Uterus cervix during pregnancy: the standard of weekly length in the table and causes of deviations
Examination of the state of the cervix is an important diagnostic tool of the obstetrician-gynecologist. The condition of this part of the main reproductive female organ can speak of the well-being or distress of developing pregnancy, the timing of gestation, and it is possible to make predictions about upcoming birth. About what should be the cervix during pregnancy, and why there may be deviations, we will tell in this material.
What it is
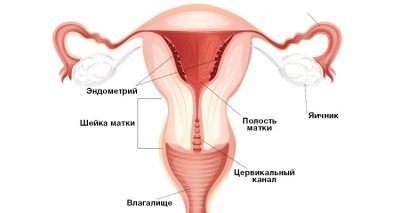
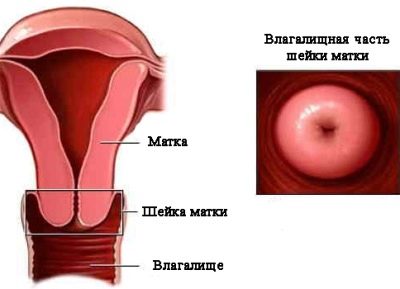
Cervix uteri is the Latin name for the cervix, the lower part of the main reproductive organ of women. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, the lower part of the neck goes into the vagina, and the upper part communicates with the uterus.
Nature has assigned important functions to this cylindrical part of the uterus.
Before pregnancy, the neck plays the role "Gatekeeper" tightly closing the entrance for infection, germs and even sperm, if they arrive at the wrong time. The mucus completely covers the cervical canal.
Once a month the neck arranges an “open day” - this happens before ovulationwhen under the influence of hormones mucus becomes fluid, freeing passage to the cervical canal for male germ cells.
If the pregnancy has occurred, the cervix again “seals” the passage with a mucus plug, reliably protecting the developing embryo, and subsequently the fetus, from microbes, fungi, destructive microflora and everything that can harm.
In addition, it is the responsibility of the neck to keep the baby in the uterus before delivery. If it is weak and unable to cope with this task, there is a real threat of abortion.
During childbirth, the small cervix does a great job - it opens up so large that the baby’s head can pass through it. It is through the cervical canal that, after 9 months, the baby leaves the womb to begin an independent life in this world.
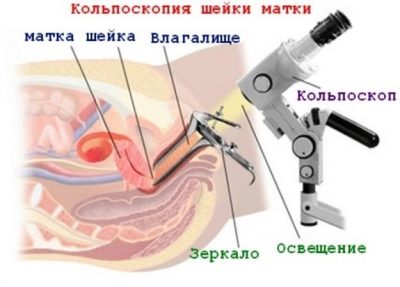
Anatomically, the cervix is quite complex. She has a vaginal part - the doctors examine her on a routine examination with a mirror. The deeper structures are the vaginal vaults, through which the cervix is connected to the uterine cavity. To inspect them, one gynecological mirror will not be enough, you need a special colposcope device, and the inspection procedure will be called colposcopy.
How and why does the measurement take place?
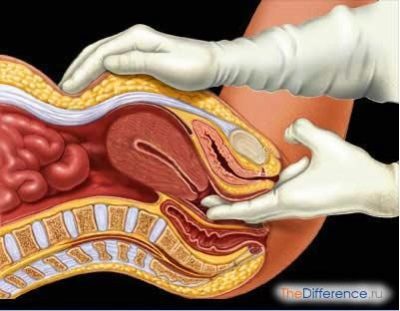
The parameters of the cervix are measured in two ways - on the gynecological chair using a mirror and colposcope and on ultrasound diagnostics.
In a manual study, the doctor can determine the condition of the external os, the density of the cervix and the closing or opening of the cervical canal.
The ultrasound measures the length and also provides a more accurate picture of the state of the internal os (the junction with the uterine cavity), which cannot be examined by other means.
When registering, the doctor conducts a manual examination, and at the same time smears of the vaginal flora are taken for analysis. In the first trimester, a colposcopy is also carried out for the woman; she gives more information than the usual mirror examination.
Measurements of the length of the cervix are advisable only after 20 weeks of pregnancy, when the baby begins to actively grow, and the load and pressure on the cervix increases.
Up to 20 weeks, the length of the cervix in different pregnant women is different, much depends on the individual values. However, by the 20th week, the sizes of the lower part of the uterus in different women come to the same averaged values, and the length becomes diagnostically important.
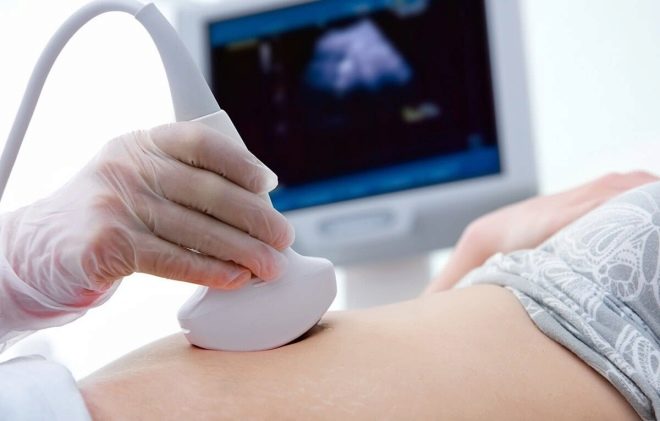
In the middle of pregnancy, ultrasound usually do transabdominalpositioning the scanner sensor on the abdomen of a pregnant woman, conducting an inspection through the anterior abdominal wall. If there is a suspicion of lengthening or shortening of the cervix, as well as other abnormalities, the doctor applies an intravaginal ultrasound method in which the sensor is inserted into the vagina. Through a thinner vaginal wall, the cervix is clearly visible.
Control over the size and other parameters of the cervix is necessary to ensure that the child is not threatened with premature birth, that there is no threat of intrauterine infection, which also becomes possible if the cervical canal opens slightly or opens completely
For the entire period of carrying a baby healthy a woman undergoes cervical examinations four times. If there is reason for concern, then diagnostics will be prescribed more often, as many times as necessary.
Changes during pregnancy
In a non-pregnant woman, the length of the cervix is about 3-4 cm with a width of 2.5 centimeters. These values are not absolute, there may be certain individual variations.
If a woman is not pregnant, but is only planning to conceive a baby, her cervix is pink and smooth, and when examined by a mirror she looks somewhat shiny.
In the early stages
When pregnancy occurs, the cervix undergoes major internal and external changes. Due to the increased blood supply, the pink delicate color is replaced by purple, bluish, and bluish.
The process of "ripening" begins, which will last all nine months, because the little neck will have to thicken, grow, become thicker and more elastic, to ensure the passage of the baby in the generic process.
In the first trimester, the condition of the cervix doctors can judge about the possibility of spontaneous abortion, miscarriage. If the neck is loose, during examination it misses the finger of the gynecologist, then such adverse events are very likely.
Normally, in the early stages of the neck should be slightly deviate towards the anus, to be tightly closed.
A loosely closed cervical canal creates not only the risk of miscarriage, but also the threat of the penetration of pathogenic microbes, fungi, and viruses into the uterus, which can damage the fetal membranes and lead to the death of the fetus.
Sometimes intrauterine infection turns into abnormalities and malformations of the baby’s development, congenital diseases.
The first changes in the neck begin approximately 4 weeks pregnantwhen a growing fetal egg begins to bulge somewhat the wall of the uterus to which it is attached. This creates a slight asymmetry.
The cervix changes its position in space, if during ovulation it rose higher to increase the chances of sperm penetration, now the main task is not to miss the fertilized egg, for this the lower segment of the uterus has to fall and lean back.
Many women who want to quickly find out whether the pregnancy has come, are interested in what the neck should be to the touch, it’s no secret that many people who plan pregnancy are carried out at home on their own. Approximately 8-10 days after conception under the influence of the hormone progesterone, the cervix becomes softer. The cervical canal, on the contrary, more densely closed.
A stiff cervix at an early period may indicate a threat associated with the increased tone of the uterus itself. This can happen, for example, with autoimmune diseases or with a lack of progesterone.
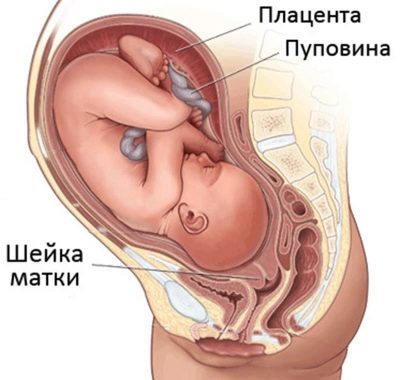
On late terms
In the third trimester, as the cervix is uteri, doctors judge the timing of the oncoming labor. This part of the uterus becomes softer. The length of the cervix gradually decreases by about half; on ultrasound, you can see how the internal pharynx expands, preparing for the upcoming delivery.
This process is slow, gradual, and takes several months. Changes occur under the influence of hormones - estrogen.
At 38 -39 weeks, the doctor may begin to check the cervical readiness for labor.. Such a readiness can be judged by the ability of the cervical canal to pass through the finger of an examining physician.
It is strictly forbidden to perform such a palpation on your own, and technically it is fortunate enough to do this.
Sometimes a week or several days before giving birth, a woman may notice a discharge of the mucus plug, the one that during the entire pregnancy served as an obstacle to the pathogenic microbes. The neck is gradually smoothed, begins to expand. For some women, such preparation of the cervix "starts" only at 40 weeks, and for some - even later.
If a woman gives birth to a firstborn, it is possible that the neck can begin to change in advance, and it will do so rather slowly. For multiparous, preparation begins later and proceeds faster. They have a neck "remembers" how to behave in the circumstances.
If the cervix is not in a hurry, doctors can prescribe a preparatory treatment that will help the neck to “ripen” faster. The expediency of such stimulation by modern gynecologists is regarded as controversial.
Some doctors believe that there is a need for stimulation, others believe that it is necessary to wait and trust in nature, which knows better than any doctor when the child comes to be born.
Weekly Lengths
If you notice abnormalities in the state of the cervix in time, then the probability of preserving a problematic pregnancy is almost 95%, because in the arsenal of modern medicine there are plenty of ways to influence the behavior of the cervix - medicines, special fixatives that are installed directly on the cervix, as well as small surgical methods (closure ). That is why it is important to inspect the future mothers at least four times during the gestation period.
Routine inspections, if there is no reason to fear for the health of the mother and child, conduct at 20 weeks, 28 weeks. Then at 32 and 36 weeks. If the doctor has concerns, the woman complains of pain, discharge, which cannot be considered normal during pregnancy, the study and measurement of the length of the cervix will be carried out unplanned for emergency reasons.
What are the norms of the length of the cervix for different periods of pregnancy, how this indicator varies over the weeks, you will learn from this table.
Cervical Length:
Obstetric term | Average length, mm | At the first pregnancy | With repeated pregnancy | Normal range, mm | Possible deviation, mm |
10-14 weeks | 35,4 | 35,3 | 35,6 | 28-45 | 5,1 |
15-19 weeks | 36,2 | 36,5 | 36,7 | 30-48 | 5,3 |
20-24 weeks | 40,3 | 40,4 | 40,1 | 32-48 | 4,5 |
25-29 weeks | 41 | 40,9 | 42,3 | 34-49 | 4,3 |
30-34 weeks | 36,4 | 35,8 | 36,3 | 34-43 | 3,7 |
35-40 weeks or more | 28,6 | 28,1 | 28,4 | 20-37 | 4,5 |
As can be seen from the table, in women who are going to give birth for the first time, the length of the cervix at the beginning of pregnancy increases more slowly than that of multiparous ones. In the third trimester, the normal size of the cervix is estimated on a special scale created specifically for this.
Each indicator is estimated at a certain number of points, the result is a more or less true clinical picture.
To judge the maturity of the cervix can be based on several criteria:
- Consistency. Dense - 0 points, slightly softened - 1 point, soft - 2 points.
- Length. More than 20 mm - 0 points, 10-20 mm - 1 point, less than 10 mm - 2 points.
- Position in space.The neck is rejected back - 0 points, rejected forward - 1 point, located right in the center perpendicular to the entrance to the vagina - 2 points.
- Degree of discovery. If the doctor's finger does not pass into the cervical canal - 0 points, if 1 finger passes - 1 point, if 2 fingers pass and more - 2 points.
Possible deviations and their causes
Measurements and comparisons of results with existing norms cause many questions for women in the “position”. Deviations, indeed, can be indicators of trouble. Let's look at the most common anomalies and their causes.
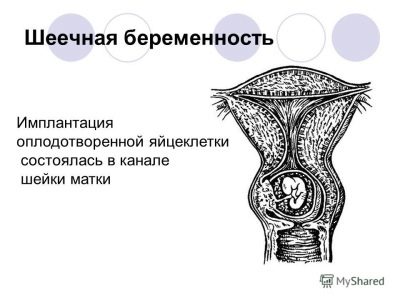
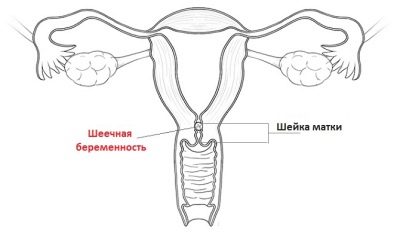
Pregnancy in the cervix
If in the early term the cervix is enlarged above the norm, the doctor may suspect a so-called cervical pregnancy. This is a type of ectopic pregnancy, in which a fertilized egg is implanted not into the uterus, as intended by nature, but into the cervix or isthmus.
There, theoretically, an embryo can live and develop approximately up to 4-5 weeks, less often up to 6-7 weeks. After that, the conditions become unbearable, and the fetus dies and is rejected, miscarriage occurs, sometimes accompanied by large blood loss.
Pathology is considered to be quite rare, it is diagnosed less frequently than in 0.01% of all pregnancies. Attaching to the walls of the cervical canal of the ovum may for a number of reasons, many of which are not known to medicine today.
Doctors tend to believe that this becomes possible, if the conditions for implantation in the uterus do not meet the requirements, the blastocyte simply can not be fixed and in the search for shelter there is a descent into the neck.
The reason may be a recent abortion., after which the woman ignored the recommendations to protect themselves for some time. A pregnancy that a young mother decided upon after a cesarean section can become a cervical if less than 3 years have passed since the operation.
Women with previously diagnosed uterine myoma and adhesions are also at greater risk than others.
Any interventions - surgery, trauma, inflammation of the uterus can be the cause for subsequent cervical or ischemic pregnancy. Symptoms may not be. The first thing that the doctor will notice during the examination will be just too large cervix with too small of the uterus. After this, ultrasound and colposcopy are prescribed.
A blood test for the determination of chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone that is common to all pregnant women from the day of implantation, shows a very low level of hCG, which is not typical for the last monthly period stated by the date.
On ultrasound, the doctor will not find the ovum in the uterus, and a careful examination of the cervical canal will find it there. A few decades ago there was no other way to solve this problem, how to remove the uterus completely. Many women with cervical pregnancy have lost the opportunity to have children in the future.
Now there are less cruel ways to help a woman and save her chances for motherhood in the future - vacuum aspiration and laser excision of the place of ingrowth of the embryo into the cervix. The risks of complications after such interventions are quite high, but modern medicine quite successfully copes with the task.
Short neck
The short neck (at the very beginning of pregnancy is less than 25-27 mm) may be a congenital feature of the female reproductive organs, and the consequence of traumatic effects - abortions, for example, or inflammatory processes that caused the shortening of the lower uterus segment. In any case, the insufficient length of this part of the reproductive system carries with it a serious danger to the child and the woman.
Normally, the neck is extended at the beginning of pregnancy and shortened closer to childbirth. Short neck with great difficulty it will be able to cope with the load of holding a growing baby in the uterine cavity. Miscarriage, premature labor, rapid delivery, rupture of the cervix may occur.
A shortened cervix creates an increased risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus, since it cannot serve as a reliable protection against pathogens and viruses.
The doctor will be able to detect shortening at the first admission, if it took place before the onset of pregnancy. However, with the subsequent development of a short cervix, for example, against the background of hormonal insufficiency in the first trimester, the problem can be detected only at the 12th week of pregnancy, when the expectant mother comes for a screening examination.
Symptoms sometimes appear after this period, closer to the fourth month of pregnancy.
A growing baby begins to exert more tangible pressure on the short neck, and the woman may begin to complain that it hurts in the lower abdomen, and sometimes even slightly bleeds.
Allocation in this case are of the character of blood or bloody, sometimes with impurities of mucus. If the shortening is confirmed by the results of a vaginal ultrasound, then the question of how to assist is decided. In some cases, the neck may get stronger under the influence of drugs, for example, hormones, if they are not enough, but it cannot lengthen under any circumstances.
During pregnancy, such a future mother will be more closely observed as necessary to hospitalize, to provide treatment aimed at the preservation and prolongation of pregnancy.
On the cervix can install pessary - A special ring that will fix it and reduce the load of the growing genital organ on the short neck.
Another method is Circle. It is based on the stitching of the neck, which will mechanically prevent its premature opening. It is reasonable to perform suturing only in the early stages and up to 26-29 weeks of gestation, after this period they try not to carry out the dial.
Long neck
The long cervix of the uterus may be from birth, or it may become after experienced operations, including abortions and curettage, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system - the uterus, appendages, ovaries. Quite often, the first symptoms of this pathology appear just during pregnancy.
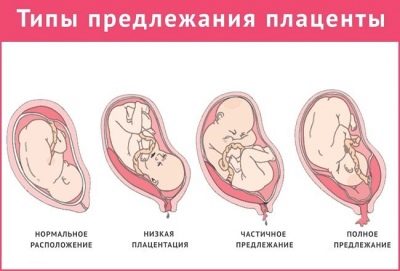
Elongation of the lower segment of the uterus leads to incorrect proportions of the reproductive organ, and therefore increases the risk of pathological attachment of the placenta when this temporary organ is located in the center, too low or laterally.
The height of the placenta is of great importance, especially in the second and third trimesters, it depends on how well the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients and oxygen.
Women with a pathologically elongated cervix risk in childbirth. The very process of the birth of a child into the world is protracted in nature, giving birth to first-timers lasts almost 14 hours, and for multiparous ones - 9-12 hours.
The elongated organ opens longer, slower, more painful.
When a child passes through such a channel, the risk of hypoxia increases, since the head and neck are in the same plane.
The difficulty lies in the fact that It is impossible to determine the pathology on a routine examination by a gynecologist. An anomaly can be suspected only during colposcopy, and it can be confirmed or disproved only by ultrasound diagnostics.
Such a deviation does not require special treatment, because the long neck diagnosed at an early date can smooth out and decrease towards childbirth. If this does not happen, then doctors are likely to use one of the methods of stimulating labor.
Before childbirth, a woman is recommended massage, which contributes to the outflow of lymph, and also strengthens the muscles of the pelvic organs. Medication is rarely prescribed.mainly in case of post-pregnancy pregnancies.
Erosion
According to the results of the biometrics of this body, as well as a manual examination, the doctor may report that the length is normal, but there is erosion.Over 60% of pregnant women face this phenomenon. In some, changes in the mucous membrane of the cervix were observed even before the onset of the “interesting” position It is possible that erosion can develop during pregnancy.
The reasons are varied. The mucosa can change under the influence of hormones, if a woman before the onset of pregnancy took oral contraceptives, as well as in the event of a deficiency or excess of certain hormones during gestation of the baby. The cause may be the inflammations that were previously transferred, and at the same time, erosion can sometimes manifest itself only after the onset of pregnancy.
Women who have a history of venereal ailments and sexually transmitted infections, difficult labor, traumatizing this organ, and multiple abortions have suffered from erosion. Even the inability to properly do syringing and extra pounds can lead to the development of such complications.
Symptoms a woman can feel herself. At any stage of pregnancy, when erosion occurs, there may be uncomfortable sensations “inside” during intercourse, sometimes expectant mothers complain about the appearance of scanty pink or bloody discharge. More than half of women do not experience any symptoms.
During pregnancy, erosion is not treated.
Standard methods of dealing with this unpleasant problem - cautery and laser exposure - expectant mothers are contraindicated because of the risk of a scar, which can cause a lot of problems and pain during childbirth, and may also create an additional threat of organ rupture. Therefore, the treatment is postponed for later.
By the way, in many women erosion after childbirth passes on its own. On the fetus and during pregnancy, this problem has no effect.
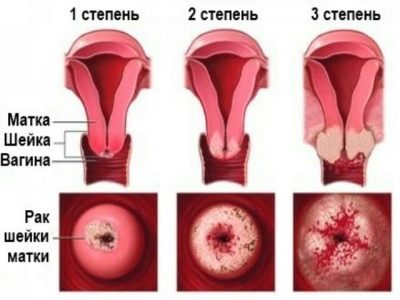
Dysplasia
Colposcopy can show another problem - cervical dysplasia. This term refers to changes in the epithelium that have precancerous prerequisites. Most often, the disease is found in women aged 25 to 33-35 years. If the disease can be determined in the early stages, dysplasia is considered to be completely reversible, and negative consequences can be avoided.
Externally, with manual examination, dysplasia may be confused with erosion, since the clinical picture is similar, but colposcopy and laboratory tests allow us to establish the main difference. It lies in the fact that during erosion damage to the epithelium is of a superficial mechanical nature, and in case of dysplasia it is cellular, that is destruction takes place at a deeper, cellular level.
Most often, the disease is caused by human papilloma viruses 16 and 18 types. They are actively “helped” by other factors that contribute to the development of the disease - smoking, weak immunity or immunodeficiency, chronic inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs that have not been treated for a long time.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes that have changed for natural reasons can affect the development of dysplasia. Too early sex life and early childbirth are also risk factors.
Prevent the development of cancer allow modern methods of treatment - drug and surgicalas well as constant monitoring of the further state of the body. However, during pregnancy, the use of medicines and even more so the operation is undesirable. Mild dysplasia rarely turns into cancer, and therefore only requires observation.
A severe form of the disease can make a woman a choice - to leave the child or have an abortion and agree to an emergency operation.
In each case, the issue is solved individually.
Medical statistics are not too optimistic - about 30% of expectant mothers who chose pregnancy, and therefore gynecological surgery was postponed, they were subsequently registered at the oncology center due to the development of cervical cancer.
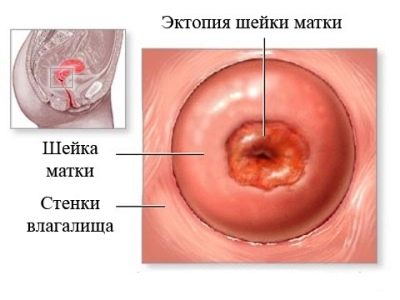
Ectopia
Ectopia also resembles erosion, it is even called pseudo-erosion.In this pathology, part of the cylindrical epithelium will mix in the vagina. On examination, the doctor sees a red spot that resembles erosive changes.
A woman may complain of copious discharge of yellow, white or greenish color with an unpleasant odor. The causes of this phenomenon can be traumatic, but most often they are infectious and indicate either the presence of infections, or that the infections have been carried over in the past.
Earlier abortions, hormonal disruptions, sex life started too early can increase the likelihood of ectopia. However, in most cases, doctors are quite optimistic, because ectopia has physiological reasons.
Changes that undergo the lower segment of the uterus during gestation of the baby, lead to changes in organ tissue. After childbirth, ectopia, which is not caused by pathologies, inflammation or infections, usually goes away without a trace.
Conclusion
Cervical biometrics - an important study, to abandon which is impractical. This study is recommended by the Ministry of Health, but not charged. Thus, a woman is always entitled to refuse to undergo smear, colposcopy, ultrasound.
Why this should not be done, no need to explain, because the health of a woman and her child should be monitored in order to notice any changes in time and take urgent measures.
Obstetrician-gynecologist I. Yu. Skripkina will tell you how the cervix is opened before delivery.