the clinical analysis, which is also called general, are the most unstable of all studies. They can change daily if you do a new study every day:
- The most informative indicator is hemoglobin. He talks about how much the future mom's blood cells are saturated with oxygen. Do not forget that the baby receives it with blood and in the womb. A slight decrease in hemoglobin is not considered a pathology. However, significant lags in this indicator indicate anemia and the need for treatment.
- ESR all pregnant women slightly increased. There is nothing terrible in this - it is simply “the costs” of the spicy position of the future mother. However, a decrease in ESR may indicate development of problems with blood circulation and blood vessels.
Only experienced doctors can correctly do the decoding of leukocyte formula and understand how to help the expectant mother and her child.
- Platelets in insufficient quantities may be a consequence of an infectious disease, viral infection, as well as malnutrition and malnutrition. At the beginning of pregnancy, a woman can be accompanied by a strong toxicosis, which is able to increase the number of platelets, causing blood clots. And liquid blood (if these cells are not enough), and thick dangerous for pregnant. Broken hemostasis threatens to result in severe bleeding during childbirth, and too thick blood does not allow the child to get the maximum amount of nutrients and oxygen from the maternal blood.
- Increased content red blood cells often found in the blood of pregnant women who smoke, are obese, are in a situation in which they are subjected to severe stress for a long time. The reduced level of red blood cells becomes with anemia, bleeding.
- Increased amount reticulocyte indirectly indicates the likelihood of developing anemia. If no action is taken, these cells will begin to destroy hemoglobin, reduce the number of red blood cells, and anemia will be inevitable. Low reticulocyte levels may indicate kidney and blood disorders.
- If the blood is elevated white blood cellsThis may be evidence of a viral or bacterial infection, an inflammatory process, including purulent. Leukocytosis - an increase in the level of leukocytes is a dangerous pregnancy disease that requires the provision of prompt medical care.
Deviations in biochemistry
The results of the biochemical analysis are quite difficult for the philistine understanding, but some indicators are heard even in people far from medicine:
- For example, blood protein or urea. Reduced urea can only indirectly indicate a future mother’s liver problems. Increased content of this substance is a much more alarming sign. He can talk about serious problems with the kidneys - from dysfunction of elimination to severe renal failure. This indicator must be considered together with creatinine, since kidney problems are characterized by the same increase in these two substances.
- Elevated bilirubin suggests that the breakdown of hemoglobin proceeds too quickly. This becomes possible with liver diseases, as well as with infectious hepatitis B and C, with syphilis and other dangerous infections. The level of this substance rises in women who have been taking drugs for a long time. A jump in bilirubin can be observed after poisoning and intoxication. Often, a woman with high bilirubin has an icteric effect - the sclera of the eyes, the skin can become yellow pigmented.
- Reduced protein - ferritin - should make you think about why a woman has prerequisites for anemia. The condition is quite easily corrected with iron preparations and special treatment.
- Increased ALT enzyme level may indicate liver disease, and the AST enzyme can tell a lot about the condition of the heart and the entire cardiovascular system. Its excess in excess of normal values often indicates cardiac pathologies.
In the framework of the same analysis, the norms of iron in the blood are determined, as well as calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus and other minerals that are useful and necessary for life and health.
Deviation in screening studies
The most attention of future mothers is focused precisely on screening analyzes for chromosomal pathologies. At the same time, women completely forget that they do not make diagnoses with the help of screening. Such a diagnosis is only calculates individual risks.
High risk of Down syndrome 1: 90 - for many, this is a bad analysis. But if you think about it, the probability of having a child with Down syndrome in this woman is only 1 out of 90, and this is not a sentence at all, because 89 children who can be born in women with similar biochemistry screening rates will be completely healthy.
However, the excitement of moms can be understood, because every woman wants to give birth to a strong and healthy baby. At the same time, serious passions are boiling around the screening results on the mummies' forums. And many questions arise because of a misunderstanding of the very essence of the prenatal screening examination. And it lies in the fact that Separately evaluate the laboratory data of blood tests can not.
Only in conjunction with the results of ultrasound scanning can something be assumed. Only to assume, and not to assert with confidence. When detecting alarm markers on an ultrasound scan, special attention will be paid to blood testing, as it will be able to complete the diagnosis.
In the first trimester, when passing the double test, the numerical values of hCG and PAPP-A can be very different. It depends on the laboratory in which the study was conducted. Therefore, it is customary to correlate data from different medical institutions in MoM.
Increased plasma protein PAPP-A may indirectly indicate:
- an error in calculating the duration of pregnancy;
- insufficiency of the placenta, the threat of spontaneous abortion;
- excessive proliferation of the placenta;
- twinning or triple pregnancy.
Lowering PAPP-A has other prerequisites:
- increased risks of chromosomal abnormalities;
- non-developing pregnancy;
- toxicosis.
Increased hCG may indicate:
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- errors in calculating the duration of pregnancy;
- double or triple pregnancy;
- diabetes or mom's recent infectious disease;
- the presence of tumors in a woman.
Lowering HCG is peculiar to:
- Edwards syndrome;
- delayed fetal development;
- ectopic or undeveloped pregnancy;
- threatened miscarriage.
Increasing AFP above the norm sometimes speaks about:
- total severe defects of fetal development, in which the child is essentially not viable outside the mother's body;
- ectopic pregnancy or death of the baby;
- improper functioning of the placenta, its dysfunction;
- developing and gaining momentum Rh-conflict between a woman and her baby;
- cancer in the maternal organism;
- the presence of pregnant viral hepatitis.
AFP may be lowered due to:
- high risk of down syndrome in a child;
- diabetes in mom;
- intrauterine death of the baby.
The level of free estriol in the triple test may be overestimated due to:
- pregnancy two or three babies at the same time;
- large or giant fetus (in the first case, birth weight is projected to be more than 4 kilograms, in the second - more than 5 kilograms);
- renal failure in the future mother;
- liver disease.
The underestimated level of this hormone becomes due to:
- the threat of spontaneous abortion;
- high risk of down syndrome in a child;
- intrauterine infection;
- gross abnormalities of the brain structure of the fetus up to the complete absence of the brain;
- lack of function of the placenta;
- taking antibiotics and some hormonal drugs.
If you receive a disappointing forecast, you should not abandon additional diagnostic measures, which with higher accuracy will allow to establish the true reason for the change in the biochemical blood formula.
The terrible diagnoses are not confirmed as often as the impressionable future moms think. Screening is a kind of “reinsurance”.
Conclusion
Attempts to interpret the results of blood tests on their own can bring to a nervous breakdown even a woman with strong nerves. Finding deviations and explaining them with possible pathologies, and then suffering about this is not the best solution.
Only an experienced doctor is able to see not only deviations from the norms, but also the relationship between different research indicatorsFor example, to identify iron deficiency anemia by hemoglobin level, iron content, ferritin protein and a decrease in the number of red blood cells in a complex. It is with this approach that all other values that are calculated by laboratory technicians are considered.
Therefore, entrust the decoding of your analysis to the doctor. If he finds warning signs, he will definitely inform the patient.
For more information on what kind of blood tests you need to pass pregnant, see the next video.