Causes and effects of high blood sugar during pregnancy
Conditions in which a high glucose level is recorded during pregnancy are quite common. In some cases, they occur in a future mom for the first time in their lives during the carrying of the baby.
This situation requires the mandatory intervention of physicians.
Reasons for raising
A variety of causal factors can lead to an increase in glucose in the female body during pregnancy. Quite often it happens that they act simultaneously, reinforcing the action of each other. Doctors call a persistent increase in blood glucose hyperglycemia.
According to statistics, 5% of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes mellitus during gestation. This pathology is accompanied by constant elevated blood sugar levels. This disease can be dangerous for both mom and her baby.
For a long time, researchers tried to establish why it was during pregnancy that the risk of developing diabetes mellitus significantly increased. The main reason was associated with an altered hormonal background.
Progesterone metabolites, as well as other pregnancy hormones, have a pronounced effect on metabolic processes, including glucose metabolism in the body.
The change in the concentration of certain hormones in the blood of a pregnant woman leads to the fact that she has the phenomenon of insulin resistance. This condition contributes to an increase in blood glucose levels.
Sugar with this pathology increases almost constantly. The degree of severity of the disorders depends largely on how much the hormones are changed, and whether the woman has any concomitant diseases of the internal organs.
It often happens that the level of blood sugar in the future mom begins to rise by the second half of pregnancy. This feature is largely related to the altered work of the kidneys. The growing uterus puts pressure on these urinary organs, leading to the appearance of congestion in them.
Reducing glucose excretion by the kidneys contributes to its accumulation in the blood, which also increases the manifestations of hyperglycemia. In this case, an increased concentration of sugar is also determined in the urine, when it is submitted for testing to the laboratory.
Glucose appears when its plasma concentration is above 9 mmol / l. This situation is extremely unfavorable and requires urgent medical correction.
Pancreatic diseases are another common cause leading to the development of gestational diabetes.
Such diseases, as a rule, occur even before the onset of pregnancy.
Chronic pancreatitis, occurring with frequent exacerbations, may contribute to the development of persistent hyperglycemia during carrying a baby. Without prescription treatment in this case is not enough.
Scientists have found that heredity plays a huge role in the development of persistent hyperglycemia. In women with a family history of diabetes, the risk of developing a gestational option increases by 50%.
All future moms with risk factors must necessarily be observed by a therapist. Women suffering from diabetes or frequent episodes of hyperglycemia, are at the dispensary at the endocrinologist, including during pregnancy.
Many concomitant diseases of internal organs can also cause the development of resistant mom in the future mom. Usually, this leads to persistent pathologies of the liver, gallbladder, metabolic disorders in the endocrine system, chronic kidney disease. Injuries to the organs of the gastrointestinal tract or previously performed operations may also contribute to an increase in blood glucose.
Scientists have found that prolonged prolonged stress has a negative impact on the endocrine system. This is manifested by a persistent increase in blood sugar.
Many pregnant women note that hyperglycemia in them first appeared after some kind of severe stress in life. During pregnancy, even low intensity effects are sufficient to increase blood sugar.
Symptoms
The complex of various clinical signs that occurs in a pregnant woman with signs of high blood sugar levels is quite large. It includes many different symptoms that can bring a future mother significant discomfort and change her habitual behavior.
Women with elevated blood sugar levels feel:
- Growing and constant thirst. This symptom appears much brighter if blood sugar exceeds the normal values by more than 30%. It leads to the fact that the expectant mother begins to drink much more water and various beverages. Women who have a strong tendency to develop edema can complain about the appearance of swelling in their legs and face.
- Frequent urination. Increased thirst leads to frequent urge to urinate. The amount of urine discharge increases significantly.
It becomes pale and less bright in color.
- Dryness and itching of the skin. High sugar levels contribute to irritation of the nerve endings, which is manifested by such symptoms. The intensity of their manifestation depends largely on the level of sugar in the blood.
- Very dry mouth. This symptom also provokes the development of thirst. A woman feels dry mouth almost constantly throughout the day. Even after taking water mucous membranes begin to dry in a couple of minutes.
- Increased appetite. Violation of carbohydrate metabolism leads to the fact that glucose can not fully enter the internal organs. Prolonged starvation of cells and manifested a strong sense of "unbearable" hunger.
- Great weakness and constant sleepiness. Throughout the day, even in the morning after waking up, the future mom wants to sleep. Often this symptom is accompanied by a feeling of great fatigue. Some women may experience headache and severe dizziness.
Implications for the child
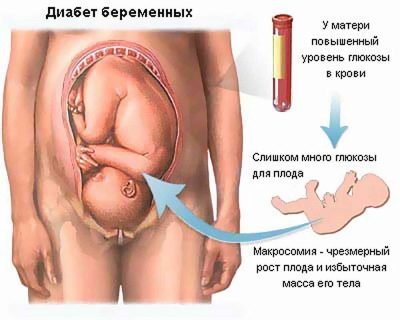
Elevated blood glucose adversely affects the fetus. Pronounced metabolic disorders lead to the fact that the baby begins to experience a real shortage of nutrients that are necessary for its active and full development. The brain and heart of the baby are most sensitive to the decrease in the glucose concentration in the blood.
Hyperglycemia can be dangerous in the development of preterm labor. Usually this situation arises in women who have a pathological course of pregnancy and many associated diseases of internal organs.
The lack of nutrients in the early stages of pregnancy threatens the development of multiple abnormalities and defects in the development of the fetus. This condition is especially unfavorable during the first trimester of pregnancy when all vital organs and systems are laid. With the most unfavorable prognosis of the course of this pathology, even a spontaneous abortion or miscarriage is possible.
Diagnostics
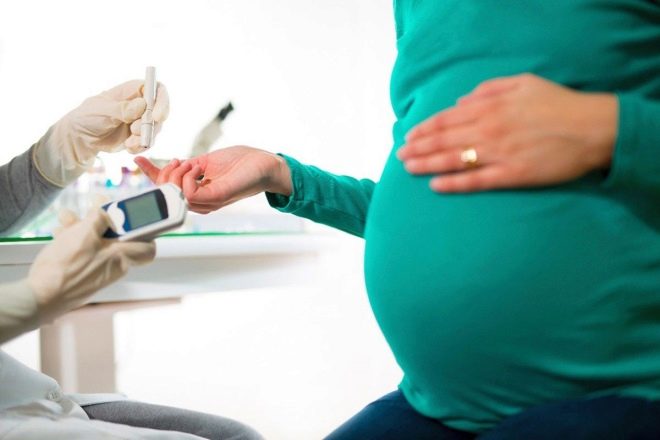
To identify "mute" hyperglycemia, doctors recommend taking an analysis to determine the level of glucose several times during the entire pregnancy. So, the expectant mother is desirable to visit the laboratory from 9-12 weeks of pregnancy and closer to childbirth. This is a necessary minimum that must be met.
A blood test for sugar strictly on an empty stomach. This should be done in the morning.
Before the study should not eat 8-9 hours.
If a woman already has an established early diabetes mellitus, then such a long interval "without food" is not necessary. For this, only 3-4 hours is enough. Long-term hunger can lead to a very dangerous condition - hypoglycemia.
Before passing the analysis, you can only drink a little ordinary boiled water. Do not eat sweet carbonated drinks or sweetened tea. In the morning before the analysis, all sugar-containing components should be strictly excluded.
A cheerful and good mood is an obligatory component with which the future mom should come to the clinic. To do this, she should definitely sleep on the eve of the study. Nervous and worry about the test is not worth it, as this may affect the result of the analysis.
Before taking this study, if possible, should eliminate strong physical exertion. They can lead to an unreliable, slightly underestimated result. A day before going to the laboratory, it is better to exclude cleaning the apartment or jogging along the stairs.
Doctors believe that normal blood sugar levels are 3.3–5.5 mmol / l. In this case, a restriction is made that these values are adequate for capillary blood. She is taken during the puncture of the finger.
In venous blood, these values are somewhat different. They are 4.0-6.1 mmol / l. Currently, more and more studies are done venous blood. They are more convenient and not less informative. Most private medical laboratories prefer to use just this method of research.
If for some reason the blood glucose values change and deviate from normal values, then the doctors prescribe a number of special auxiliary laboratory tests. They are necessary in order to accurately diagnose, as well as to exclude or confirm the presence of diabetes.
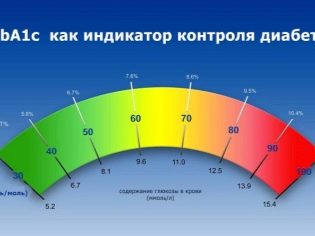
Such studies include the glucose tolerance test and the determination of glycated hemoglobin.
For information on how to pass the glucose-tarantine test, see the following video.
How to reduce?
There are several ways to lower blood glucose levels.
The first of them is home-keeping of a special hypo carbohydrate diet. It eliminates many foods that trigger hyperglycemia. Follow this diet should throughout the pregnancy if the future mommy was diagnosed with gestational diabetes. Women who are at risk for the development of this pathology should also use this therapeutic food.
In the opinion of many mummies, such a hypo-carbohydrate diet not only helped them to cope with high levels of sugar without the use of medicines, but also contributed to maintaining a normal weight. After the birth of babies, they noted that they did not have a significant weight gain.
To normalize blood sugar levels, all sweet sodas, industrially made sweets and chocolate are excluded, and fruits are significantly limited. The acid fruits are saved in the menu. These fruits include green apples and citrus fruits. Bananas and grapes should still be excluded.
The emphasis in the diet of future moms suffering from hyperglycemia, should do on protein and grain foods. Fear croup should not be. They are rich in "slow" carbohydrates that do not lead to jumps in blood sugar levels. It is better to supplement such food with fresh or stewed vegetables, collected according to the season.
With the ineffectiveness of diet and the growing level of sugar, doctors have resorted to the use of drugs that reduce hyperglycemia. When prescribing these drugs, the risk of their potential impact on the fetus is necessarily evaluated.
The selection of drug therapy is done by an endocrinologist. It is this specialist who determines the multiplicity, dosage and treatment regimen.