The rates of progesterone during pregnancy by week in the table and causes of deviations
People tend to underestimate the value of hormones. But a slight excess or decrease in the concentration of these substances can have a tremendous impact on a person’s life. In this article we will talk about one of the main hormones in the body of a woman - progesterone, how it affects pregnancy and what its normal amount should be in the body.
What it is?
Progesterone is a steroid hormone. It is also called a progestogen. He actively participates as an intermediary in the formation of other hormones, both sex and corticosteroids. Progesterone helps the brain to function normally, performing the function of a neurosteroid.
The hormone is in both men and women, but in the female body, progesterone gets more extensive functions, combined with female sex hormones - estrogen. For men, this hormone helps in the implementation of reproductive function - it affects the quality characteristics of spermatozoa, providing them with greater mobility when passing through the path to the egg. For women, progesterone plays a crucial role allowing you to endure and have a baby.
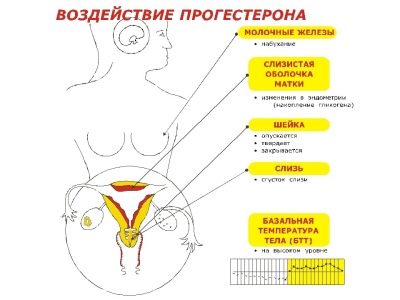
Progesterone regulates menstrual cycles. If the hormone level is low, then ovulation may not occur. It affects the feminine beauty, in particular, the health of the skin, its elasticity.
So, in menopause, when this substance in the woman's body becomes small, the skin begins to fade, grow old. A sufficient level of hormone provides sexual desire.
Role in carrying a baby
Not by chance, progesterone is called a pregnancy hormone. Without this substance, the normal development of the embryo in the early stages would be impossible. After fertilization takes place, the hormone takes on the role of protector and “guardian” of the future baby. It prepares the walls of the uterus for implantation of the ovum, softens them, translates into the secretory stage.
At the same time, progesterone causes thickening of the cervical mucus, tightly closing the entrance to the uterine cavity and for sperm and microbes. All these metamorphoses occur during the first 6-7 days after conception, while the fertilized egg has not yet completed its way into the uterine cavity.
This whole process is repeated monthly, regardless of whether fertilization has occurred. If there is no pregnancy as such, the level of the hormone begins to decrease and the next menstruation begins.
If fertilization has occurred, the blastocyte will descend into the environment prepared for it, where it will be easier to consolidate (implant) and begin to develop rapidly.
From this point on, progesterone begins to perform its protective and protective functions. It is produced in large quantities and somewhat suppresses the immunity of the woman so that he does not reject the embryo. In fact, the embryo is half foreign to the female body, and its immune defense cannot ignore this. Progesterone has an immunosuppressive effect, contributing to the preservation of the baby.
All women know how dangerous is hypertonus of the uterus muscles during pregnancy. Normal levels of progesterone can partially solve this problem. It relaxes the smooth muscles of the female reproductive organ, relieves spasms, reduces the risks of abortion. At the same time, progesterone stimulates the physical growth of the uterus during the child's pregnancy.
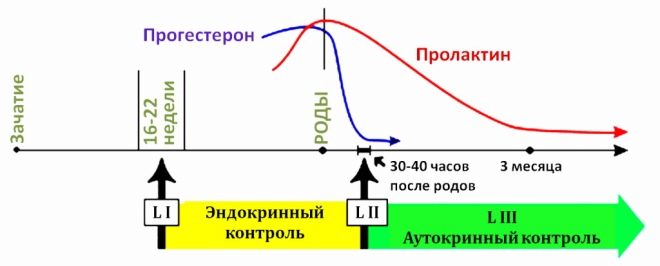
During childbirth progesterone "Prohibits" the production of breast milk. It is not required while anyone, and a woman needs to accumulate vitamins and nutrients. Therefore, lactation is temporarily inhibited. After childbirth, when progesterone levels fall, the body receives a “signal” that lactation is no longer prohibited, and milk begins to be produced.
The pregnancy hormone softens the pelvic muscles and ligaments before delivery, to facilitate the passage of the baby through the birth canal. Throughout pregnancy, the hormone has a significant effect on the nervous system of the woman, and is also directly involved in the formation of certain tissues in the embryo.
Everything 9 months this important hormone stimulates the appetite in a pregnant woman, contributes to the deposition of fat, to provide mom and baby with a supply of nutrients. That is why the waist of expectant mothers increases in girth. The promotion of food through the intestines is slowed down again under the influence of progesterone, so that the female body has time to take from it as much as possible useful substances, minerals and vitamins.
Thus, a sufficient level of this hormone allows pregnancy to occur, to flow easily, without complications. Disruption of hormonal balance, shortage or excess of substances can have a negative effect on reproductive functions.
How is the analysis done?
The concentration of progesterone in the body of a pregnant and non-pregnant woman is determined by blood analysis, which is carried out by ELISA. If a woman fails to get pregnant for a long time, the doctor will certainly suggest such an analysis, because a low level of the hormone when planning pregnancy prevents normal ovulation and implantation of a fertilized egg. Planning a pregnancy, the doctor prescribes the day of blood donation, depending on the duration and characteristics of the cycle. Usually the analysis is done on days 21-23 of the cyclebut there may be exceptions. For example, a woman who usually has very few monthly periods can be assigned a test from the 15th day of the cycle.
Pregnant women can donate blood to determine the concentration of progesterone on any given day. To get more accurate results, you should prepare. 12 hours before visiting the laboratory, a woman should refrain from smoking and taking alcoholic beverages, exclude physical activity and limit herself to food intake. If a woman takes any medications, for a few days it is worth refusing them. If this is not possible, then you should inform the technician what medicines are taken and in what dosage.
It is not necessary to take a blood test for progesterone immediately after the ultrasound scan, fluorography, X-ray. In the treatment room should go in the morning, on an empty stomach, making sure in advance that the health "will not fail" - there is no fever, intestinal disorders, respiratory symptoms that may indicate SARS or other infection.
The amount of progesterone, especially in early pregnancy, may indicate the exact timing of the baby, but usually this method of determining the date of conception is not used. There are more simple and informative analyzes - hCG, for example. Blood for progesterone can be assigned as a diagnostic:
- if an ectopic or frozen pregnancy is suspected;
- with the threat of miscarriage;
- when planning a pregnancy to establish the exact time of ovulation;
- in the treatment of infertility;
- with pathologies of the placenta in pregnant women (analysis in the dynamics allows you to monitor the status of the "children's place");
- when a woman has a cyst or tumor on the reproductive organs, especially if the pathology is combined with pregnancy;
- before replanting and after embryo transfer during IVF;
- to control the condition after the woman was treated with progesterone.
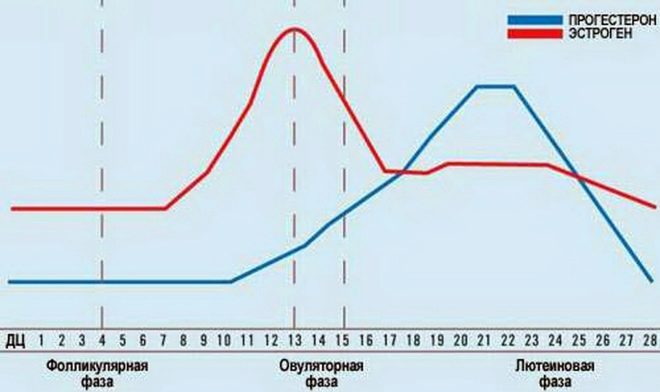
Weekly rates
In various laboratories, the concentration of progesterone in the blood of a woman is determined in different units. As a result of the analysis, “ng / ml” (nanograms per milliliter) or “nmol / l” (nanomoles per liter) may stand after the numerical value. To get the value of progesterone in nmol / liter, you must conduct some simple mathematical calculations - multiply the value in ng / ml by 3.18.
To save our readers from the need to calculate the dosage, we have compiled the table of normal values of progesterone level by week in two units:
Deadline (weeks) | The rate of progesterone in ng / ml (range) | Norm progesterone nmol / liter (range) |
1-2 | 12,0 -18,20 | 38,15 – 57,80 |
5-6 | 18,60 – 21,70 | 59,10 – 69,0 |
7-8 | 20,30 – 23,50 | 64,80 – 75,0 |
9-10 | 23,0 27,60 | 73,10 – 88,10 |
11-12 | 29,0 – 34,50 | 92,10 – 110,0 |
13-14 | 30,20 – 40,0 | 96,0 – 127,20 |
15-16 | 39,0 – 55,70 | 124,0 – 177,10 |
17-18 | 34,50 – 59,50 | 111,0 – 189,0 |
19-20 | 38,20 – 59,10 | 121,70 – 187,80 |
21-22 | 44,20 – 69,20 | 140,60 – 220,0 |
23-24 | 59,30 – 77,60 | 188,90 – 247,10 |
25-26 | 62,0 – 87,30 | 197,20 – 277,80 |
27-28 | 79,0 – 107,20 | 251,20 – 340,90 |
29-30 | 85,0 – 102,40 | 270,20 – 326,0 |
31-32 | 101,50 – 126,60 | 323,10 – 402,80 |
33-34 | 105,70 – 119,90 | 336,30 – 381,40 |
35-36 | 101,20 – 136,30 | 321,70 – 433,10 |
37-38 | 112,0 – 147,20 | 356,10 – 486,10 |
39-40 | 132,60 – 172,0 | 421,0 – 546,0 |
Thus, on average, the rate in the first trimester of pregnancy is about 11.2-90.0 ng / ml, in the second - 25.6-89.4 ng / mg, and in the third - 48.4-422.5 ng / mg. For the period of ovulation when planning pregnancy, a concentration of 0.8-3.0 ng / mg is considered normal.
You should not expect the laboratory assistant to write if there are any deviations in the indices of this hormone, and with what they are connected. Decoding analysis - the task of the doctor.
Causes of deviations
If during pregnancy or before its onset, progesterone levels are different from normal values, then this is a reason to look for the true cause and start treatment.
Elevated level
If the analysis showed that progesterone in a pregnant woman is high, exceeding the norms indicated in the table, then there may be several reasons for this. An increased concentration of the hormone is observed in pregnant twins or triplets. It is clear that in the first days of pregnancy there will be no difference, but already in 4 months of pregnancy (approximately from 15-16 weeks) each fetus will “acquire” its own placenta, and each placenta will produce progesterone. There is nothing strange in the fact that the hormone in the blood of a woman will be more.
Much depends on the period in which the progesterone increased in the child's birth. For example, its slight excess at week 5-6 does not mean anything pathological, and at the end of the second and third trimester, high values may indicate that the placenta is maturing too slowly.
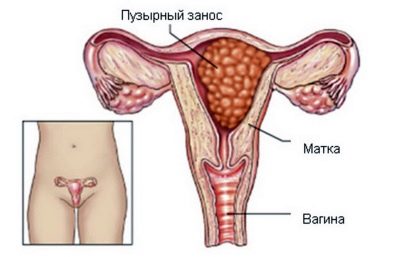
Elevated levels of progesterone can indicate the presence of tumors, tumors in the adrenal glands, ovaries, as well as in cystic formations. An abnormally high level of progesterone at the very beginning of pregnancy can be a sign of a blistering. Such a term refers to abnormal fertilization, in which cysts that resemble a bunch of grapes develop in the uterine cavity. This bunch is growing rapidly, causing a significant rise in progesterone levels.
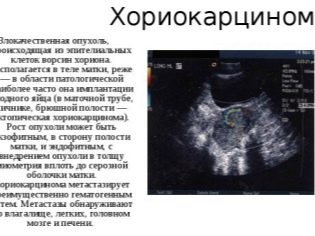
An excess of progesterone accompanies choriocarcinoma - uterine tumor, which can develop after childbirth, during ectopic pregnancy. Also, the level of the hormone will be increased in women who have taken or are taking hormonal drugs, for example, "Duphaston" to save pregnancy when threatened. Elevated levels of the hormone can also be found in pregnant women suffering from kidney and liver problems.
Thus, the excess of indicators must necessarily be reviewed by a doctor. To find out the exact reasons, a whole range of additional examinations is prescribed - ultrasound examinations of the minor tala organs, kidneys, liver, blood and urine tests, consultations of related specialists such as a gastroenterologist, nephrologist, oncologist and reproductive specialist will also be required.
Low values
A low level of progesterone compared to normals may be a sign of insufficiency of the corpus luteum, if the analysis was carried out during the planning period of pregnancy or in the very first weeks after fertilization.Lack of hormone prevents normal implantation, even if fertilization was quite successful. If even the blastocyte can consolidate in the uterine wall, then there is no guarantee that reducing the hormone in the early stages will not lead to miscarriage.
You can get pregnant against the background of reduced levels of progesterone hormone, but It’s not always possible to preserve a pregnancy without medical assistance. In later periods, when the placenta is formed, an insufficient level of progesterone may indicate that the “baby seat” is underdeveloped and does not cope well with its direct responsibilities - to nourish and protect the child. Lack of growth levels of the hormone may indicate a high probability of spontaneous abortion.
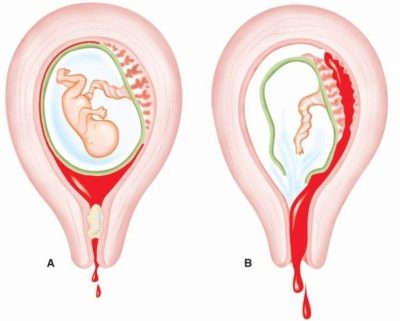
Lack of progesterone leads to uterine bleeding of varying intensity. A very slow growth of a hormone in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates placental insufficiency, in particular that the “baby seat” produces too little of the hormone that is necessary for the prolongation of pregnancy.
The reduced level of progesterone in a woman who is still preparing for a future pregnancy may indicate that ovulation does not occur, especially if estrogen levels are elevated. A disappointing test result also occurs in women with underdeveloped sex glands, ovarian dysfunction.
If progesterone levels are below normal throughout pregnancy, this may indicate about delayed fetal development. Such laboratory data are confirmed by the results of ultrasound - the baby is far behind the values normal for a certain period of pregnancy in terms of fetometric indicators. A sharp drop in the level of progesterone occurs during a frozen pregnancy, when the fetus, under the influence of certain factors, stops growing, dies, and miscarriage does not occur.
Antibiotics, oral contraceptives, anti-epilepsy drugs and some hormonal drugs can lower progesterone levels.
Symptoms
A lack or excess of progesterone in the body of a pregnant woman can be suspected herself, even before receiving a referral for laboratory testing of blood. Many early pregnancy planners and women measure basal temperature levels daily. A lack of hormone may indicate low temperature in the rectum. Excess and lack of hormone has its own characteristics.
Disadvantage
Progesterone deficiency is manifested by weight gain, especially fat is deposited in the abdominal area. During menstruation before pregnancy, a woman with a reduced hormone level experiences fairly strong menstrual pains.
With a lack of progesterone reduced sexual desire, and also often observed headaches. A woman in the early stages may experience private strong mood swings. The lack of progesterone is inherent in a constant enduring feeling of tiredness, lethargy. Sleep can be disturbed, hair becomes greasy, ugly pigment spots and acne appear on the skin.
Bloody and serous discharges from the genitals, edema, as well as high water or low water can indicate atypical for an “interesting situation” the insufficiency of the progesterone level during pregnancy. The uterus in the early stages (up to 12 weeks) is in good shape, a woman may experience pain in the lower abdomen and in the lower back.
The causes of progesterone deficiency can be poor nutrition of the future mother, lack of vitamins and microelements, bad habits - smoking, taking alcohol or drugs, severe stress, feelings, discontinuation of hormonal contraceptives in the month preceding the onset of pregnancy.
Oversupply
An excessive amount of progesterone in the process of carrying a child in the earliest terms may indicate headaches like a migraine, a decrease in visual function, a feeling of extreme fatigue and apathy.Quite often, an overdose of this substance is not felt by a woman in the early period at all. And therein lies the main danger of the situation.
Excess progesterone in the first weeks may indicate a strong toxicosis.when a woman is sick not even from food, but only from her one smell. Such an unpleasant symptom as hair loss in a woman, as well as gaining weight too quickly, can indicate an increased level of the hormone that exceeds normal values. Especially dangerous is the rise of the hormone in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, because it can be a sign of abnormal work of the placenta.
High concentrations of progesterone in the middle and end of pregnancy can talk about premature aging of the “baby seat”, which means that the baby does not receive enough nutrients that are so necessary for it to grow and develop. An aging premature placenta may even cause the death of a baby.
Swelling of the legs, ankles - the most common symptom of increasing progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. That is why obstetricians and gynecologists are so attentive to the signs of preeclampsia. Oily acne, which covers the body and face of the expectant mother, as well as oily seborrhea can also speak about hormonal imbalance in the direction of increasing progesterone. The mammary glands do not just swell and grow, which is characteristic of all pregnant women, they begin to get very sick. The woman has expressed problems with the work of the intestines.
In terms of the impact on the psyche of the future mother, a surplus of progesterone can make a quiet and peaceful woman aggressive and unrestrained person - the hormone provokes attacks of anger, which are replaced by periods of apathy and unwillingness to see anyone, as well as panic attacks and depression.
The reasons for the increase in the level of the hormone beyond the permissible norms during pregnancy may be severe stress, abnormalities in the kidneys and liver, problems with the thyroid gland. In any case, the approach to finding reasons is individual for each expectant mother.
Treatment
Lack of progesterone is considered more dangerous than its excess, especially in early pregnancy. And therefore, without medical care, a woman who wants to endure and give birth to a healthy child is indispensable. Treatment in case of shortage and oversupply of the hormone is assigned to different.
Failure
Regardless of the reasons for which progesterone levels were reduced, a woman is recommended to calm down. And this is not the doctor’s on-call advice “for all occasions”. With stress in the body of a pregnant woman increases the level of another hormone cortisol, which is also called "stress hormone." He is a kind of "competitor" of progesterone, and begins to quickly suppress the production of his "opponent".
Women who are in a stressful situation (divorce, death of a loved one) are prescribed mild sedatives, herbal remedies.
With the threat of miscarriage, if the deficiency of progesterone is accompanied by obvious symptoms, the woman is hospitalized and treated in hospital. Peace and maximum rest are important, full and long sleep. To compensate for insufficient levels of the hormone, drugs are prescribed that contain the necessary substance - "Utrozhestan", "Duphaston" or "Endometrine". The specific drug should be prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the severity of progesterone deficiency.
At the same time in the treatment regimen include preparations containing magnesium, zinc and vitamin B 6. Such a "trio" in the interaction with each other contributes to the development of its own progesterone. To remove the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus is used antispasmodic drugs ("No-shpu", "Papaverine»).
A blood test for the concentration of this hormone is carried out in the dynamics - once a week or once in 2 weeks, in order to track the slightest changes in the future mother's body.
Pregnant women with low progesterone in the process of treatment and after it is important to eat right, in no case do not overeat, do not eat large amounts of protein foods and carbohydrates, give up cakes and white muffin, as well as fatty foods. Preferred are products such as mackerel, pumpkin seeds, dairy products, spinach.
Increased concentration
With an excess of progesterone in early pregnancy, there is no need for specific therapy. Only symptomatic treatment is prescribed - sedatives in case of psychological instability, mood swings, depression, and mild laxatives of plant origin for the normalization of the bowels. General recommendations include long walks in the fresh air, a balanced diet, taking vitamins, a good night's sleep, sufficient in time for the future mother's body to have time to rest and recover.
If an excess of progesterone is detected in the second or third trimester, the woman may be hospitalized to be treated under the constant supervision of qualified medical personnel. If you leave the problem without attention, the baby will no longer receive enough food and oxygen, and may die.
Women are prescribed medications that improve uteroplacental blood flow - «Actovegin"," Curantil "often they are administered intravenously. Injections are administered to the treatment regimen of B vitamins, as well as sedatives and antispasmodics.
In post-term pregnancy, when after 40 weeks the hormone level continues to remain high and does not even decrease, a woman is hospitalized, if necessary, from 41-42 weeks, if labor has not begun, they are stimulated, including the introduction of hormonal agents that lead to a drop in the level progesterone.
Prolonged pregnancy can be, by the way, and because of insufficient levels of progesterone. In this case, stimulation is done with progesterone preparations, including "Progesterone" in ampoules.
About progesterone and its effects on the female body during pregnancy, see the following video.