The length of the cervical canal during pregnancy and the causes of deviations
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes many changes at both the physiological and morphological levels. The functioning of the reproductive system at this time is aimed at one goal - normal childbearing. Therefore, any violation in the process of natural transformation of various elements of the sexual apparatus of the expectant mother can be an obstacle to the normal course of pregnancy.
Of great importance during pregnancy are the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the cervical canal. A special role in this period is played by its length, shape and functional activity. What should the cervical canal look like during pregnancy? What do the deviations of shape and length from the norms adopted in obstetrics say, what pathologies during pregnancy can develop in the cervical canal?
What is the cervical canal?
The cervical canal is the part of the cervix that joins the vagina and the uterus. In clinical obstetrics, this hole is also called the pharynx or cervical canal. During menstruation, uterine bleeding occurs on it. According to it, sperm get into the uterine cavity, due to which fertilization of the female reproductive cell occurs.
The cervical canal on two sides has two sheds - internal and external. They are holes with a diameter of 2-3 mm. The external pharynx is clearly visible with a standard inspection in the mirrors: the woman who did not give birth, it has the shape of a point, and the one who gave birth has a slit.
The size of the pharynx is about 33-34 mm (maximum 40 mm) in women who have not given birth, and 70-80 mm in those who have already undergone childbirth or abortion.
In women in "position", the neck acquires a somewhat bluish tint. In the usual state of the cervix pink.
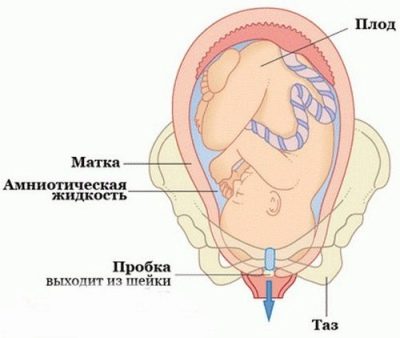
After fertilization, the so-called mucus plug begins to form in the cervical canal, which during the gestation period will perform a barrier function, protecting the baby from all sorts of pathogens penetrating into the future genital tract of the future mother. The mucus is formed by the endocervix cells.
Towards the onset of generic activity, the mucus plug disappears. This happens for every single parturient woman in different ways: for someone a few hours before giving birth, for someone for a week.
How should he be normal?
In the normal course of pregnancy, the throat of the cervical canal is closed, and the cervix is closed in a tight ring. Due to this position, the fetus is securely fixed in the uterus until delivery.
Closer to childbirth, the structure of the cervix gradually begins to change: it softens, smoothes out and no longer looks so tense: so the birth canal “prepares” for the process of expelling the fetus.
At this time, the cervical canal begins to gradually open. Normally, during the first stage of labor, the opening of the cervical canal should be about 10 cm.
For this magnitude, obstetricians understand how soon the immediate expulsion of the fetus will come. And when the width of the pharynx reaches 10 cm, then the birth canal is fully prepared for the unobstructed passage of the baby through it.
Pathological increase
During an ultrasound examination of the cervical canal it may be found that the opening of the pharynx occurs much earlier than the planned completion of pregnancy.It often happens that a doctor may notice such a violation during a gynecological examination. In addition, in the patient, the pharynx can become slit and “skip” one or two fingers.
Open mouth means that premature labor can develop at any time. Such a threatening symptom most often occurs in the second half of pregnancy.
Endocrine disorders can provoke premature cervical dilatation. - excessive production of male sex hormones leads to untimely activity of the cervix. Also, a similar pathology can be observed in multiple pregnancies, when there is excessive pressure from the uterus on the cervical canal.
Another reason for premature expansion of the throat - anomalies of the structure of the cervix or its trauma in history.
This complication of pregnancy requires immediate medical intervention, otherwise the situation may result in spontaneous abortion. A patient with such a pathology needs emergency hospitalization.
If she is provided with qualified assistance in time, the chances of a safe pregnancy will remain high.
Norms of the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy, depending on the gestational age by week, are shown in the following table.
Complications
The main task of the cervical canal during pregnancy is its preservation and protection of the fetus from harmful effects. If there are any anatomical defects of the cervix or its functional impairment, pregnancy is in jeopardy.
One of these pathologies is cervical insufficiency, in which the cervix cannot fully cope with its function, so the pressure exerted on the fetus can lead to spontaneous abortion. In this case, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes the expectant mother drugs that strengthen the walls of the cervical canal.
Also with this diagnosis can be applied installation on the cervix obstetric pessary - a device that can prevent the opening of the pharynx before the prescribed time. This method of preserving pregnancy is quite effective and has a large number of advantages over the surgical suturing of the cervix, which was previously widely used for this diagnosis.
Another common pathology of the cervical canal found in pregnant women is the throat polyp. This tumor may appear due to the following reasons:
- hormonal imbalance;
- weakening of the immune system;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- cervical injuries;
- incomplete discharge of particles of the placenta after previous birth.
The symptom in which the polyp is bloody and the woman feels pain in the area of the cervix is quite threatening and may indicate the development of an oncological process.
The danger of a polyp in the cervical canal during the gestational period is that an inflammatory process may develop against this background. To prevent such a development, antimicrobials may be given to women.
If the results of diagnostic examinations confirm that the tumor is benign, appropriate treatment will be given to such a patient after delivery. It happens that after a child is born, a polyp disappears without the help of doctors.
Sometimes pregnancy becomes a kind of "trigger" for the growth of a polyp in the cervical canal. Then we are talking about the decidual polyp, which appears due to hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman. The decidual polyp does not pose a threat to the expectant mother and her baby and may itself disappear after giving birth.
If a polyp grows in size too quickly, it becomes a real threat of spontaneous abortion. In such a situation, most likely, the attending physician will offer the patient surgical removal of the neoplasm. After surgery, pregnant women are given specific hormonal treatments, as well as antibiotic therapy.
Another frequent pathology that can complicate the course of pregnancy is endocervicitis. Under this term understand the inflammatory process, which is localized in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. It can take a chronic or acute course.
The cause of the development of this disease is the accumulation of pathogenic microflora in the female genital tract. The causative agents of this pathology often become gonococci, staphylococcus, Candida fungi, E. coli, some viruses.
In the normal course of pregnancy, the cervical canal is in good shape and completely sterile. but at the slightest damage to it, pathogenic pathogens can enter the wound and provoke an inflammatory process.
If you do not start treatment for this condition in time, the inflammation can spread to the neighboring tissues and lead to serious consequences.
How can I get a cervical injury? There are several fairly common options for its mechanical damage, which include:
- diagnostic curettage of the cavity and cervix;
- violation of the rules of antiseptics during a variety of gynecological procedures;
- self-introduction of intrauterine devices into the uterus;
- induced abortion;
- hypersensitivity of the cells of the mucous layer of the cervical canal to the active components of oral contraceptives.
It happens that the inflammatory process begins to develop in the mucous layer of the cervix without prior injury to its structure. For example, staphylococcus or chlamydia are highly pathogenic and can cause endocervicitis.
The symptomatology of endocervicitis is quite indicative, therefore, it is easy to diagnose this disease. In the presence of this pathology, a woman notes the appearance of abundant vaginal mucous discharge, in severe cases with an admixture of pus.
During urination, the expectant mother feels severe itching and "baking." The above-mentioned signs may be joined by a pain of a pulling character localized in the lower abdomen.
To confirm the diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe the following laboratory tests: a smear from the vagina, as well as a smear and backwater from the cervical canal. The results of the analyzes will show the type of pathogenic pathogen and the degree of extensiveness of the inflammatory process.
The consequences of untreated endocervicitis can be the following pregnancy complications:
- uterus tone;
- fetal hypoxia;
- placental degeneration;
- the onset of labor activity ahead of time.
A treatment plan for a woman suffering from endocervicitis is drawn up depending on the duration of the pregnancy. However, there is a list of methods of complex therapy, which are most often used for this diagnosis.
- Destruction of pathogenic microflora. Depending on the type of pathogen (bacteria, fungi, parasites, etc.), appropriate preparations are selected. Before proceeding with the immediate administration of drugs, the patient should be tested for sensitivity to antibiotics. Often in the treatment of endocervicitis used a combination of different antimicrobial agents.
- Determination of the order of introduction of certain drugs. For the treatment of gynecological pathologies often used drugs for local exposure - such as vaginal suppositories and tablets, baths, douching, etc. The doctor must explain in detail to the patient the procedure and method of taking the drug.
- Restoration of healthy vaginal microflora.
- As an additional therapeutic methods can be applied physiotherapy.
Prevention of cervical canal damage
The state of the cervix has a great influence on the process of intrauterine development of the child, therefore any deviations from the generally accepted physiological norm in the functioning of this organ should attract the attention of a specialist observing pregnancy.
In order to minimize the risk of possible complications during pregnancy, An expectant mother should be extremely responsible in relation to medical supervision, which can begin to take place before the planned conception.
In order to avoid the development of any gynecological pathologies during pregnancy, it is necessary to register as soon as possible at the antenatal clinic and regularly undergo all the necessary examinations.
Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, endocrine pathologies, as well as correction (including surgical) of structural anomalies of the genital organs before the onset of the planned pregnancy can prevent the development of associated complications in the gestational period when treatment may be difficult. therefore Before becoming pregnant, a woman who dreams of becoming a mother must visit the gynecologist at least once.
On the importance of examining the cervical canal during pregnancy, see the following video.