Table of probability of Rh-conflict during pregnancy, the consequences and prevention
Childbearing time is one of the most beautiful in a woman’s life. Every future mother wants to be calm for the health of the baby, to enjoy the waiting period of addition. But every tenth lady, according to statistics, has Rh-negative blood, and this fact worries both the pregnant woman herself and the doctors who observe her.
What is the possibility of occurrence of rhesus-conflict mother and baby, and what the danger lies, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
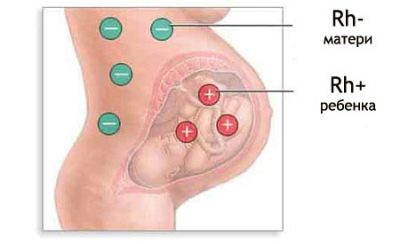
When a woman and her future karapuz have different blood counts, an immunological incompatibility can begin, it is called the Rh-conflict. The representatives of mankind, who have a Rh factor with a +, have a specific protein D, which contains red blood cells. A person with Rh has no negative value for this protein.
Scientists still do not know for sure why some people have a specific rhesus macaque protein, while others do not. But the fact remains that about 15% of the world's population have nothing in common with macaques, their Rh factor is negative.
There is a constant exchange between the pregnant woman and the child through the uteroplacental blood flow. If the mother has a negative Rh factor, and the baby has it positive, then protein D, which enters her body, is for the woman nothing more than an alien protein.
Mother's immunity very quickly begins to respond to the uninvited guest, and when protein concentration reaches high values, rhesus conflict begins. This is a merciless war that the immune defense of a pregnant woman declares to the child as a source of foreign protein-antigen.
Immune cells begin to destroy the baby's red blood cells with the help of special antibodies that it produces.
The fetus suffers, the woman experiences sensitization, the consequences can be quite sad, even to the death of the baby in the womb, the death of the baby after the birth or birth of a disabled child.
Rhesus-conflict can happen in a pregnant woman with Rh (-), if the crumb inherited father's blood characteristics, that is, Rh (+).
Much less often, incompatibility is formed according to such an indicator as blood type, if the man and woman groups are different. That is, a pregnant woman whose own Rh factor has positive values has nothing to worry about.
There is no reason to worry and families with the same negative Rh, but this coincidence happens infrequently, because among the 15% of people with "negative" blood - the vast majority of the fair sex, men with such characteristics of blood, only 3%.
Own hematopoiesis in the tots in the womb begins at about 8 weeks of gestation. And already from this moment in the maternal blood tests a small number of fetal red blood cells is determined by laboratory. It is from this period that the possibility of the Rhesus conflict appears.
Probability tables
From the point of view of genetics, the probability of inheritance of the main characteristics of the blood - the group and the Rh factor from the father or mother is estimated equally to 50%.
There are tables that allow you to assess the risks of Rh-conflict during pregnancy. And in time, weighted risks give doctors time to try to minimize the consequences. Unfortunately, medicine cannot completely eliminate the conflict.
Rh factor
Daddy rhesus factor | Mom rhesus factor | Fetus rhesus factor | Will there be a conflict |
Positive (+) | Positive (+) | Positive (+) | Not |
Positive (+) | Negative (-) | Positive or negative with a probability of 50% | Conflict probability - 50% |
Negative (-) | Positive (+) | Positive or negative with a probability of 50% | Not |
Negative (-) | Negative (-) | Negative (-) | Not |
By blood type
Dad's blood type | Mom's blood type | Baby blood type | Will there be a conflict |
0 (first) | 0 (first) | 0 (first) | Not |
0 (first) | A (second) | 0 (first) or A (second) | Not |
0 (first) | B (third) | 0 (first) or B (third) | Not |
0 (first) | AB (fourth) | A (second) or B (third) | Not |
A (second) | 0 (first) | 0 (first) or A (second) | Conflict probability - 50% |
A (second) | A (second) | A (second) or 0 (first) | Not |
A (second) | B (third) | Any (0, A, B, AB) | Conflict probability - 25% |
A (second) | AB (fourth) | 0 (first), A (second) or AB (fourth) | Not |
B (third) | 0 (first) | 0 (first) or B (third) | Conflict probability - 50% |
B (third) | A (second) | Any (0, A, B, AB) | Conflict probability - 50% |
B (third) | B (third) | 0 (first) or B (third) | Not |
B (third) | AB (fourth) | 0 (first), A (second) or AB (fourth) | Not |
AB (fourth) | 0 (first) | A (second) or B (third) | The probability of conflict is 100%. |
AB (fourth) | A (second) | 0 (first), A (second) or AB (fourth) | Conflict probability - 66% |
AB (fourth) | B (third) | 0 (first), B (third) or AB (fourth) | Conflict probability - 66% |
AB (fourth) | AB (fourth) | A (second), B (third) or AB (fourth) | Not |
Causes of conflict
The likelihood of the development of rhesus conflict strongly depends on how and how the first pregnancy of the woman ended.
Even a “negative” mother can safely give birth to a positive baby, because during the first pregnancy the woman’s immunity does not have time to develop a killing amount of antibodies to protein D. The main thing is that before pregnancy she is not transfused, not taking into account the rhesus, as sometimes happens in an emergency life saving situations.
If the first pregnancy ended in miscarriage or abortion, then the likelihood of Rh-conflict during the second pregnancy is significantly increased, since the woman’s blood already has antibodies ready for an attack at the earliest term.
In women who suffered a cesarean section during first birth, the probability of conflict during the second pregnancy is 50% higher compared with women who gave birth to a firstborn child naturally.
If the first birth was problematic, the placenta had to be separated manually, there were bleeding, then the probability of sensitization and conflict in the subsequent pregnancy also increases.
Danger for the future mother with a negative Rh factor in blood and diseases in the period of carrying a baby. Influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, preeclampsia, diabetes in history can provoke a violation of the structure villi of the chorion, and mother's immunity will begin to produce antibodies harmful to the baby.
After childbirth, the antibodies that have been developed in the process of carrying the crumbs do not disappear anywhere. They represent a long-term memory of immunity. After the second pregnancy and childbirth, the number of antibodies becomes even greater, as after the third and subsequent ones.
Danger
The antibodies that maternal immunity produces are very small in size, they can easily penetrate the placenta into the bloodstream of the crumbs. Once in the baby’s blood, the protective cells of the mother begin to inhibit the function of the blood formation of the fetus.
The child suffers, suffers from a lack of oxygen, since the decomposing red blood cells are the carriers of this vital gas.
In addition to hypoxia, fetal hemolytic disease may develop.and later the newborn. It is accompanied by severe anemia. The fetus increases the internal organs - the liver, spleen, brain, heart and kidneys. The central nervous system is affected by bilirubin, which is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells and is toxic.
If the doctors do not start taking measures in time, the baby may die in utero, be born dead, be born with severe damage to the liver, central nervous system, and kidneys. Sometimes these lesions are incompatible with life, sometimes they lead to deep lifelong disability.
Diagnosis and symptoms
The woman herself cannot feel the symptoms of the developing conflict of her immunity with the blood of the fetus. There are no such symptoms, according to which the future mother could guess about the destructive process that takes place inside her. However, laboratory diagnostics at any time can detect and track the dynamics of the conflict.
To do this, a pregnant woman with Rh-negative blood, regardless of which group and Rh blood factor from the father, take a blood test from a vein for the content of antibodies in it. The analysis is done several times in the course of pregnancy; the period from 20 to 31 weeks of gestation is considered especially dangerous.
About how severe is the conflict, said antibody titer obtained as a result of laboratory research. The doctor also takes into account the degree of fetus maturity, because the older the baby is in the womb, the easier it is for him to resist an immune attack.
In this way, a titer of 1: 4 or 1: 8 for a period of 12 weeks of pregnancy is a very alarming indicatorand a similar antibody titer for a period of 32 weeks will not cause a panic in the doctor.
When a titer is detected, the analysis is done more often in order to observe its dynamics. In severe conflict, the titer is growing rapidly - 1: 8 can turn into 1: 16 or 1: 32 in a week or two.
A woman with antibody titers in the blood will have to visit the ultrasound room more often. By ultrasound, it will be possible to monitor the development of the child, this method of research provides sufficiently detailed information about whether the child has hemolytic disease, and even about what form it has.
In an edematous form of hemolytic disease of the fetus, an ultrasound will show an increase in the size of the internal organs and the brain, the placenta thickens, the amount of amniotic fluid also increases and exceeds normal values.
If the estimated fetal weight is 2 times the norm, this is an alarming sign. - fetal edema is not excluded, which may be fatal in the womb.
Hemolytic disease of the fetus, associated with anemia, cannot be seen on ultrasound, but can be diagnosed indirectly on CTG, since the number of fetal movements and their character will indicate the presence of hypoxia.
About lesions of the central nervous system will be known only after the birth of the child, this form of hemolytic disease of the fetus can lead to a lag in the development of the baby, to the loss of hearing.
Diagnostics doctors in the antenatal clinic will be engaged from the very first day of setting a woman with a negative Rh factor on the account. They will take into account how many pregnancies were, how they ended, whether children with hemolytic disease were already born. All this will enable the doctor to suggest a possible likelihood of a conflict and predict its severity.
During the first pregnancy, a woman will donate blood once every 2 months, at the second and subsequent ones - once a month. After 32 weeks of pregnancy, analysis will be done once every 2 weeks, and from week 35 - every week.
If there is an antibody titer that may occur at any time after 8 weeks, additional research methods may be prescribed.
With a high titer that threatens the life of a child, a cordocentesis or amniocentesis procedure may be prescribed. Procedures carried out under the control of ultrasound.
When the amniocentesis is injected with a special needle, a certain amount of amniotic water is taken for analysis.
When cordocentesis, blood is taken from the umbilical cord.
These analyzes make it possible to judge which blood group and Rh factor are inherited by a baby, how severely his red blood cells are affected, what the level of bilirubin in the blood, hemoglobin, and with 100% probability determine the sex of the child.
These invasive procedures are voluntary, women are not forced to do so. Despite the modern level of development of medical technologies, such intervention as cordocentesis and amniocentesis can still cause miscarriage or premature birth, as well as the death or infection of a child.
An obstetrician-gynecologist, who is leading her pregnancy, will tell the woman about all the risks associated with carrying out procedures or refusing them.
Possible effects and forms
Rhesus-conflict is dangerous both in the period of carrying a baby, and after his birth. The disease with which such children are born is called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). Moreover, its severity will depend on the amount of antibodies that the blood cells of the baby attacked during pregnancy.
This disease is considered severe, it is always accompanied by a breakdown of blood cells, which continues after birth, edema, jaundice of the skin, severe intoxication with bilirubin.
Edematous
The most severe is the edematous form of HDN. With her, a peanut comes into the world very pale, as if “bloated”, edematous, with multiple internal edemas. Such crumbs, unfortunately, in most cases are born already dead or die, despite all the efforts of resuscitation specialists and neonatologists, they die as soon as possible from several hours to several days.
Icteric
The icteric form of the disease is considered more favorable. In a couple of days after their birth, such babies “acquire” a rich yellowish complexion, and this jaundice has nothing to do with common physiological jaundice of newborns.
The baby has a slightly enlarged liver and spleen, blood tests show the presence of anemia. The level of bilirubin in the blood is growing rapidly. If doctors can not stop this process, the disease can go into nuclear jaundice.
Nuclear
A nuclear type of HDN is characterized by lesions of the central nervous system. The newborn may begin convulsions, he can involuntarily move his eyes. The tone of all muscles is reduced, the child is very weak.
With the deposition of bilirubin in the kidney, the so-called bilirubin infarction occurs. A strongly enlarged liver cannot normally perform the functions assigned to it by nature.
Forecast
In the prognosis for HDN, doctors are always very careful, because it is almost impossible to predict how damage to the nervous system and brain will affect the development of the crumbs in the future.
Children are given detoxification infusions under resuscitation, and very often there is a need for a replacement transfusion of blood or donor plasma.If for 5-7 days the child does not die from paralysis of the respiratory center, then the predictions change to more positive ones, however, and they are rather conditional.
After suffering a hemolytic disease of the newborn, the children suck poorly and sluggishly, they have reduced appetite, sleep is disturbed, and there are neurological abnormalities.
Quite often (but not always) in such children there is a significant lag in mental and intellectual development, they are sick more often, and hearing and vision impairments can be observed. Cases of anemic hemolytic disease end most successfully, after the level of hemoglobin in the blood of the crumbs can be raised, it develops quite normally.
The conflict, which has developed not because of the difference of Rh factors, but because of the difference in blood groups, proceeds more easily and usually does not have such devastating effects. However, even with this incompatibility, there is a 2% chance that the baby after birth will have serious enough disorders of the central nervous system.
The consequences of the conflict for the mother are minimal. She cannot feel the presence of antibodies in any way, difficulties can arise only during the next pregnancy.
Treatment
If a pregnant woman has a positive antibody titer in the blood, this is not a reason for panic, but a reason to start therapy and to be seriously treated by the pregnant woman.
It is impossible to save a woman and her baby from such a phenomenon as incompatibility. But medicine can minimize the risks and effects of maternal antibodies on a baby.
Three times during pregnancy, even if no antibodies appear in the gestation process, women are prescribed treatments. At 10-12 weeks, at 22-23 weeks and at 32 weeks, the expectant mother is recommended to take vitamins, iron supplements, calcium supplements, metabolism enhancers, and oxygen therapy.
If up to 36 weeks of the gestational term, the titers did not show up, or they are low, and the child’s development does not cause the doctor’s concern, then the woman is allowed to give birth naturally by herself.
If the captions are high, the child’s condition is severe, then delivery can be carried out ahead of time by cesarean section. Doctors are trying to support the pregnant woman with medicines before the 37th week of pregnancy, so that the child has the opportunity to “ripen”.
Such an opportunity, unfortunately, is not always available. Sometimes you have to make a decision about an earlier cesarean section to save the toddler's life.
In some cases, when the baby is clearly not ready to come into this world, but it is also very dangerous for him to remain in the mother’s womb, they conduct intrauterine blood transfusions to the fetus. All these actions are performed under the control of an ultrasound scanner, each movement of the hematologist is calibrated so as not to harm the baby.
In the early stages, other methods of preventing complications can be applied. So, there is a method of filing a pregnant piece of the skin of her husband. The skin graft is usually implanted on the lateral surface of the chest.
While the immunity of the woman throws all the forces to reject the skin fragment that is foreign to itself (several weeks ago), the immunological load on the child is somewhat reduced. The effectiveness of this method does not abate scientific debates, but the feedback from women who have gone through such procedures is quite positive.
In the second half of pregnancy, with established conflict, the expectant mother can be given plasmapheresis sessions, this will slightly reduce the amount and concentration of antibodies in the mother's body, respectively, the negative load on the baby will also temporarily decrease.
Plasmopheresis should not frighten a pregnant woman, there are not so many contraindications to it. First, it is SARS or other infection in the acute stage, and, secondly, the threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
There will be about 20 sessions. In one procedure, approximately 4 liters of plasma are cleaned.Together with the infusion of donor plasma, protein preparations are injected, which are necessary for both mother and baby.
The babies who have suffered hemolytic disease are shown regular check-ups by a neurologist, massage courses in the first months after birth to improve muscle tone, as well as vitamin therapy courses.
Prevention
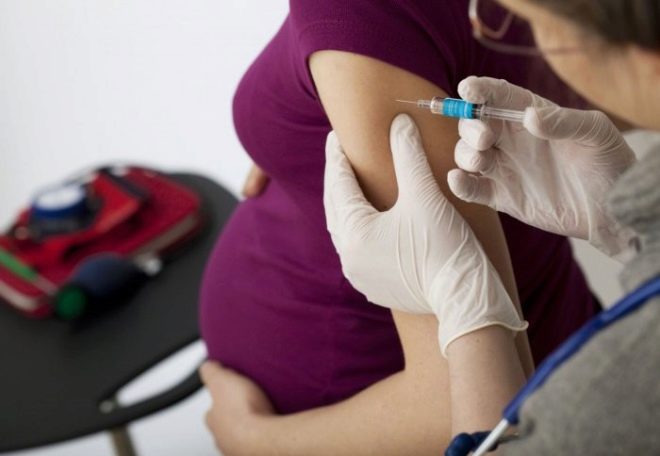
A pregnant woman at the 28th and 32th week is given a kind of vaccination - anti-rhesus immunoglobulin is administered. The same drug must be administered to the woman in labor after the birth no later than 48-72 hours after the birth of the baby. This reduces the likelihood of conflict in subsequent pregnancies up to 10-20%.
If a girl has a negative Rh, she should know about the consequences of abortion during the first pregnancy. So the fair sex is desirable keep the first pregnancy at any cost.
Blood transfusion without taking into account the donor's and recipient's Rh accessories is not acceptable, especially if the recipient has his own Rh with a “-” sign. If such a transfusion takes place, an anti-rhesus immunoglobulin should be administered to the woman as soon as possible.
A complete guarantee that there will be no conflict can only be given by a Rh-negative man, moreover, preferably with the same blood type as his chosen one. But if this is not possible, you should not postpone the pregnancy or abandon it only because of the fact that men and women have different blood. In such families, planning a future pregnancy plays an important role.
A woman who wants to become a mother needs to undergo blood tests for detection of antibodies to protein D even before the onset of an “interesting situation.” If antibodies are detected, this does not mean that the pregnancy will have to be interrupted or you cannot be pregnant. Modern medicine does not know how to eliminate the conflict, but knows how to minimize its consequences for the child.
The introduction of anti-rhesus immunoglobulin is important for women in whose blood there are no antibodies, not sensitized. They need to make such an injection after an abortion, after even a small bleeding during pregnancy, for example, with a slight detachment of the placenta, after surgery for ectopic pregnancy. If there are already antibodies, then you should not expect any special effect from vaccination.
Common Questions
Can I breastfeed?
If a woman with a negative rhesus born a baby with a positive Rh factor, and there is no hemolytic disease, then breastfeeding is not contraindicated.
Babies who have experienced an immune attack and were born with hemolytic disease of the newborn, for 2 weeks after the introduction of the mother of immunoglobulin is not recommended to eat mother's milk. In the future, the decision on breastfeeding is taken by neonatologists.
In severe hemiliac disease, breastfeeding is not recommended. To suppress lactation, women after childbirth are prescribed hormones that suppress milk production in order to prevent mastopathy.
Is it possible to endure the second child without conflict if there was a conflict during the first pregnancy?
Can. Provided that the child inherits a negative Rh factor. In this case, there will be no conflict, but the antibodies in the mother’s blood can be detected during the entire gestation period, and in sufficiently high concentrations. They will not affect the baby with Rh (-), and you should not worry about their presence.
Before getting pregnant again, mom and dad should visit genetics, which will give them comprehensive answers about the likelihood of their children’s inheritance of a particular blood characteristic.
Dad's Rh factor unknown
When a future mother is registered at the antenatal clinic, immediately after the negative rhesus is detected, the future baby’s father is also invited to the consultation for a blood test. Only in this way the doctor can be sure that he knows the exact data of the mother and father.
If the dad's rhesus is unknown, and it is impossible to invite him to donate blood for some reason, if the pregnancy came from IVF donor sperm, then women will be tested for antibodies a little more oftenthan other pregnant women with the same blood. This is done in order not to miss the moment of the beginning of the conflict, if it takes place.
And the doctor's offer to invite her husband to donate blood for antibodies is a reason to change the doctor to a more competent specialist. Antibodies in the blood of men does not happen, because they do not become pregnant and in any way physically do not contact the fetus during the pregnancy of the wife.
Is there an effect of fertility?
There is no such connection. The presence of a negative rhesus still does not mean that it will be difficult for a woman to become pregnant.
The level of fertility is influenced by completely different factors - bad habits, caffeine abuse, overweight and diseases of the urogenital system, burdened history, including a large number of abortions in the past.
Medical or vacuum abortion is not dangerous for abortion in the first pregnancy in an Rh-negative woman?
This is a common misconception. And, unfortunately, often this statement can be heard even from medical professionals. The method of abortion does not matter. Whatever it is, the child's red blood cells still enter the mother’s bloodstream and cause the formation of antibodies.
If the first pregnancy ended in an abortion or miscarriage, how high are the risks of conflict in the second pregnancy?
In fact, the magnitude of such risks is a rather relative concept. No one can say with precision to percent whether there will be a conflict or not. However, doctors have certain statistics that estimate (approximately) the likelihood of sensitization of the female body after an unsuccessful first pregnancy:
- miscarriage on a short term - + 3% to a possible future conflict;
- artificial interruption of pregnancy (abortion) - + 7% to the probable future conflict;
- ectopic pregnancy and surgery to eliminate it - + 1%;
- delivery in time by living fetus - + 15-20%;
- delivery by caesarean section - + 35-50% to a possible conflict during the next pregnancy.
Thus, if a woman’s first pregnancy ended in an abortion, the second - a miscarriage, then during the carrying of the third, the risk is estimated at about 10-11%.
If the same woman decides to give birth to another baby, provided that the first birth went well in a natural way, then the probability of the problem will be more than 30%, and if the first birth ended with a cesarean section, then more than 60%.
Accordingly, any woman with a negative Rh factor who conceived to become a mother once again can weigh the risks.
Does the presence of antibodies always indicate that a child will be born sick?
No, this is not always the case. The baby is protected by special filters that are in the placenta, they partially inhibit aggressive maternal antibodies.
A small amount of antibodies will not cause much harm to the child. But if the placenta is aging prematurely, if the amount of water is small, if the woman has become ill with an infectious disease (even an ordinary ARVI), if she takes medicine without control from the doctor, then the probability of reducing the protective functions of the placenta filters increases significantly and the risk of giving birth to the sick baby will increase .
It should be borne in mind that during the first pregnancy, antibodies, if they appear, have a rather large molecular structure, it can be difficult for them to “penetrate” the protection, but when the pregnancy is repeated, the antibodies are smaller, more mobile, fast and “evil”, therefore the immunological attack becomes more probable.
Does a conflict during pregnancy, despite all the predictions and tables, have two negative parents?
This cannot be excluded, despite the fact that all existing genetic tables and teachings indicate that the probability tends to zero.
One of the three mom-dad-child may be a chimera.Chimerism in people sometimes manifests itself in the fact that once transfused blood of another group or rhesus “takes root”, and a person is the carrier of gene information about two types of blood at once. This is a very rare and unexplored phenomenon, although experienced doctors and it will never be discounted.
Everything related to the issues of genetics is not well understood yet, and any “surprise” can be obtained from nature.
There are several cases in history when a mom with Rh (-) and a dad with similar rhesus had a baby with positive blood and hemolytic disease. The situation requires careful study.
Read more about the likelihood of Rh-conflict during pregnancy, see the following video.