What if D-dimer is elevated during pregnancy?
The fact that there is such an analysis as D-dimer, many women find out only during pregnancy. The time of childbearing is a very crucial period for the whole body, the load grows on the internal organs, on all systems, including the blood circulation. It is to diagnose the quality of blood and prescribe this analysis. Why D-dimer is raised, and what to do in this case, we will tell in our article.
What it is
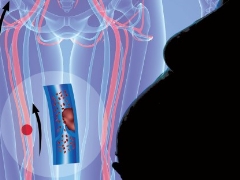
D-dimer (d-dimer) is a fragment of fibrin protein. When the body has a need for blood clot formation (wounding, surgery, childbirth, etc.), fibrin protein paired with the enzyme thrombin begins to create a protective mechanism that will prevent excessive bleeding, large blood loss. This is how blood clots are formed, which “seal” the places of injury to the vessels.
As soon as the danger has passed, the body needs to be natural by getting rid of blood clots so that they do not clog up the vessels, and the fibrin filamentous anti-coagulation system, which starts the process of fibrinolysis, takes over the clotting process. The thrombus is absorbed, the vessels become clean and healthy, but after the collapse of the thrombus, part of the protein remains. This is the D-dimer, a kind of marker for the normal activation of the hemocoagulation system.
The amount of this substance is estimated in the analysis of blood clotting. For pregnant women, such an examination is prescribed several times during the period of carrying the baby. If the future mother's blood is too thick, then it is fraught with thromboembolism and other serious vascular consequences, if it is, on the contrary, liquid, then the danger lies in the risk of internal bleeding, critical blood loss during labor.
Regulatory Values
There is no fixed rigid frame for the density of this substance in the blood. It is considered normal if, in humans, the value of this marker does not exceed 500 ng / ml. The lower threshold is not set, that is, it is understood as 0 or 0.5 ng / ml. However, in all pregnant women, D-dimer is slightly elevated, and it usually increases with the length of time the baby is born.
In the first trimester, it increases by 1.5 times, in the second - by two, in the third - by three times compared with the baseline level that the woman had before pregnancy. Knowing this, the recommendations of doctors to get tested not only during pregnancy, but also at the planning stage, become more understandable.
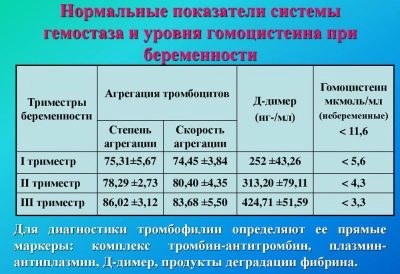
Table of acceptable values in pregnant women
Obstetric term | The density of D-dimer, µg / ml |
4 -13 week | 0.0 – 0.55 |
13 -21 weeks | 0.20 – 1.40 |
21-29 week | 0.30 – 1.70 |
29-35 week | 0.30 – 3.00 |
35-41 week | 0.40 – 3.10 |
Permissible level after IVF
Obstetric term | The value of D-dimer, ng / ml |
4-13 week | No more than 280 |
3-21 weeks | No more than 700 |
21-29 week | No more than 850 |
29-35 week | No more than 1000 |
35-40 week | No more than 1550 |
Different laboratories and medical facilities may use different units of measure - micrograms, non-grams, µg FEU / ml (micrograms fibrinogen-equivalent units per milliliter). It is clear that the numbers will also be different. In order to avoid confusion, it is worth checking with the doctor in which measurements this hemostasis marker is calculated and what its norms are for a particular laboratory.
Reasons for raising
Physiological
The increased protein formation of D-dimer in the blood of a pregnant woman is easily explained by natural, physiological processes. For birth, the body of the future mother begins to prepare as soon as the pregnancy has come. Childbirth is a traumatic process associated with blood loss. According to some reports, during childbirth a woman loses from half a liter of blood.
The most dangerous moment is the birth of the placenta, its discharge from the wall of the uterus causes bleeding. If the body is not ready for it, if the platelets are too low, then quickly “close” the path of blood with blood clots will not work, and the woman will lose a lot of blood, which can be fatal for her.
To prevent this from happening, the body begins to "thicken" the blood, reduce the clotting time. In laboratory tests, this process is reflected as an increase in the amount of D-dimer, an increase in the concentration of platelets, a decrease in the time required for the formation of a blood clot.
Physiological "thickening" of the blood should not cause serious concerns, treatment in this case is not required. The fact that inflated rates are not a sign of the disease, says the general condition of the woman, the results of other tests.
If a pregnant woman has no visible disorders, complaints of feeling unwell, pain in the extremities, swelling and drops in blood pressure, cyanosis of the skin, vomiting and nausea, then an elevated level of D-dimer is not considered dangerous and pathological.
Pathological
If the density level of D-dimer in the blood is increased significantly, there was a sharp jump upwards, if the level is too high for a given period (for example, in the early stages), then no one will expose the diagnosis on this basis. A woman will only be assigned additional examinations and consultations, which should help to find the true cause of the variance in the analyzes.
Most often, significant exceeding the allowable values are observed in diseases such as thromboembolism, DIC syndrome. In thromboembolism, an existing thrombus is detached and clogs the vessel, making it difficult for the blood to circulate normally. The consequences can be very sad: if a vital vessel is blocked, for example, the pulmonary artery, then death occurs in a matter of minutes.
DIC syndrome - disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. When it disrupts the formation of blood clots, and small vessels in large quantities may be clogged. The lesion is large-scale, the condition worsens dramatically, the skin turns pale, cyanosis, vomiting, pain in the sternum and abdominal cavity are observed. Blood is detected in the urine.
Deep thrombosis (deep vein thrombosis), in addition to an increased level of D-dimer, is accompanied by severe pain in the legs, especially during prolonged standing, as well as a change in skin color in a sore spot, swelling, and arterial pressure drops.
Sometimes an increase in this marker indicates not only problems with the cardiovascular system. A moderate excess of the density of D-dimer can lead to a false-positive result. This happens when:
- liver diseases in the future mother;
- with strong inflammatory processes;
- excessive mobilization of the coagulation system after surgery, injuries;
- with cancer and other tumors.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, a significant increase in this marker in the blood can be a sign of placental abruption, a sign of carrying two or three fetuses, as well as a symptom of severe toxicosis or diabetes mellitus (even at its initial stages).
Enhancement after IVF
After IVF, increased D-dimer values are a familiar phenomenon. It is believed that in this way the body reacts to outside interference. Level markers are trying to measure twice - before replanting and after embryo transfer on the fifth day.
Elevated protein fragment may be due to the implantation process itself, because the fertilized egg is embedded in the wall of the uterus and violates its integrity. The hormonal level can also affect the level of D-dimer. Any ultrasound protocol is accompanied by strong hormonal support with progesterone and estradiol.
Pregnant women who decide to become mothers through IVF, after embryo replanting, monitor blood clotting parameters several times, this analysis will be done 2 or 3 times for 1 trimester, and then the same amount in the second and third trimester.
Treatment
Before prescribing treatment, if the doctor sees the need in it, the woman is sent for a consultation with a cardiologist, a nephrologist and a therapist. A detailed analysis is made on all indicators of blood clotting - coagulogram. If necessary, a woman is advised to consult a hematologist. Then the question of the presence of a specific pathology is decided, and ways are being sought to assist the pregnant woman.
To normalize blood clotting prescribe special drugs - anticoagulants. Most often it is "Nadroparin calcium" ("Fraxiparin") and "Reopoliglyukin." "Nadroparin calcium" in the form of shots put in the stomach, in the area of the umbilical ring. You should not be afraid of the procedure, for injections use thin and small needles, which are also called insulin. The expectant mother will not feel strong pain during the injection. After the injection, there may be a slight burning and tingling sensation at the injection site.
"Reopoliglyukin" is administered as part of droppers in a day hospital or in a hospital. The drug helps the process of resorption of blood clots, cleans the blood vessels, restores normal blood circulation in them. The course of treatment usually helps to lower the level of D-dimer to normal values for gestational age.
To reduce the level of this indicator, a woman is recommended to change lifestyle. “Thick” blood is an indication for abundant drinking regime; if a woman consumes more clean drinking water, the blood will become more fluid. Useful walks in the fresh air, minimizing salty foods, which will contribute to the retention of water in the tissues and the formation of edema.
Typically, women are assigned B vitamins and vitamin K. If a violation is detected in the early stages, special attention is paid to taking folic acid, the deficiency of which may also be one of the reasons for the increase in D-dimer blood.
Woman strictly contraindicated unbearable physical exertion, lack of sleep, emotional distress and stress. Moderate physical activity is welcome - exercise and walking will benefit as a good means of preventing thrombosis.
Do not be afraid if an obstetrician-gynecologist advises visit genetics. Usually, pregnant women whose close relatives have problems with blood vessels, if they have been diagnosed with strokes or heart attacks, can hear such advice. Consultation with such a specialist is needed to more accurately calculate the probability of a hereditary pathology in a woman and her child, this will allow doctors to choose the right tactics for managing pregnancy and delivery.
About what is dangerous D-dimer during pregnancy, see the following video.