Causes and symptoms, treatment and effects of polyhydramnage during pregnancy
In pregnant women, obstetric practice is less common. This pathology needs special attention and treatment, because it can be a serious danger to both women and children. About why the quantity of amniotic fluid increases, and what to do if this happens, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
Amniotic fluid, limited by the walls of the amnion (fetal bladder), is an ideal nutrient medium for the growth and development of the baby before it is born into the light. They protect the crumbs from injury, acting as a reliable shock absorber. They take baby waste products and remove them, nourish the baby and protect its delicate skin.
If for some reason the amount of amniotic fluid increases relative to the norm, we are talking about polyhydramnios - dangerous condition that can lead to tragic consequences. Waters can arrive gradually, then the excess will be smooth, and can increase in volume rapidly.
In medical language, the problem is called polyhydramonion. Such a pathology is recorded in approximately 1-2% of the total number of pregnancies. The amount of water in a healthy pregnancy arrives gradually, and by 15-16 weeks it can already be determined and measured using an ultrasound machine.
Since they can not be drained and measure the volume, to determine the amount of amniotic fluid is used a special indicator - the amniotic fluid index (IAG). In normal pregnancy, not burdened by pathologies, it looks like this:
The norms of the amniotic fluid index (IAG) - table:
|
Obstetric term (week) |
IAG (limits), mm |
Obstetric term (week) |
IAG (limits), mm |
|
16 |
73 -201 |
30 |
82-258 |
|
17 |
77-211 |
31 |
79-263 |
|
18 |
80-220 |
32 |
77-269 |
|
19 |
83-225 |
33 |
74-274 |
|
20 |
86-230 |
34 |
72-278 |
|
21 |
88-233 |
35 |
70-279 |
|
22 |
89-235 |
36 |
68-279 |
|
23 |
90-237 |
37 |
66-275 |
|
24 |
90-238 |
38 |
65-269 |
|
25 |
89-240 |
39 |
64-255 |
|
26 |
89-242 |
40 |
63-240 |
|
27 |
85-245 |
41 |
63-216 |
|
28 |
86-249 |
42 |
63-192 |
|
29 |
84-254 |
Exceeding the upper threshold of norms for a certain period and is the basis to judge the presence of polyhydramnios in women. Most often, the problem becomes apparent in the 2 and 3 trimesters of pregnancy.
Classification
Polyhydramnion is conditionally divided into moderate and pronounced. If the amount of water exceeds the upper limit of normal values by no more than 10%, we are talking about a moderate degree. But for the assessment of polyhydramnios during pregnancy, the role is not so much the exact amount of excess water, but the speed with which they arrive.
The index of amniotic fluid, determined in dynamics, allows you to set this speed. If the increase is slow, then we are talking about chronic polyhydramnios. With this pathology, the forecasts are most favorable, in most cases pregnancy can be brought to the appointed time and give birth to a completely normal baby.
If the waters arrive very quickly, their quantity increases rapidly, literally within a few hours or days, then such high water is considered acute. This is a severe pathology.
If it develops in the early period (14-16 weeks of pregnancy), it usually leads to abortion, because amniotic membranes simply cannot withstand the pressure of large amounts of water. If the gap does not occur, the risks of congenital malformations of the child increase. Acute polyhydramnios may also occur in the later periods, and then the risk of losing the child will also be significant.
In addition, polyhydramnios can be light (with a slight excess), medium (with an approximate amount of amniotic fluid of 3-5 liters) and heavy (if the amount of water exceeds 5 liters).
In each particular case, the forecasts are purely individual: it is very difficult to predict how the organisms of the mother and the baby will behave, what will be the condition of the amnion and the placenta.
Causes
Even with the present level of development of medicine and science, it is not yet possible to find out the true causes of the occurrence of polyhydramnios. But many years of observation and practice give obstetrician-gynecologists reasons to assert: polyhydramnios is a very controversial pathology.
On the one hand, the secretory ability of the villi of the amniotic membrane is disturbed due to excess fluid. On the other hand, excess fluid begins to accumulate due to the fact that the membranes begin to suck up the liquid worse.
Water updated every three hours. To replace the former portion of the fluid, which is almost completely absorbed by the amniotic membrane, as well as the lungs and intestines of the child, a new portion is produced. If the old is not completely absorbed, it causes an increase in the amount of fluid. Such, if to speak briefly, is the mechanism of the development of pathology. There are still heated scientific debates about the reasons that trigger this mechanism.
Most often polyhydramnios develops in women suffering from the following pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus and gestational diabetes (this cause accounts for almost 30% of all cases of polyhydramnios);
- infectious diseases, including chronic and sexually transmitted diseases (infection of the herpes viruses, rubella pathogens, toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections are most common);
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- chronic and acute diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- chronic or acute diseases of the kidneys and urinary system;
- anemia of different origin.
The reason for the development of polyhydramnios may be some features of the pregnancy itself:
- preeclampsia;
- multiple pregnancy;
- immunological incompatibility between mother and fetus (usually due to the difference in Rh factors).
Some pathologies of the development of the baby can also lead to polydramnion:
- congenital malformations (most often abnormal development of the brain and spine - anencephaly, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, etc., as well as malformations of the stomach, intestines - artesia of various parts of the digestive tract);
- genetic chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, etc.).
The probability of occurrence of polyhydramnios is also influenced by some pathologies of the placenta, in particular chorionangioma.
Women with chronic diseases who have had an early gestation, including ARVI and influenza, as well as women in disadvantaged social conditions are at risk for the development of polyhydramnios - poor nutrition, lack of essential vitamins and minerals. Often polyhydramnion is accompanied by pregnancy in women who abuse alcohol, narcotic substances and smoking.
Specialists at risk include women who have a high risk of having a child with chromosomal abnormalities (who become pregnant after 35 years, have disabled children with chromosomal ailments, have relatives with genetic pathologies, and have several miscarriages in a row).
Among all the identified cases of polyhydramide in pregnant women about 20% falls on polydramnioncaused by fetal abnormalities.
All of the above factors can cause the accumulation of amniotic fluid. If a woman has infections or inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs, the amnion can produce components of the amniotic fluid too active, and their excretion will be delayed.
If the baby has a malformation of the esophagus, it will less actively swallow the water or will not swallow it at all, which will also lead to an overflow of the amniotic bladder.
Symptoms and signs
The severity of symptoms in polyhydramnios depends on the type of pathology. If chronic polyhydramnion is observed, then the woman's body adapts to the gradual accumulation of amniotic fluid, compensatory mechanisms begin to work.
As a result, the future mother there is no pronounced clinical picture, the symptoms are "smoothed out", sometimes even almost unnoticed. It is usually found by the middle of the second trimester, not earlier.
Acute polyhydramnion happens much less frequently, and a woman’s complaints appear almost immediately. She complains about the deterioration of the condition, the pain and the feeling of "bursting" in the stomach.
Most of the acute pathology develops from the 14th to the 24th week of pregnancy, most often up to the 20th week. With such a violation, in almost 95% of cases, the most terrible suspicions are confirmed - fetal chromosomal abnormalities, whereas in chronic polyhydramniation, defects and anomalies are not always present.
To determine the chronic polyhydramnios in her own future mother practically can not. Symptoms characteristic of polyhydramnion, more pronounced in acute impairment. But sometimes in a calmer form, they may be present in the gradually developing pathology.
In case of high water flow:
- the fruit moves too actively;
- a woman often feels heaviness and fullness in the stomach;
- there is severe pain in the abdomen (in acute polyhydramnios);
- the woman has severe shortness of breath even after a minor exercise;
- the future mother will have all the signs of premature birth or spontaneous abortion if the problem has been identified in the last months of pregnancy.
In the third trimester, late toxicosis is the most prominent and characteristic sign of polyhydramnios. In contrast to the early, it becomes rampant - sometimes with polyhydramnios, the frequency of vomiting in a pregnant woman reaches several episodes per hour.
In the later periods, swelling of the anterior abdominal wall becomes noticeable. Half of patients with high water observed fluctuation. Such a term denotes a characteristic sound accompaniment - “squelching” of amniotic fluid in different situations, for example, when the body position changes.
The uterus, which has a much larger size in the presence of polyhydramne, puts pressure on the diaphragm, because of this difficulty breathing occurs, problems with cardiac activity can begin to be felt - women most often have tachycardia.
Another characteristic external feature of polyhydramnion is the formation of extensive and coarse stretch marks on the skin of the abdomen.
Danger and consequences
Plutonization is dangerous abortion. The amniotic membranes surrounding the baby along with the waters are elastic and durable, but not to such an extent as to withstand too much fluid.
The most tragic scenario is the rupture of the membranes and the death of the baby. Spontaneous interruption ends approximately every third pregnancy with polyhydramnios.
Stretched fetal bladder and a large amount of fluid inside it create a large space for the movement of the child, and he actively uses it. Because of this, cordial entanglement, pelvic or transverse presentation, which will require a special approach to delivery, is quite often found. Most often, a child is born using a cesarean section.
In childbirth polyhydramide threatens to turn into massive bleeding. Medical statistics report that fairly heavy postpartum bleeding is observed in about half of pregnant women with a confirmed diagnosis of polyhydramnios.
In 7-8% of women, premature rupture of water is observed, which threatens with a long anhydrous period and the onset of hypoxia or infection of the baby. In 5% of pregnant women with polyhydramnage, premature detachment of the placenta is observed.
A morbid condition in every fifth expectant mother at a late period causes nausea and vomiting, an increase in blood pressure. In 6% of cases, the child has intrauterine growth retardation.
Diagnostics
The first suspicions about probable polyhydramnios usually occur at the obstetrician-gynecologist. On examination of a pregnant woman, at each scheduled visit, the height of the uterus standing (UDS) is measured. The future mother with polyhydramnios this size, which normally corresponds to the period (18 weeks - 18 cm, 38 weeks - 38 cm), is exceeded significantly. Also increased abdominal circumference.
"Manual" gynecological examination shows that the uterus has a tugoelastic consistency, its walls are "stretched", the doctor's manipulations in trying to probe parts of the fetus's body cause “gurgling” and “squelching”, and it is rather difficult to probe the baby because in the large space of the enlarged uterus it is easier for him to hide from such an examination.
Quite often, the baby is located in the uterine cavity in the pelvic or transverse presentation, with the presenting part of his body rather high above the entrance to the pelvis. The heart tone of the baby, who can easily listen to any obstetrician at the reception, is heard indistinctly, deafly. It is normal to listen to the baby’s heart by interfering with a large amount of the surrounding liquid.
If a woman has other symptoms of polyhydramnion, the problem of an experienced doctor becomes clear almost immediately. But to make such a diagnosis, he must be sure of the correctness of his assumptions. But because a woman receives a referral to the office of ultrasound diagnostics.
Somnolog doctor examines the amount of amniotic fluid. This is done by a very interesting method. The doctor visually divides the abdomen into four equal sectors. In each of them with the help of an ultrasonic sensor, the amount of amniotic fluid is measured, loop-free umbilical cord and crumbs of the body parts. The amount of fluid is measured by the depth of these "pockets".
Then all four results are added up, and the same index of amniotic fluid is obtained, which is the main criterion of the norm or pathology. Border overshoot is a tendency towards polyhydramnios. This condition is also studied in detail and carefully monitored.
If IAH exceeds the norm, the doctor on the ultrasound examines the baby carefully, trying to detect possible signs of genetic pathologies, malformations of the internal organs. Then a detailed study is made of the state of the placenta and uteroplacental blood flow. For this, a USDG is used, popularly known as “Doppler Ultrasound”.
A lot of information can be given by screening studies of the first and second trimester. If they have not shown an increased risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities, then doctors will consider other reasons for the development of polyhydramnios. In some cases, the expectant mother may be recommended to donate blood for hormones, in particular, the concentration of prolactin. An increase in amniotic fluid is often accompanied by a drop in the level of this hormone.
Required unscheduled delivery of general clinical blood and urine tests, and also takes a smear from the vagina to identify possible infections that could be the root cause of problems with amniotic fluid.
If a woman and her baby have different Rh factors, then if you suspect polyhydramnios, the expectant mother will also go to donate blood for antibodies. When the increase in the amount of water is associated with the immune rejection of the fetus by the maternal organism, which occurs during rhesus conflict, the antibody titer also shows growth.
Invasive diagnostic methods, in particular amniocentesis or cordocentesis, are rarely prescribed for suspected polyhydramnios.
If there is such a need, you should not abandon the procedure. It will allow to know with great precision whether the crumbs of hereditary or chromosomal pathology.
An alternative to an unsafe and ambiguous invasive diagnosis is a non-invasive DNA test, in which mothers extract fetal blood cells from a mother's venous blood sample in the genetic laboratory and make a conclusion on the child's health status using their DNA. Such an analysis is expensive - several tens of thousands of rubles, and therefore not everyone is available.
Treatment
Confirmed high water requires doctors to be more attentive to the expectant mother. She is required to go to the reception more often - depending on the degree of polyhydramnios - up to 1 time per week.
Starting from the 28th week of pregnancy, she will receive weekly CTG, According to the results of which it will be possible to monitor the baby’s well-being, his heart rhythms, and the possible state of hypoxia.
Treat polyacid taken in the hospital. The expectant mother is instructed to observe complete rest in order not to provoke premature birth or rupture of water by her actions and physical activity.
She is strictly forbidden to be nervous, to worry, to sort out relations with members of the household. If necessary, the doctor prescribes light soothing drugs on a natural basis that will help the pregnant woman cope with anxiety and feelings.
The ban is also imposed on sex, because contractions of the uterine muscles accompanying an orgasm can provoke a rupture of the amnion.
It is impossible to cure polyhydramnios, but you can support a woman and her baby with medication. This is exactly what the doctors are doing. Treatment is based on the treatment of the underlying disease, which caused an increase in water.
If these are inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs of the mother, then the course of treatment is chosen by the gynecologist, if the cause is heart disease, then the main therapy is a cardiologist. In diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes, the doctor-endocrinologist will decide on the prescription of certain drugs.
If malformations in a child are detected, a woman is offered to terminate a pregnancy for medical reasons. If she refuses to do this, doctors will do everything possible to maintain the life of the baby and the health of his mother. When pathologies of the placenta is prescribed a course of drugs that improve the placental blood flow, and multivitamins.
If the true reasons for the increase in the amniotic fluid remain unknown, then the standard scheme of medical care for polyhydramnione is used - antibiotic treatment. The purpose of this therapy is avoid the development of intrauterine infection.
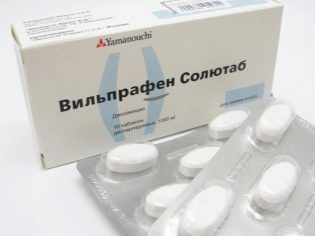
Among antibacterial drugs, most often expectant mothers are prescribed «Cefotaxime», «Vilprafen"And"Ceftriaxone». Antibiotics of the tetracycline group are not prescribed during pregnancy.
At the same time, it is recommended reception “Kurantila” and “Actovegin» multivitamin complexes are also prescribed to improve uteroplacental blood flow. To remove excess fluid from the body in the standard treatment regimen include diuretics - means with a diuretic effect.
If the dynamics is positive, then the pregnancy will remain up to 37-38 weeks. The future mother will need to come to the maternity hospital earlier to meet 37 weeks under the supervision of specialists around the clock, ready to give her away at any time if the baby’s condition worsens.
On what method of delivery to stop, doctors decide during the last weeks of pregnancy. It is not recommended to give birth in a natural way, because abundant outpouring of water under the pressure of their mass can literally wash out small parts of the fetus from the uterus. In addition, the likelihood of the development of weak tribal forces. If natural childbirth and allow, then open the bubble by artificial means.
90% of women with polyhydramnios give birth by performing a planned cesarean section. So the risks in childbirth, associated with a large amount of amniotic fluid, can be minimized.
If a woman enters the hospital with an acute stage of polyhydramniosa, she is advised to terminate the pregnancy. When this happens in the third trimester, especially with a large fetus, it is inappropriate to keep the pregnancy, because the baby is already viable.
A Caesarean section performed in time will save both the woman and her child’s life.
After giving birth, doctors pay special attention to the baby. Mortality among these newborns is more than two times higher than among other groups of children. On the very first day, the baby takes blood for infections, for determining the group and Rh factor (in case of conflict), and also carries out the necessary therapy if it is necessary.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies polyhydramnage is not treated. There is no such weed and root, which could affect the internal processes in the amniotic membrane. The only reasonable treatment regimen is considered to be classical medicine therapy.
However, in some cases, a woman may turn to traditional medicine recipes, but only to replace the symptomatic pill with an alternative method. For example, diuretic drugs with a small chronic polyhydramnios can be replaced with cranberry juice or parsley, which also have a diuretic effect.
With increasing pressure, the expectant mother can drink carrot juice or weak camomile tea in small quantities. With diabetes, she will have to follow a strict diet. However, all these methods do not cancel traditional medical treatment, including antibiotics.
Refusing to undergo treatment can not be, because no folk remedies can not affect Rh-conflict or congenital malformations of the baby, and especially not treated with plantain and nettle TORCH-infections and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Forecasts and Prevention
If polyhydramnios is detected at an early stage, and it is not of an acute nature, is not associated with genetic defects and fetal abnormalities, then the forecasts are quite favorable. Prompt treatment helps to eliminate the complication completely.
Acute polyhydramnios has unfavorable predictions, especially in the early stages - most of these babies die in utero. Death is not excluded in case of acute polyhydramnios at a late period.
Specific measures for the prevention of violations does not exist. However, to minimize the possibility of a pathological increase in amniotic fluid can be, if you plan to conceive a child in advance.
A woman should be examined in advance by a cardiologist, an endocrinologist and a nephrologist, and should visit a female doctor to rule out diseases of the reproductive system.
Before conceiving, you need to take a blood test for infections, including sexually transmitted infections, urine for bacposa, blood and urine for sugar. If pathology is found, should be treated before conceiving a son or daughter. If there are risks of genetic pathologies, it is advisable to visit in advance the genetics and consult with him.
Women in order to avoid the development of polyacid should register as early as possible in the antenatal clinic and do not refuse to undergo mandatory screening studies in the first and second trimesters.
Regular testing, adherence to the principles of proper nutrition, prevention of large weight gain and the development of preeclampsia - these are the main tasks facing the future mother. If she has bad habits, such as smoking, and she did not quit doing it at the planning stage of the child, then you should say goodbye to a cigarette as soon as possible, because, according to the doctors, the probability of polyhydramnios appearing in a smoking pregnant woman is three times higher than women leading a healthy lifestyle.
To prevent an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid, the woman is “in position” need to comply with sleep and restenough to rest, not to burden yourself with excessive physical exertion, not to be nervous, to follow the drinking regime (moisture should be enough, but it should not be too much), as well as walk more in the fresh air.
Reviews
Despite the level of development of medicine and diagnostic capabilities, in approximately 50-60% of cases, doctors in antenatal clinics cannot establish the true cause of polyhydramnios. This is reported by pregnant women themselves, who know about this complication firsthand. In this situation, future mothers, according to their reviews, are very afraid of prescribing antibiotics for possible infections.
Many even refuse to take antibacterial drugs, but this is a fundamentally wrong tactic.. According to reviews of future mothers, left by them in specialized parent forums on the Internet, one or other problems associated with a large amount of amniotic fluid were observed in each of the women. Unnoticed mnogovodie not passed from anyone.
Most often, women complained about the last weeks of the term of carrying a baby, because by the end of the period of gestation, many legs and abdomen were swollen and physical capacity to move and move freely disappeared.
The perspective of natural childbirth seems to many to be the most ideal option. There are positive reviews about childbirth in case of polyhydramnios, and even complicated by entanglement by the umbilical cord. A lot depends on the doctor’s attitude to the problem of high water.
According to women, not all doctors are in a hurry to begin searching for the causes and selecting the method of delivery. A somewhat “treasury” attitude has been formed towards this pathology, in which doctors try not to go beyond the limits of the therapeutic scheme. And future mothers need an individual approach.
Read more about high water and low water in the next video.