Screening of the second trimester: dates and indicators
It is simply impossible to determine how a fetus grows and develops without a series of studies. A very important medical method for such a diagnosis is screening for the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
What it is?
Doctors call screening a whole range of examinations, which is necessary in order to detect various developmental abnormalities in the fetus, as well as to determine how well it develops in the womb. Pregnancy is a unique period in the life of every woman. At this time, hormonal background changes significantly. This leads to the fact that the basal hormone levels change. Also in the blood may appear specific biochemical markers that indicate the possible development of genetic and chromosomal pathologies.
In each of the periods of childbearing, pathology manifests itself in different ways. They can only be determined by the method of laboratory diagnostics and ultrasound. Appointed such studies obstetrician-gynecologist. The future mommy learns what screening is, usually at the very first visits to the women's clinic. Screening during pregnancy is a recommended procedure. Not all women decide on his passing.
Quite often, only future moms who have any associated diseases of internal organs undergo prenatal screening.
The introduction of prenatal screening in our country occurred relatively recently. The development of such recommendations of doctors led a frightening demographic situation. Doctors note that the introduction of prenatal screening has significantly reduced maternal mortality rates. Thanks to this diagnostic complex, doctors began to identify dangerous genetic anomalies in the very early stages of their formation.
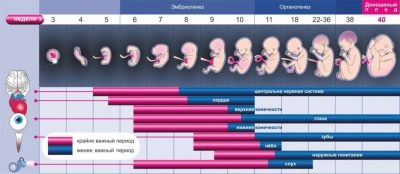
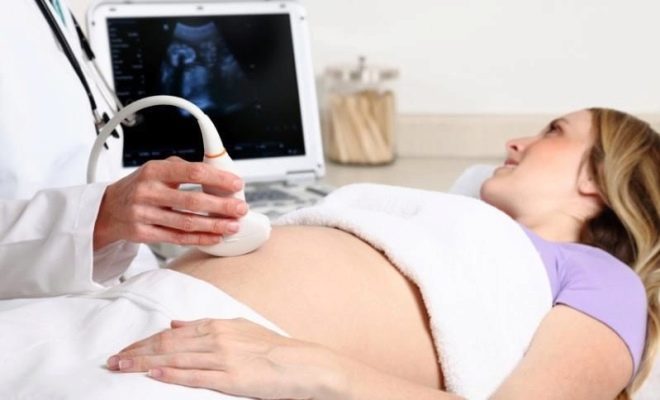
The second trimester is the period when the embryo has moved to the next stage of its development. At this time, the future baby doctors already determine how the fetus. The child continues to undergo differentiation of all vital systems of the body. This time is no less important than the first trimester of pregnancy. Complete second screening includes a set of general clinical and biochemical analyzes, hormonal studies, and is also complemented by the mandatory ultrasound. In some cases, doctors may slightly expand the list of necessary tests.
Quite often, this happens in a situation where any deviations from the norm were found in the expectant mother during the screening of the first trimester of pregnancy.
Many mommies believe that screening can prevent the formation of congenital genetic diseases in their babies. Immediately it is worth noting that, unfortunately, it is not. To prevent the appearance of chromosomal abnormalities in the baby can be at the stage of preparation for pregnancy.
If conception has already occurred, then the formation of a specific genetic disease cannot be affected. However, it is possible to quite often identify certain pathologies with the help of screening.Such dangerous diseases as Down's syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome and many other diseases can be identified with the help of a certain complex of diagnostics, which is carried out during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Screening also allows you to identify various malformations and anomalies of the structure of the tubular bones.
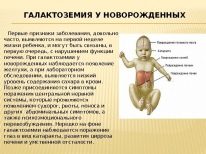
Quite often, these tests also reveal congenital metabolic diseases, such dangerous pathologies include galactosemia, phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis and many others.
Dates
Doctors have established several decreed periods of pregnancy, in which screening is most rational. In each of the trimesters of carrying a baby, there is one such diagnostic complex. Deadlines are determined for all women. There are also certain clinical situations where they can be shifted somewhat.
In this case, the specific dates of screening are determined by the obstetrician-gynecologist who is observing the patient.
In most situations, a complex of studies is carried out at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy. As an exception, screening may be conducted after 21 weeks. Usually this situation occurs when a pregnant woman has any tumors in the ovaries. With these pathologies, hormonal changes significantly. For more accurate biochemical analysis results, screening is delayed by 1–2 weeks.
Many mommies believe that ultrasound needs to be done on the same day as going to the laboratory. To do this is not necessary.
Even a few weeks may pass between the blood tests and the ultrasound examination, this situation is quite normal.
Who should be screened?
Obstetricians and gynecologists recommend passing such a complex to all women carrying babies, but there are certain groups that simply need to be screened. Women who have indications for conducting a study should not miss the complex of prenatal diagnosis. This may lead to the fact that doctors simply do not find out in time about the presence of dangerous pathological conditions in the future mom and her baby. Doctors distinguish several decreed categories of women who need to be screened.
These groups include the following:
- Future moms who have conceived a baby after 35 years;
- Pregnant women with congenital malformations or an aggravated family history of genetic or chromosomal diseases;
- Future moms who have deviations from the norm in tests or by ultrasound during the first pregnancy screening;
- Pregnant women suffering from severe diseases of the internal organs;
- Expectant mothers who have a burdened period of 1 trimester of pregnancy with frequent threats of spontaneous miscarriage;
- Pregnant women who are forced to take immunosuppressive or hormonal drugs for medical reasons while carrying a baby.
If the future mommy during the first screening or later on an ultrasound scan, doctors identify dangerous pathologies of fetal development, then in this case she is sent for additional diagnostics to the perinatal center. There, more experienced doctors conduct an ultrasound examination of the expert level.
In some situations, pregnant women with certain medical conditions are screened only in such perinatal centers.
Training
To obtain reliable and accurate results, the future mommy is very important to properly prepare. A few days before the delivery of biochemical analyzes, she should definitely follow a lipid-lowering diet. It implies a restriction in the daily diet of all fatty and fried foods. Fast food, smoked meats and pickled dishes are also completely excluded. Dinner on the eve of the study must be light. It is optimal if it consists of a protein dish, complemented by a side dish of any cereal.Vegetables and fruits before ultrasound should be limited, they can lead to increased gas formation, and the presence of gas in the stomach will not allow the ultrasound doctor to examine the fetus and all the membranes.
Also, 2-3 days before the ultrasound examination, legumes and all types of cabbage are necessarily excluded. Drinking kvass or carbonated drinks also significantly increases gas generation. It is better that on the eve of the planned testing and ultrasound all the food was as light as possible, but nutritious.
It is very important for a pregnant woman to eat enough protein even before carrying out laboratory tests.
Inaccurate results can result from physical exertion. Doctors have long noticed that a simple climb up the stairs could trigger a change in biochemical parameters. For, so that the results of laboratory studies are accurate, the expectant mom should limit all physical activities. Cleaning an apartment or visiting yoga for pregnant women in this case, it is better to postpone for several days after the screening.
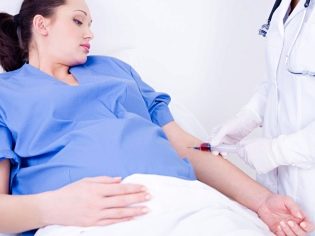
Biochemical tests should be taken necessarily on an empty stomach. Some experts allow future moms to drink some water before researching. Breakfast before going to the laboratory should not be.
To be tested in the morning. Studies conducted in the evening give less truthful results.
Currently, doctors recommend that future mothers should limit all highly allergenic products before passing biochemical tests. This is due to the fact that every day there is an increasing amount of scientific research, which suggests that such food may affect obtaining reliable results.
For a week before testing for screening for the 2nd trimester, it is better to exclude all citrus fruits, seafood, chocolate and honey from your menu.
Test Standards
Biochemical screening for the 2nd trimester has a very important diagnostic value. The results of the obtained blood tests are not a diagnosis at all, they only help the doctors to orient themselves in the possible pathologies of the course of pregnancy and abnormal development of the fetus at this stage of its intrauterine development. HCG is an important laboratory marker that allows you to identify certain "hidden" pathological conditions. Its dynamics throughout the pregnancy varies. In the first weeks of fetal development, the concentration of this hormone in the blood is maximal. Then over time it begins to decline.
Before giving birth, the concentration of hCG in the blood rapidly decreases.
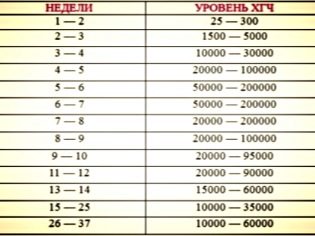
At the 16th week of pregnancy, normal blood counts for hCG reach 4.7-50 ng / ml. By week 20, this value already rises above 5.3 ng / ml. Quite often, an increase in hCG occurs in multiple pregnancies. A significant excess of this indicator may indicate a possible development of Down's disease or Edwards syndrome.
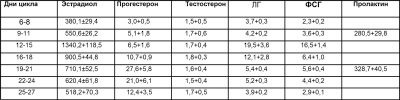
Alphafetoprotein is another specific pregnancy hormone that is used to assess the intrauterine development of a future baby. It is formed by the gastrointestinal tract and liver of the fetus. By the end of 10-11 weeks, it begins to flow through the general uteroplacental blood flow system and into the maternal organism. Normal values of this indicator in the 16-19 week of pregnancy are 15-95 units / ml.
Free estradiol is the third indicator that shows how well a particular pregnancy goes. To a greater extent, it reflects the functional ability of the placenta. The normal course of pregnancy is accompanied by a gradual increase in the hormone in the blood of the expectant mother. By week 16, the values of this hormone are 1.17-5.5 ng / ml.
To assess the risk of various chromosomal abnormalities, doctors are increasingly prescribing non-invasive haemophilus to expectant mothers. It allows you to identify fetal DNA and assess the presence of any genetic diseases.Significant disadvantages of this study are the possibility of conducting it only in the largest Russian cities and the high cost.
Such studies are prescribed only under strict genetic medical indications.
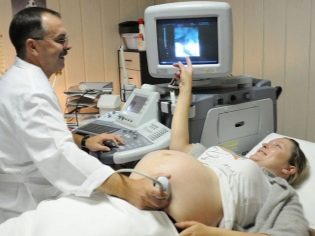
Interpretation of ultrasound results
The second trimester of pregnancy is a time when it is already possible to determine not only the outlines of the body of the fetus, but also to evaluate the work of its internal organs. For this, doctors have developed a number of special indicators. They help doctors conduct a more comprehensive assessment. Expectant mothers should remember that the conclusion of an ultrasound is not a diagnosis. It only describes all the visual changes that the specialist saw during this study.
Fetometry is one of the methods of ultrasound diagnostics, with the help of which the doctor determines the size of the main anatomical elements of the fetus. During the study, the doctor takes measurements of the head, shoulders, limbs of the future baby. Also necessarily determined and his presentation. However, it is worth noting that quite often babies begin to actively move in the third trimester of pregnancy. This contributes to the fact that the previa can change.
To assess the normal development of the child’s skeleton, doctors use the following indicators:
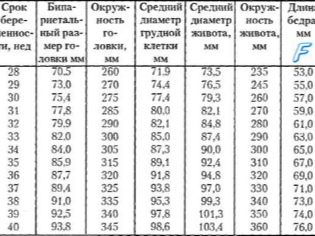
- Biparietal fetal head size. At week 16 it is 26-37 mm, and by week 20 it changes to 39-56 mm.
- Frontal-nuchal size. At week 16, its values are 32-49 mm, at week 20 they change to 53-75 mm.
- Femur Length. At the 16th week of pregnancy, the indicator values are 13-23 mm. By week 20, they increase to 23-38 mm.
- The diameter of the chest. At the 16th week of pregnancy, the normal values of the index are 11-21mm. By week 20, they increase to 21-34 mm.
- Humerus length. At the 16th week of pregnancy, the normal values of the index are 13-23 mm. By week 20, they increase to 24-36mm.
- Chest circumference. At the 16th week of pregnancy, the normal values of the index are 112-136 mm. By week 20, they increase to 154-186 mm.
- Abdominal circumference. At the 16th week of pregnancy, the normal values of the index are 88-116 mm. By week 20, they increase to 124-164 mm.
The next step in assessing the development of the fetus is to determine the anatomy of its internal organs. To do this, the specialist determines the boundaries and parameters of the liver, stomach, intestines, heart, gallbladder. At this time of development of the fetus, it is already possible to evaluate its heartbeat. This indicator is also quite important for the assessment of intrauterine development.
It is very important to evaluate the parameters of the fetal brain on 2 ultrasound screening. The normal size of the cerebellum at week 16 is 12-15 mm. By the end of the 20th week, it is already 18-22 mm. Also during the study, an ultrasound specialist evaluates the size of the lateral ventricles and cisterns. The values of these indicators at this stage of development of the baby are 10-11 mm.
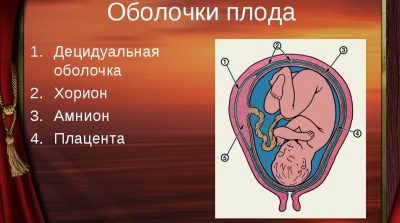
Fetal membranes are very important anatomical structures. They protect the fetus from various external factors. In the second trimester, determine the index of amniotic fluid, also this indicator is called the amniotic fluid index. It helps doctors assess whether a pregnant woman has low fluid levels.
Normally, in the 16th week of pregnancy, the amniotic fluid index should be 73-201 mm.
In more detail about what the second trimester screening includes, you can find out by watching the following video.