Why do cordocentesis during pregnancy and what does it show?
Invasive diagnostic methods during pregnancy cause a lot of questions and concerns. But sometimes without them it is impossible to obtain reliable information about the condition of the baby, which the woman is carrying. Cordocentesis belongs to one of such high-precision methods. We will discuss what this survey is about and what it shows in this article.
What it is
Invasive prenatal diagnosis is an attempt by a person to look into the unknown, to touch the sacrament. Previously, it was considered impossible and unthinkable, but now there are methods that allow you to learn a lot about the baby, even if it was conceived only a few months ago.
Invasive methods of obtaining information about the health of the crumbs are always associated with the penetration into the uterine cavity long before delivery.
There are various ways to find out if the baby is healthy - cordocentesis, amniocentesis, chorionic biopsy and others. They are carried out at different times and differ in the material that is taken for genetic analysis.
In case of amniocentesis, amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) is taken, and chorionic biopsy is taken with particles of the fetal membranes. Cordocentesis is the collection of fetal cord blood.
Excessive curiosity is always punishable. This law also applies to invasive diagnosis. All her methods can not be considered absolutely safe, the probability of complications is always there, and this is the price paid for trying to outwit nature. But the value of the information received is unparalleled. No other diagnostics can be compared with an invasive one.
If the baby’s health causes questions from the doctor who is watching the pregnant woman, if the usual screening tests show a bad result, the risk of having a baby with chromosomal gross abnormalities is high, invasive methods can accurately answer the main question - is the baby healthy.
The procedure of cordocentesis from the 18th week of pregnancy. Often it is done simultaneously with amniocentesis in order to have a greater amount of material belonging directly to the baby, for detailed study in the genetic laboratory.
To whom
Given that invasive methods can be dangerous to the life of the child and the health of the expectant mother, cordocentesis is not one of the studies that a woman can go on of her own free will and free will.
For a time consuming and unsafe procedure. strict medical indications are necessary. Most often, pregnant women are sent to cordocentesis, during the screening of the first and (or) second trimesters, markers of chromosomal abnormalities were detected.
Biochemical blood tests, as well as ultrasound scanning of the fetus in the first and second trimester can determine abnormalities inherent in one or other gross pathologies. In this case, the woman is given a conclusion that she has high risks of having a child with Turner syndrome or Down syndrome, with Edwards disease, with abnormal development of the brain, spinal cord.
Many of these diseases and anomalies lead to the death of a child either in the womb or after birth.With some pathologies, for example, with Down syndrome, you can live long enough.
The future mother and her relatives have every right to know whether the baby is healthy, as well as the right to decide for themselves whether to leave such a child or have an abortion for medical reasons. The choice is difficult, painful, but much harder - the unknown until the birth. Therefore, a woman is offered cordocentesis.
Even if the planned screening did not reveal any warning signs, but the woman already has a child with a genetic disease in the family, or a history of childbirth, during which the baby was born with total developmental anomalies, she will also be asked to go for cardiocentesis.
Women who have chromosomal ailments, as well as in the case of such pathologies of the husband’s relatives, also receive a referral to the procedure.
Cordocentesis in some cases is prescribed to pregnant women who previously suffered from habitual miscarriage, gave birth to dead children who had 2 or more miscarriages in a row, with suspected hemophilia of the fetus, intrauterine infection, severe Rhesus-conflict.
Sometimes a procedure similar to the technique of execution is necessary in order to make a blood transfusion to a baby who has not yet been born in this way, as well as to introduce a life-saving drug into his bloodstream.
The need for cordocentesis is considered by several experts. obstetrician-gynecologists and a medical geneticist are included in the commission. If, after examining all the circumstances of the medical history, they make a positive decision, special health care institutions, mainly medical and genetic centers licensed for invasive diagnostics, will take the material and analyze it.
How is the procedure?
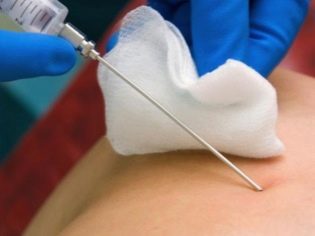
In sterile stationary conditions, a woman is pierced through the abdominal wall in front of the place where the umbilical cord rests on the placenta. Such a puncture allows you to make the cord blood collection.
1-2 ml is usually enough. In some cases, the volume of cord blood taken is increased to 5 ml. Anesthesia, which is so afraid of pregnant women, is not required. Enough local anesthesia.
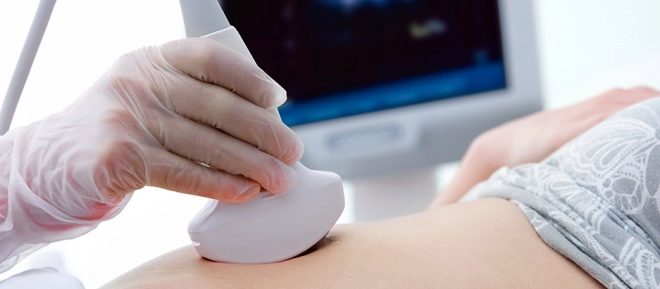
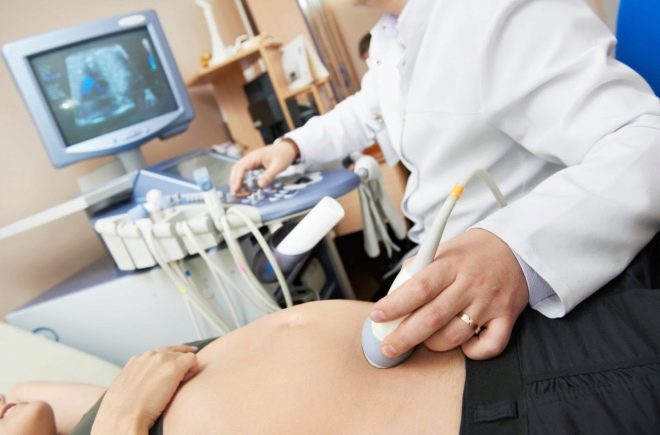
In order to better understand how the crumb feels, the whole procedure is accompanied by continuous observation of him through the ultrasound scanner sensor. The whole process of puncture is monitored, the observation continues for some time after the completion of cordocentesis.
If cordocentesis is performed on a long term, after 29 weeks, additional cardiotocography (CTG) is performed synchronously with ultrasound. This allows you to get a more detailed picture of what is happening inside the uterus.
A long puncture needle is introduced to bypass the placenta, unless otherwise indicated, into the region of the umbilical cord and placenta. For manipulations, special devices are used in which the puncture adapter is connected with an ultrasound sensor, the needle is located in one doctor's hand, and the sensor in the other.
Sometimes cordocentesis is performed by a two-needle method, while amniotic fluid is also taken. The sequence of actions involves the primary sampling of amniotic fluid, and then attaching the second needle to move it to the umbilical vessels and take cord blood for analysis. With the single needle method, there is one needle for taking water and cord blood.
About a day or more, if circumstances so require the woman will be under the supervision of doctors, observing bed rest. After that, she can go home and wait for the results from the genetic laboratory. And here the most important question is how long it will take.
Cordocentesis is one of the fastest methods of invasive diagnostics, for it does not need to grow anything from a sample in an incubator, because blood is the finished material. The study takes no more than one and a half weeks.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparing for cordocentese in advance is not necessary.From the future mother is not required neither dieting nor other preliminary measures, except for the delivery of mandatory tests for this case. They are discharged immediately after the decision on cordocentesis is taken, a woman must surrender them before the day of planned manipulation.
It is usually recommended to carry out a standard "set" of laboratory tests - urine and blood tests, blood for RW and HIV status, hepatitis B and C, and vaginal secretions for the determination of microflora.
After hospitalization, an expert ultrasound is first conducted, the task of which is establish the location of the baby, placenta, umbilical cord.
If the “baby seat” is located on the back wall, cordocentesis will be longer and more difficult, this will require a certain experience from the doctor in order not to injure the baby with a needle. Therefore, tactics and strategy is determined by the doctor in advance on the basis of a detailed ultrasound.
Diagnostic capabilities
The possibilities of cordocentesis are wide. The procedure allows to determine with great accuracy Does the child have one of the following pathologies:
- Chromosomal abnormalities associated with the violation of the number of chromosomes in a particular pair. An inappropriate number of chromosomes in 21 pairs leads to Down syndrome, in 18 pairs - to Edwards syndrome, in 13 pairs - to Patau syndrome, etc. Karyotyping allows you to detect a mixed karyotype of the fetus, a double or threefold set of chromosomes.
- Hereditary diseases that are not associated with chromosomal disruptions. About thousands of such diseases are known in medicine, and about 950 can be detected from this amount using even the most accurate methods. These are the most common cystic fibrosis, Duchenne dystrophy, chronic granulomatosis, “royal disease” - hemophilia, etc.
- Severe Rhesus-Conflict, during which the child could develop a GBP (hemolytic disease). If the Rh factors (less often the blood type) of the mother and the child are different, and the mother is Rh-negative, then the beginning of the immune conflict in which the antibodies in the mother’s blood literally seek to destroy the red blood cells of the fetus, the blood test for antibody titer initially says.
- It is impossible to confirm the PFS even on ultrasound, although an experienced diagnostician can see some signs of a conflict. To give an exact answer, how severe is the condition of the child, can only cordocentesis.
- Cord blood will determine the group and Rh factor of the child, find out what the level of bilirubin, whether the child has hemolytic disease and in what form it occurs.
Intrauterine infections
If the result of the analysis confirms that the child has a certain pathology, then this is considered to be quite reliable, but if the result of cordocentesis refutes the suspicions, then there is no guarantee that the baby is 100% healthy, alas, not all genetic pathologies known to medicine .
However, 100% health guarantees are not provided by any diagnostics., and even after delivery the question of the health of the crumbs may remain open.
When is the diagnosis contraindicated?
Like any other diagnostic procedure, cordocentesis has certain contraindications, in the presence of which the diagnosis will not be performed by a woman:
- The examination is temporarily postponed due to any infectious diseases in the expectant mother, with an increase in her body temperature, with exacerbation of chronic diseases, and it does not matter what organs or systems are affected.
- The procedure can not be carried out when a woman has dermatological, infectious or other skin lesions on the abdomen, especially in the place where the puncture is supposed to be done. First, the woman will have to undergo treatment and get rid of skin ailments.
- Cordocentesis can not be done if a woman is diagnosed with a threat of miscarriage.This is not only bloody or blood-like discharge from the vagina, but also signs that only doctors see - on ultrasound this is a thickening and thickening of the uterine wall, a partial detachment of the placenta, on a “manual” examination - smoothing and shortening the cervix.
- If a woman has problems with the cervix, it is short or long, her inner or outer pharynx is slightly opened, the woman is not only threatened with miscarriage, but also has cervical insufficiency, cordocentesis is contraindicated.
- It is impossible to carry out an invasive diagnosis with placenta previa, which is complete.
- Tumors, cysts, uterine fibroids are also a full contraindication to umbilical cord puncture.
Possible complications
The probability of complications during cordocentesis exists. A woman warned about them in advance. And only after she knows about all the theoretically possible consequences, she will be offered to sign an informed consent to the procedure or the rejection of it.
There is a popular opinion among people that invasive diagnostics is very dangerous for a child, and such manipulations almost through one end in miscarriage and death of a baby.
In fact damage to invasive diagnostic procedures is greatly exaggerated. Indeed, the risk that fetal membranes will be infected as a result of puncture is the same as the risk of subsequent miscarriage, but according to official medical statistics, it is about 5%.
In reality, miscarriage occurs in about 1.5% -2% of cases. The rest of the women manage to provide timely and proper medical care and end up with pregnancy.
Among other possible complications of cordocentesis are:
- Post-traumatic bleeding caused by exposure to the umbilical cord during the puncture. If puncture adapters with large-diameter needles were used, this probability increases. If the bleeding lasts no more than a few minutes after the end of the manipulation, this is considered normal. Longer bleeding requires urgent, skilled care.
- The formation of hematomas at the puncture site. This may establish an ultrasound scan, which will be conducted a little later. Do not be afraid, because small hematomas do not interfere with the development and growth of the baby, the functions of the placenta are not impaired.
- The blood of the child during cordocentesis and in the first minutes after it can enter the maternal bloodstream. This may cause an immune conflict in the mother.
- The deterioration of the child's well-being. This complication has the physiological feature of all vessels, including the umbilical cord, to the spasm during injury.
When the umbilical cord vessels are punctured, a spasm of the entire bloodstream develops, as a result, the child may begin to experience an acute lack of oxygen.
On ultrasound or CTG, this is expressed in bradycardia - baby's heart starts to beat slower. Most often, the child's body can compensate for this lack of oxygen.
If before future cordocentesis, the future mom was diagnosed with placental insufficiency, fetal hypoxia, such physiological spasms can cause serious disturbances.
The risks of an adverse outcome increase if the woman hid any chronic diseases from the doctor, if a preliminary study on ultrasound was performed poorly, and if the qualifications of the doctor performing cordoenthesis leave much to be desired.
The shorter the gestation period at the time of puncture, the higher the likelihood of severe tragic consequences - the death of the baby.
The consequences can be severe if during cordocentesis there occurs a mixing of the blood of the mother and the fetus, different in Rhesus accessories during an already existing conflict. Maternal immunity will immediately respond to this by releasing a huge amount of antibodies, and the child may die in utero or be born with severe toxic lesions of the liver and brain.
Infrequently, but it happens that a long puncture needle mechanically wounds the fetus, causes rupture of the amniotic fluid. Cordocentesis is more dangerous for the child than for his mother, and therefore a woman is always given time to weigh all the risks and agree or disagree on an invasive procedure.
Probability of error
The possibility of error in cordocentesis is small, but it is present and is associated primarily with the human factor. If, for some reason, the doctor makes technical mistakes during the puncture, then the analysis may not include pure fetal blood, but a mixture of his blood and maternal blood, and then the results will not be reliable. If the fence is carried out correctly and correctly, then the accuracy of diagnosis is about 99%.
The erroneous test is mostly false negative (the fetus has a disease, but the analysis has not confirmed it), may be due to the use of poor quality or expired reagents by the laboratory technicians. This percentage of errors does not exceed 0.02%.
Alternative
Prenatal DNA diagnostics of chromosomal pathology is an ideal alternative to invasive methods. The analysis is safe for the fetus and pregnant, it is done from the 9th week of pregnancy.
Simply donating your venous blood, you can find out the risk of developing Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, as well as the sex of your unborn child.
The analysis is based on the fact that 5-10% of fetal DNA is circulating in the mother’s blood, and this test extracts fetal DNA from the blood of a pregnant woman, which is analyzed using the latest technology. This analysis is paid and, as a rule, costs more than 30 000 r.
Reviews
Those who are just deciding whether or not to agree to the passage of cordocentesis should be more attentive to the feedback that pregnant women have left on various ladies 'and parents' forums.
Very often, you may encounter reviews that the procedure was wasted - the analysis failed, because the researchers did not manage to “grow some cells” in the laboratory. Obviously, the moms who wrote such reviews confused amniocentesis and cordocentesis, that is, they did not really understand what and how they were taken for analysis.
During amniocentesis, the epithelial cells of the baby, which are present in the amniotic fluid, have indeed been cultivated in the laboratory for quite a long time, and there are no guarantees that the number of cells in the waters taken for analysis will be sufficient, that they will grow in nutrient media. When cordocentesis, nothing is grown anywhere. The blood is simply sent for genetic analysis.
Therefore, to obtain the result “analysis failed” with this method does not seem to be any possibility. Given this confusion, it will be easier to figure out which reviews give a more accurate picture of the procedure.
In general, pregnant women argue that everything goes smoothly. The most embarrassing moment is waiting for a puncture, it is psychologically difficult for most expectant mothers. The study lasts, according to women, not for long - from 10 to 20 minutes. After a day it is quite possible to go home.
The results of the analysis, according to reviews, are different - both negative and, alas, positive, when the disease is indeed confirmed. There are fewer women who then decide to leave the child than those who decide to use the legal right to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons. This is a difficult and difficult decision, to judge someone for this or that choice is a thankless task.
The main thing is that the analysis, according to the women themselves, makes it possible to bring clarity, since other methods only plagued by conjectures from which the nervous systems of both the mother and the fetus suffered.
For information on how cordocentesis occurs, see the next video.