What to do with a cold, runny nose or cough in the second trimester of pregnancy?
The common cold and viral infection are usually perceived as the easiest of all possible evils. But everything changes when a woman falls ill while waiting for a child.
A cold during pregnancy can significantly harm both mother and baby, and the list of means available for therapy for the future mother is significantly limited. Treatment in early and late periods has its own specifics. This article will discuss the second trimester of pregnancy.
Is it dangerous?
As such, the term "cold" in medicine does not exist. Usually, such a name in the people means a wide range of various viral diseases - adenovirus, rhinovirus infections, SARS, influenza, etc. In total there are about 300 different respiratory viruses that cause common symptoms - cough, runny nose, sore throat, fever, deterioration, muscle aches, photophobia, etc.
Viruses are extremely dangerous for the fetus in the early stages - in the first trimesterwhen organogenesis processes occur. A virus entering the mother’s bloodstream through the respiratory tract disrupts the formation of the baby’s organs, can cause intrauterine death at an early stage, and can cause multiple fetal malformations.
In the second trimester, the baby is better protected.. Starting from week 13-14, the young placenta begins to fully perform its functions. It reliably protects the crumb from many threats, feeds it, serves as a natural shock absorber. All internal organs completed the formation at the end of the first trimester, and therefore malformations due to viral illness of the mother are no longer so likely.
You need to know that the 2nd trimester is the time of system genesis. This means that the previously formed children's organs begin to debug functions and interactions. And the main danger of a viral infection lies in the theoretical possibility of disrupting the functioning of the normal organs of the fetus.
In practice, this does not happen very often, but the woman must be aware of the probability. As the process of placentation continues, acute respiratory viral infections or influenza can cause a violation of the structure and functions of the “children's place”.
In the world of viruses and bacteria, there is still so much unknown and unexplored that no one can say with great accuracy whether the second trimester flu will be safe. It all depends on the severity of the disease, on the state of immunity of the woman and the characteristics of the course of pregnancy.
To refer to the "cold" symptoms frivolously no time is impossible. Already, at least, because a more dangerous disease can be masked by ARVI - herpes infections, toxoplasmosis, mononucleosis, etc.
The placenta will by all means protect the fetus from viruses and other pathogens, but it can also be under attack. Improper second trimester treatment can harm a pregnant woman and the fetus more than the infection itself.. Some drugs with unreasonable use of them can cause late miscarriage or premature birth, and the prognosis for survival in childbirth in the second trimester, alas, is not so high.
What to do?
First of all, when symptoms are detected (cough, sore throat, fever, nasal congestion, increased nasal discharge), a woman needs to be called to the house of a district therapist. It is not recommended to go to the reception yourself. For the body of the future mother, hardly protected by a weakened immune system, bed rest and complete rest is now shown. The immune system of a pregnant woman begins to be suppressed at the very beginning of the gestation period - the hormone progesterone has an immunosuppressive effect. By the second trimester, the natural protection of the mother’s body is significantly reduced, she cannot effectively resist the invasion of viruses or bacteria, as before.
Therefore, it is necessary to leave all affairs, postpone everything for later, take a comfortable position in bed and calmly wait for the doctor. Examination is necessary - an experienced doctor will quickly determine whether a viral disease or a bacterial disease, and this is important, because they have different treatment.
Before the arrival of the doctor is better not to take any medication.
Viral ailments are terrible for their possible complications. Therefore, before the doctor arrives, it is important to create conditions under which a virus that has entered the woman’s body will cause as little damage as possible.
The room should be well ventilated, if necessary, it should be constantly aired, wet cleaning and moistening the air with any available means will not interfere - the drier the air, the higher the likelihood of respiratory mucous membranes drying, and in this case complications are more likely and the virus itself will be able to penetrate the bloodstream of a woman earlier.
Drink plenty of room temperature. - too hot liquid can increase the swelling of the inflamed larynx, if the throat is sore, besides cold and hot liquids are less digestible.
If there is a high temperature, do not wrap up in a warm blanket, in a sweater and a pair of scarves. The maximum you need to undress, stay in light summer pajamas or nightgown, cover with a sheet, not a warm blanket and in no case wear woolen socks - a woman’s body should give off heat efficiently, otherwise hyperthermia should not be avoided, in which the uteroplacental blood flow is disturbed. .
Permitted Drugs
Women who are preparing to become mothers should learn a simple truth: there are no permitted pharmaceutical preparations during pregnancy. There are only remedies that can be prescribed when there is a need for them, when the disease may have more negative consequences for the mother and the fetus than the medication itself.
After examining the doctor, when it becomes clear what exactly the woman is dealing with, recommendations on drugs will be given. The range of available funds for mom in the second trimester is much wider than in the first. If bacterial diseases are detected, for example, sore throat, sinusitis, the doctor will be required to prescribe antibiotics.. Their use on this period will not be as harmful as in the first third of the gestation term.
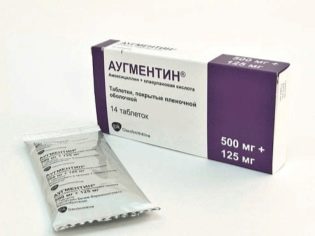
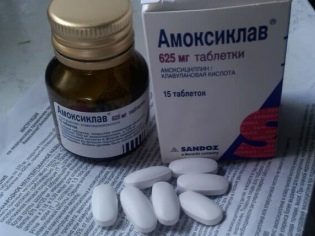
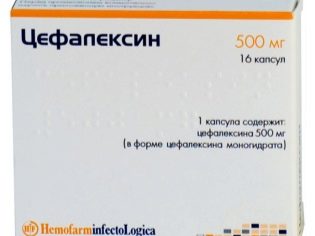
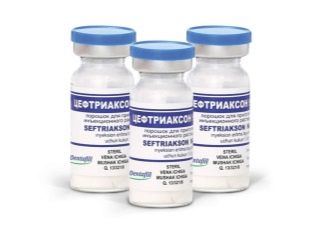
Not all antibacterial drugs are allowed for pregnant women. - preference is given to the penicillin group, for example, to such drugs as Amoxiclav, Augmentin. Also, the doctor may prescribe a cephalosporin antibiotic group - Cefalexin, Ceftriaxone.
Antibacterial drugs of the quinolone group, sulfonamides are contraindicated in the second trimester of pregnancy. Ototoxic drugs that can cause hearing problems in the mother and fetus, Gentamicin and Neomycin, should also be avoided.
If a woman has a viral disease, antibiotics are contraindicated, because they can not affect the viruses. But antiviral drugs are undesirable. Most of these drugs have no proven efficacy at all, and for the most part are homeopathic. Therefore, it is impossible to call them prohibited, but it would not be entirely fair to recommend them. "Anaferon", "Orvirem", "Oscillococcinum"," Viburkol "," Viferon "- drugs that do not harm the mother and fetus, but the effect of them will not.
Therefore, the treatment regimen in which medicines are used only to relieve strong unpleasant symptoms seems reasonable. For the rest, the immunity of the woman, despite the fact that he is visibly weakened, can easily cope with the infection in 5-6 days.
Symptomatic remedies primarily include:
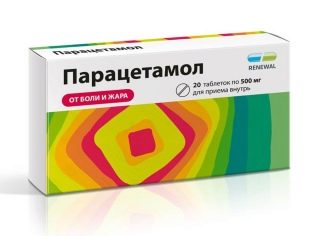
- antipyretic - all on the basis of paracetamol;
- from a cold - vegetable, sea water, saline solutions for washing the nose;
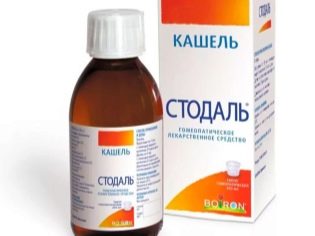
- dry cough - mucolytic "Mukaltin"," Doctor Mom "," Tussin "," Stodal ";
- if you have a sore throat – «Miramistin, Tantum Verde, Hexoral.
It is forbidden to use antipyretic in the second trimester if the temperature is below 38.0 degrees.
Such a temperature is needed for more effective work of immunity, it is not worth lowering it. Do not use "Aspirin" - it dilutes the blood, which can cause uterine bleeding, pathology of the placenta, miscarriage or premature birth.
Vasoconstrictor drugs should not be used for a cold. Their action is always systemic, and they constrict the vessels not only in the nose. The action of Nazivin, for example, can also extend to the vessels of the placenta, which means that the baby is at risk of receiving less nutrients and oxygen.
When a wet cough does not need to take anything, because the phlegm comes out, the bronchi are cleared. The preparations listed above are recommended only for a dry, unproductive cough, in which a woman cannot cough.
Prohibited actions
Expectant mothers, if they could not be saved from the disease, it is important to know what mistakes they should avoid in the course of treatment.
- Do not float your feet and put garlic and mustard in warm socks.. The consequences can be different - from increased blood flow in the lower part of the body, including the pelvic organs, to allergies.
- You can not visit the bath and try to “evaporate” the disease from the body - this contributes to overheating, hyperthermia and the development of problems with uteroplacental blood flow.
- Do not practice rubbing with ice water and vodka. - is fraught with spasm of blood vessels.
- You can not rub a badger fat, fat - this will prevent normal thermoregulation.
- Do not inhale at high temperature.
What you need to do?
During treatment, a woman should always rinse her nose several times a day and gargle with saline solution prepared by herself or bought at a pharmacy - this will help remove particles of damaged ciliated epithelium, virus particles, and also prevent mucous membranes from drying out.
Light meals should be provided with heavy drinks.but without food, which is digested for a long time and requires from the body certain energy consumption for digestion. Now all the forces of the body must be left for recovery. It is better to eat vegetables and fruits, cereals, mashed potatoes, dairy products, steamed lean fish, cutlets.
As soon as the temperature drops to 37.0 degrees or a little higher, it is necessary to breathe fresh air - go for a walk, even if it is winter outside. This will help saturate the blood with oxygen, and will also promote faster recovery.
It may not be necessary to treat the so-called catarrhal diseases during pregnancy, if a woman takes care of vaccination beforehand - pregnant women are vaccinated against flu. Even if infection occurs, the disease will be easier, and the likelihood of complications will be assessed as low.
In the next video, you are waiting for a few tips on how to avoid colds during pregnancy.