What is CTG, and what does it show during pregnancy?
After 7 months of pregnancy expectant mother can get referral to CTG. This study in the last trimester is considered one of the most informative. However, it is precisely this that causes pregnant women most of all questions, since it is not at all clear how and what is investigated and how to understand what is written in the conclusion. In this article we will talk about CTG in more detail, as well as help decipher its results.
What it is?
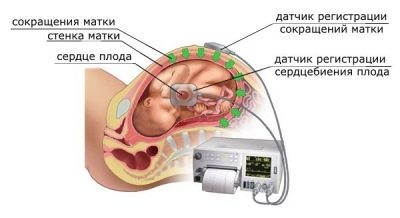
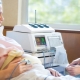
Behind the abbreviation CTG is a study called cardiotocography. At its core, it is a continuous, continuous recording of a baby’s heartbeat, uterine contractions, and a child’s motor activity. All these parameters are recorded simultaneously and immediately recorded in real time by a recorder or a computer program on a calibration tape.
The rhythm of the beating baby heart picks up the ultrasonic sensor, and the uterine contractions - the strain gauge sensor.
The first graph is called a tachogram, and the second is a histogram. Due to its simplicity, safety and informativeness, CTG is today the most popular way to get information about the state of the childwhich remains a little before birth - a couple of months.
CTG is administered to all pregnant women who are at the dispensary account in the antenatal clinic. In case of uncomplicated, normally proceeding pregnancy, the first study is carried out for the period from 30 to 32 weeks, then a similar examination is carried out immediately before birth at the maternity hospital with planned hospitalization. If the baby’s condition raises questions, then CTG can be carried out earlier, starting from 28-29 weeks. With serious complications of pregnancy, the examination can be done daily.
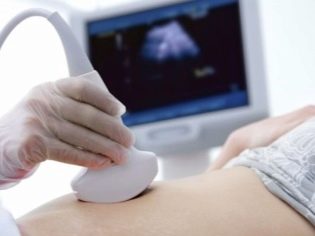
CTG is also used in the generic process itself. Examination during pregnancy, when the sensors are placed on the belly of the expectant mother, is called external or indirect CTG. Direct cardiotocography is carried out when the integrity of the fetal membrane is broken, water has been removed, and a thin sensor electrode is inserted directly into the uterus.
What shows?
CTG allows you to find out how the child feels. First of all, the device records and shows the heart rate (heart rate) - the main parameter that allows you to judge the health of the crumbs. An ultrasonic sensor based on the Doppler effect sends an ultrasonic wave. It is reflected from the tissues and moving blood cells in the blood vessels and sent back to the sensor. As a result it becomes obvious how often a small heart beats.
The tone of the uterus and the movement of the fetus measures the strain gauge, which is a wide belt encircling the belly of the future mother.
If the uterus has contracted or stiffened, if the crumb has made a revolution or stretched, the stomach will slightly change in volume, which does not escape the sensitive sensor and will immediately be reflected in the chart.
There are in the study and its nuances, very important for the correct diagnosis.So, what matters is not only the frequency with which the heart beats the baby, but also how this rhythm changes depending on the activity, perturbations and other factors. Therefore, the variability of the rhythm, myocardial reflex (when moving the heart knocks faster), as well as any other periodic changes in the heart of the child.
Indications for examination
Like any other analysis or procedure, CTG during pregnancy is only the recommended method, the Ministry of Health strongly advises pregnant women not to abandon it. But the final word, in any case, remains for the future mother - if she does not want to go for this diagnosis, no one can make her.
Doctors are trying to do research for all pregnant. But especially the procedure is shown to certain categories of future mothers:
- Any pathology of pregnancy. This includes gestosis, lack of water and high water, the threat of premature birth, infectious and non-infectious diseases that the expectant mother suffered during the term of carrying a baby, chronic illnesses that she has, increased or decreased pressure in a woman, etc.
- Strange behavior of the child. If the baby suddenly began to move rarely and sluggishly, or, conversely, his physical activity increased.
- The appearance of pain in my mother's stomach. Any pain syndrome of any nature and strength necessarily requires CTG.
- Burdened obstetric history. Cardiotography should be monitored more often if the previous pregnancies of the woman ended in preterm labor, the death of the child in utero, as well as the birth of a child with gross developmental pathologies.
- Severe previous childbirth or cesarean section. If in the past such facts took place, then the next pregnancy in the later periods necessarily requires frequent monitoring, including with the help of CTG.
Women from the designated risk group may be diagnosed several times during pregnancy. The frequency is determined by the doctor, who is well aware of the peculiarities of the course of pregnancy in a particular woman.
How is it done?
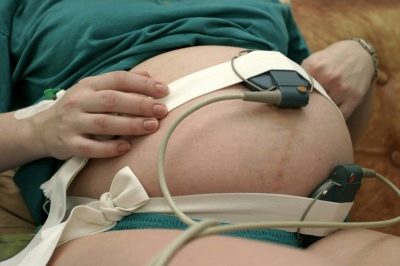
This simple examination can be done at the antenatal clinic at the place of residence, as well as at any private clinic that offers pregnancy planning and management services. The procedure is completely painless, it does not cause any discomfort.
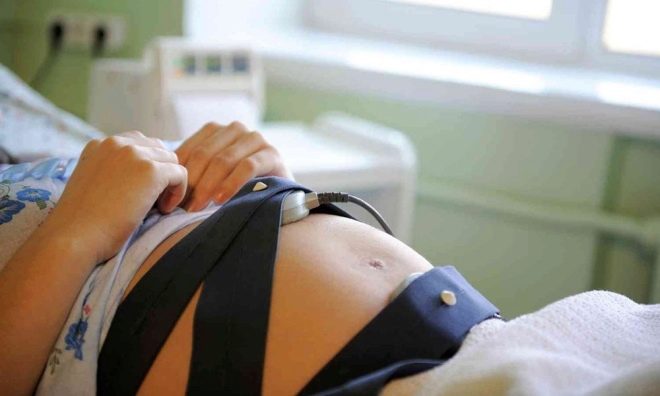
In the doctor's office, the woman will be offered to get comfortable. She can lie down, sit down or sit in a semi-sitting position, as long as she is comfortable, since CTG lasts a long time - from half an hour to an hour, and in some cases longer, if the examination passes with errors or its results are abnormal or doubtful.
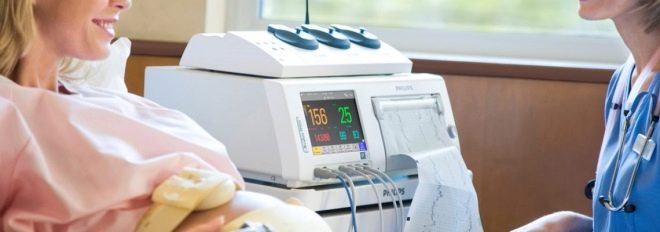
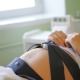
A wide special belt is put on the future mother's belly — the same strain gauge, and under it is fixed a small ultrasonic sensor of a round or rectangular shape. Ultrasound-sensor try to arrange in such a way that he was as close as possible to the heart of the baby. As soon as the doctor hears a distinct rhythm, he will fasten his belt, fix the sensors and start the computer program, which will begin to fix the indicators and draw graphs. If the examination takes place on the old machine, the recorder will draw.
The movements will pick up the strain gauge belt. If the diagnosis is made on the device, then there will be a button in the woman’s hand, which she will be asked to press every time, as soon as she feels a distinct movement of her baby. The decision to stop measurements is taken by the program itself, as soon as the volume of information necessary for calculating the results is received, the “session” is completed and the result is printed.
Preparing for the passage of CTG is quite simple. On the eve, it is desirable to have a good rest, sleep, so as not to get distorted false results.You should not go to the study on an empty stomach, it is best to eat before the exit, and before you go to the doctor’s office, go to the toilet, because you have to sit in one position for a long time. On the way it is worth walking on foot to “cheer up” the baby, because the sleeping fetus will not be able to demonstrate the necessary motor activity.
According to reviews of future mothers, a small chocolate eaten before the procedure helps to wake the baby up pretty well.
Decryption and norms
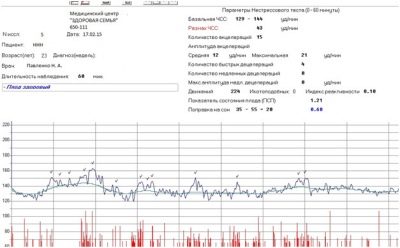
Modern devices not only immediately after the end of the survey give the result for each of the identified indicators, but also assess the general condition of the fetus in points. We will talk about scoring a little later, but for now let's look at what the basic terms mean and what it should be normal.
Basal rhythm
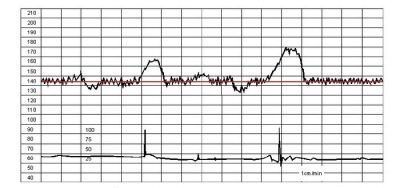
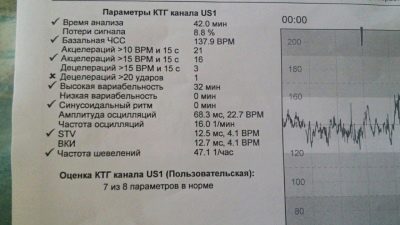
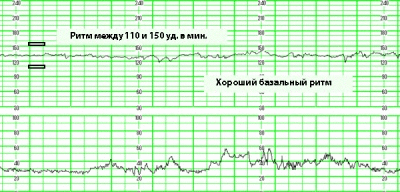
The frequency of contractions of the small heart is constantly changing. This is the first thing a woman will see. In order to average the indicators, which vary from 120 to 180 beats per minute, such a parameter as the basal rhythm was derived. During the first 10 minutes of the study, the device records the changes in the heart rate and displays the average basal value. That is what is indicated opposite the line "Basal rhythm" or "Basic Heart Rate". The norm in the third trimester is considered if the base frequency is in the range of 110 to 160 beats per minute.
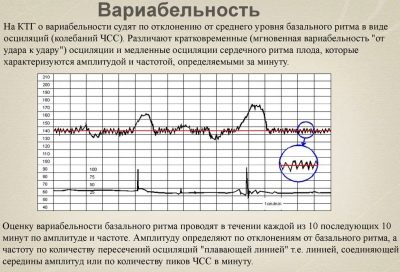
Rhythm variability
If the basal rhythm is an average value, then those very rapidly changing indices of the heartbeat frequency of the crumbs are the variability. The term is used to denote this parameter. “Oscillations”, which literally means “oscillations”.
These vibrations are fast and slow. Rapid or (instantaneous) oscillations are vibrations that occur with every beat of the crumbs heart. On the monitor, mother can see them like this: 143, 156, 136, 124, 141, and so on, because the heart changes its rhythm every few seconds.
Slow vibrations are also different. If in 1 minute of time the heart of the baby changes the rhythm in less than three beats (it was 140, it became - 142), then it is a question of low variability and low oscillations. If in a minute the heart has changed the beat rhythm by a number from 3 to 6 beats (it was 140, it became 145), then we are talking about the average variability. When the heart rate changes by more than six beats per minute (it was 140, it became 150), they talk about high variability and high oscillations.
Oscillations high and instant are considered as a norm.
If a baby has a low variability and instantaneous oscillations with the device, this may indicate serious pathological conditions of the baby. This is often observed during hypoxia.
Slow fluctuations can be monotonous (if the heart rate per minute of research has changed by no more than five beats), transient (rhythm has changed by 6-10 beats), wave-like (heart rate has changed in 1 minute by 11-25 beats), as well as jumping (more than 25 beats per minute). Wavelike slow oscillations are considered normal. Any other types of slow fluctuations are regarded as an alarming symptom. Jumping, in particular, occur during entanglement of the umbilical cord, and transitional - during hypoxia.
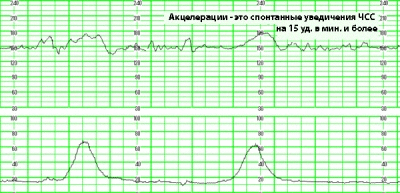
Acceleration and Deceleration
These are the same ones discussed by future moms and visible on the chart “teeth” and “dips”. Speaking in simple language, acceleration calls raising the frequency of a child's heartbeat by more than 15 beats per minute and maintaining that pace for 15 seconds or more. On the chart is a lift. Deceleration is a decrease in the rhythm, all for the same 15 beats per minute, maintaining the pace for 15 seconds or more. On the chart, they look like a failure.
2 or more accelerations for 10 minutes are considered normal. If the "peaks" on the graph repeat with the same frequency and last the same amount of time, then this may be a sign of the unhappiness of the fetus. Degeneration is not considered normal at all.Most often they talk about possible hypoxia, but minor “failures” can be a variant of the norm, it all depends on other CTG indicators.
Fetal movements
Many future moms believe that the number of movements per child per hour is the main parameter that determines CTG. This is not true. Already at least because there is no single norm of the number of movements of a child per hour. Conditionally considered a good sign if the crumb makes 6-8 or more movements per hour of diagnosis. The mood of the mother at the time of passage of CTG, and what she ate, and how her metabolism flows can affect the number of perturbations. The baby may be alert, and may want to sleep. therefore they look at the number of movements together with the rest of the diagnostic results.
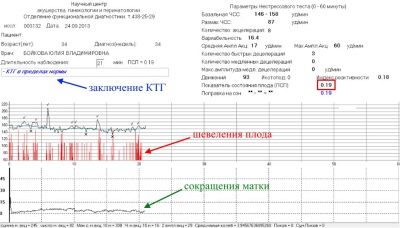
Contractions of the uterine muscles look smooth wavy lines on the graph, which is located below the chart of the fetal cardiogram.
The movements are noted in the same place, but they have the form of sharp rises, peaks.
A small amount of perturbation may indicate that the baby is sleeping or is in a resting phase, and also that he has pronounced disturbances, such as oxygen deficiency. But for this indicator alone no conclusions can be drawn.
Uterus tonus
Many pregnant women are concerned about the question whether CTG will show the tone or hypertonia of the uterus. Answer it is not as easy as it seems. As mentioned above, CTG can be performed in two ways - external and internal. The external way, which is in question, does not give a definite answer about whether a woman has an increased tone. It allows only to fix individual cuts of the reproductive organ.
Accurately know the level of pressure inside the uterus (and with a tone it increases) can only be by introducing thin electrode sensor into the uterine cavity. In pregnancy, for obvious reasons, it is impossible if the fetal bladder is safe and sound. And in childbirth in this dimension there is usually no need, because the baby has already gathered "on the way out", and the measurements of external CTG will be informative, and they will tell about it heartbeat and activity.
Therefore, by default, the intrauterine pressure at the level of 8-10 millimeters of mercury is considered the norm.
If the program in evaluating the contractility of the uterus shows the values above, the tone is said, but indirectly and very carefully.
Contractions - true and false
Contractions are contractions of the uterus muscles, and they are displayed on the CTG chart. And both the real contractions that accompany the generic process, and false, or training contractions that precede the onset of labor, sometimes long before them. On the graph, real contractions are depicted by fairly large waves in the bottom line. Training will look similar, but the "waves" will be less pronounced, and the duration from the beginning to the end of the wave will be no more than a minute.
If we simplify all of the above, then the norms of CTG, under which it can be said that everything is fine with the child, can be displayed in the following table:
| Baseline heart rate | 08-160 beats / min at rest and 120-180 beats / min during stirring |
| Heart rate variability | Instant high oscillations slow wave-like oscillations, total variability - 5-25 beats / min |
| Acceleration (acceleration) | Not more than 15 beats / min, at least 2 times per examination |
| Deceleration (deceleration) | Missing or do not exceed 15 beats / min |
| The amount of movement | 6 or more surveys |
Possible violations and their causes
Like any other diagnostic examination, CTG, or rather, its results, can cause a lot of questions, especially if the doctor says that "CTG is bad." What pathologies can be identified, we will tell below.
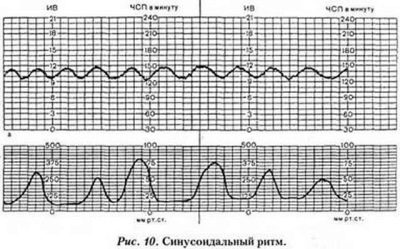
Sinusoidal rhythm
The graph of CTG, which resembles even identical sinusoids, usually does not inspire optimism to specialists. True, this happens rarely enough - once for 300-350 examinations, only one woman theoretically cardiotocography shows a sinusoidal rhythm.
On the graph there are no decelerations and accelerations (ups and downs), the basic heart rate is quite normal, the variability does not exceed 15 beats per minute. Such a schedule usually does not bode well. So is the child in severe rhesus conflict, significant hypoxia of the fetus, in case of poisoning of the pregnant woman and the baby with toxic substances or narcotic drugs.
If a woman does not take poisons and drugs, the risks for the child increase. In this case, a sinusoidal rhythm can be a harbinger of imminent death. Almost 70% of children who showed such sinusoids on CTG were born dead or died in the first hours after birth for various reasons.
In order to judge the sinusoidal rhythm, like this, the schedule should be “drawn” for 20 minutes or more. In this case, the woman is urgently hospitalized to conduct an emergency caesarean section and try to save the life of the child.
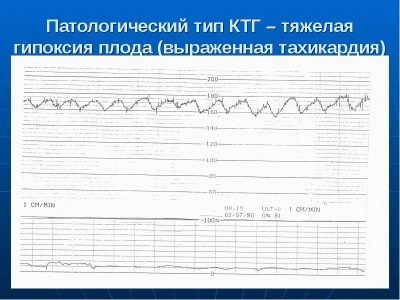
High fetal heart rate
If the CTG for 10 minutes in a child recorded a clear excess of heart rate, the baseline heart rate consistently exceeds the norm, we are talking about fetal tachycardia. At the same time, great importance is given to how much the basic values are exceeded:
- HR = 160-179 beats / min - mild tachycardia;
- HR = 180 beats / min and higher - severe tachycardia.
The reasons that can make a small heart beat so often can be different. Most often, tachycardia is a sign of oxygen starvation. When the baby does not have enough oxygen, it "turns on" compensatory mechanisms that are designed to saturate the tissues and organs with oxygen "for the future." The heart begins to beat more often under the influence of stress hormones.
With a high heart rate, the baby in the mother's womb can react to fever. If the mother's body temperature rises to at least 37.5 or 38.0 degrees, the crumb will immediately show an increase in heart rate. If the mother is not sick and does not complain about the temperature rise, the reason for such CTG may be infection in the baby itself. Intrauterine infection causes the crumbs' immunity to start producing antibodies and a variety of excipients that raise the temperature of the child and cause his heart to shrink more often.
If the mother took any medications shortly before the study, you should definitely inform your doctor about this.
Side effects of some drugs include an increase in heart rate, and not only the mother herself. Tachycardia can be observed in children of women suffering from thyroid malfunction. In this case, the baby’s body acts Wrong hormonal background of the mother.
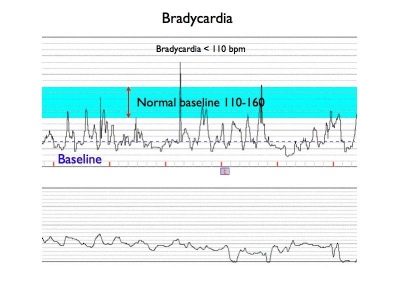
Slow fetal heartbeat
Reducing the frequency of the baby’s heartbeat below normal values is called bradycardia. The heart rate is considered an alarming indicator if it remains at a level of 100 or fewer beats per minute for 10 minutes of the test.
Slow heart rate may be the case severe hypoxia, representing a real danger to the life of the baby. Such indicators during the birth process suggest that the head of the baby was tightly pressed while passing through the birth canal. In the second case, bradycardia is considered a variant of the norm, it is called reflex arrhythmia. Some medicines that were taken by the mother on the eve of the study can slow down the frequency of contractions of the child's heart.
Monotone heartbeat
Such a violation can be discussed when the slow oscillations (oscillations) do not exceed 5 beats per minute. There are no sharp fluctuations on the graph. If such a schedule remains for 10-15 minutes of research or more, the woman will definitely be asked to undergo additional examinations, for example, an ultrasound with ultrasound, because the monotony in most cases "signals" about hypoxia and other unfavorable circumstances for the baby.
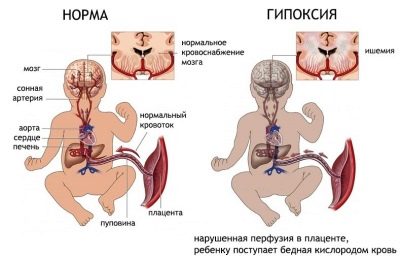
Fetal hypoxia - oxygen starvation
All future mothers know how dangerous and insidious hypoxia can be. The lack of oxygen, which the baby gets with maternal blood through the mother-placenta-fetus system, can lead to irreversible processes in the baby’s central nervous system and even provoke its death.
Signs of hypoxia crumbs on a cardiotocography examination are a decrease or an increase in heart rate.
At the early stage of oxygen starvation, the heart knocks more often than the norm requires; at the late stage of hypoxia, a decrease is observed - bradycardia.
A kid who suffers from a lack of oxygen, which is so important for its development, “will demonstrate” on CTG low variability, acceleration, which will be exactly the same in duration and severity, sinusoidal rhythm and sharp, very frequent perturbations, which doctors call “painful movements”.
If CTG determines one of these signs, then the woman is referred for additional examinations. But detection of two or more alarming indicators is the basis for hospitalization expectant mother and speedy delivery with a cesarean section.
Score by points
A system of points is used to summarize the results of cardiotocography. Evaluation of each of the above parameters includes the accrual of a completely certain number of points, which together give the final result. In obstetrics and gynecology, there are several criteria for "awarding" points.
Fisher scale
Of all the methods of calculating the results, this one is considered to be the most accurate and correct to this day. When calculating points on the Fisher scale, four basic values are evaluated - basic heartbeat, variability, acceleration and deceleration. This scale was supplemented by Dr. Krebs, who also suggested taking into account the number of fetal movements. Thus, a clear and simple scoring system was obtained:
Fischer rating table in Krebs modification:
| Determined on CTG indicator | Scoring 1 point provided: | Scoring 2 points provided: | Scoring 3 points provided: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline heart rate | Less than 100 units / min or more than 100 beats / min | 100-120 beats / min or 160-180 beats / min | 121-159 beats / min |
| Expressiveness of slow oscillations | Less than 3 beats / min | 3 to 5 beats / min | 6 to 25 beats / min |
| The number of slow oscillations | Less than 3 for the study period | From 3 to 6 for the study period | More than 6 over the study period |
| Number of acceptations | Not fixed | From 1 to 4 for half an hour | More than 5 in half an hour |
| Decoupling | Late or variable | Variable or late | Early or not fixed |
| Stirrings | Not fixed at all | 1-2 for half an hour | More than 3 in half an hour |
Normal on this scale is considered if the condition of the fetus is estimated at 9-12 points. This means that the pussy feels good, at least while the research was being done.
If the result of CTG Fisher is 6-8 points, then the woman needs further monitoring of CTG, because such an indication is a sign of the child’s distress. However, it does not represent an immediate danger to the life of the crumbs. It is recommended to repeat CTG more often in order to track the dynamics.
The most alarming indicator for Fisher is less than 5 points. This means that the child is in mortal danger, his death may occur at any time. Usually, with such results, CTG is not sent home, but immediately to the hospital, where a decision on early delivery must be made within the next hours in order to give the baby a chance to survive. This is the case in which it is more dangerous for a child to remain in the mother’s womb than to be born, even if it is very premature.
FIGO scale
This scale was created by the International Association of gynecologists and obstetricians, in order to “equalize” certain errors in the assessment of the criteria for CTG by doctors from different countries. This is an international "gold standard".
Evaluation table on the scale of FIGO:
Determined on CTG indicator | Value at normal CTG | Significance of doubtful or “suspicious” CTG | The value of pathology |
Basal heart rate | 110-150 beats / min | 100-109 beats / min or 151-170 beats / min | Less than 100 or more than 170 beats / min |
Variability | 2-25 beats / min | 5-10 beats / min in 40 minutes | Less than 5 beats / min for 40 minutes or sinusoidal rhythm |
Acceleration | 2 or more in 40 minutes | During the 40-minute survey are absent | Absent altogether |
Decoupling | Not recorded at all or there are rare variable | Variable | Variable or late |
Common Questions
We watched several dozen women's forums on the Internet, where pregnant women discussed the results of CTG. So the list of the most common questions that interest future mothers became obvious. We will try to answer them here.
What is a cap?
In conclusion, which will receive a pregnant woman on the passage of cardiotocography, it will be indicated that the CAP of the fetus = a certain numerical value. What is the CAP, it is not too difficult to guess. This abbreviation stands for: "indicator of the state of the fetus." This is a kind of summary, which is issued after analyzing all the data obtained. The CAP is calculated not by a person, but by a special program, and therefore the personal factor and the qualifications of the medical staff here have no meaning.
PSP is calculated by complex mathematical algorithms that the future mother does not need to know at all. Enough to get acquainted with the general rules of the PSP as such:
Norm - 1.0 and below. Deviation from the norm, which is considered insignificant, for example, 1.03 or 1.05 is a reason to double-check the data, to conduct CTG again, perhaps something just went wrong.
PSP = 1.1-2.0. These numerical values indicate the initial disturbance of the fetus. Repeating CTG should be done once a week, the woman is prescribed treatment depending on the reasons that caused the impairment (fetal hypoxia, placental insufficiency, etc.).
PSP = 2.1-3.0. Such indicators suggest that the baby feels pronounced discomfort, his condition leaves much to be desired. With such values, it is customary to hospitalize a woman in CTG in order to make the final decision in the hospital - to treat or give birth. If it is decided to keep the pregnancy, the cardiotogram will be shown every 2-3 days.
PSP = 3.0 and above. This result is very alarming. Most often, he points out that the crumb is in a critical condition. A woman is hospitalized immediately, sometimes by an “First Aid”, for several hours a decision is made to conduct an emergency cesarean section to save the baby’s life.
Accuracy of PSP estimation is close to 90%, and therefore, like ultrasound diagnostics, CTG provides only food for thought. Based on the “bad” CTG alone, no diagnoses are made. You need a comprehensive examination, which will include both ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound (USDG), and laboratory tests of blood, urine, smears.
Is the baby floor visible on CTG?
Genital organs of the child, as well as other features of his appearance and structure, are not indicated on cardiotocography. The sensors, which the doctor attaches to the future mother's belly, do not give the screen an image of what is happening inside, they only “write” graphics.
To find out the sex of the baby, it is better to go on an ultrasound or to donate blood for a non-invasive DNA test.
These methods with great accuracy will answer the question, who grows in the stomach - a son or daughter. Attempts on the frequency of the heartbeat, which is determined on CTG, to determine the sex of the child, it is impossible to explain with any scientific arguments. Popular rumor says that the boy’s heart beats less often than the girl’s heart. Traditional medicine neither confirm nor deny this - this pattern has not been studied.
How to make CTG during pregnancy twins?
This question interests many, but the answer is not so simple. One sensor can register parameters for only one baby. If there are two or more babies in my mother's womb, this can cause a lot of technical difficulties during the procedure.
To avoid confusion in assessing the status of two or more toddlers, the doctor will first determine the location of each of them. In the area close to the area of the heart of each baby, separate ultrasonic sensors will be attached. If there are two children, then there will be two ultrasound sensors, if there are three, then there will be three sensors. But the strain gauge, as in normal pregnancy, will be one. Thus, a woman will receive two or three schedules, the same number of conclusions about the state (CAP) of each of the babies she bears.
What is a positive and negative non-stress test?
To make the CTG results more accurate allow additional tests. CTG with functional tests can be assigned separately, if the results of the first study were “suspicious”, questionable or borderline (between normal and pathological). Tests are different. Stress test - a registration of the reaction of the fetus, its heart rhythm and other parameters after the introduction of a pregnant small dose of oxytocin, causing uterine contraction.
A woman may be asked to walk up and down the stairs, from time to time, to hold her breath, all of which will be options for stress tests.
A non-stress test is when there is no load and no provoking factors from the outside on the child, and with an increase in the heart rhythm, the crumb will react to its own movements.
If there is no increase after movement, this is an alarming sign, the test is considered positive. If in 40 minutes the pussy makes at least two movements with accelerations, then the test is assessed as negative, and this is considered normal.
What will the study show if the pussy is sleeping?
If the examination is carried out at the moment when the crumb is in the resting phase, then he, like the sleeping adult, will be kept to a minimum. On CTG, the heart rate will be recorded, as well as episodic contractions of the uterus, but there will be no movement or it will be isolated, there will be no excitations associated with them. In this case, the doctor will take all measures to wake up the "sleepy", if it does not work out, that the woman will be advised to come to the CTG again, after a few days.
What will the study show if a woman has low water?
To confirm the fact of low water (as well as polyhydramnios) cardiotocography cannot, this can only be clarified by ultrasound. However, with the established fact of lack of water, CTG will be done more often. If the results in dynamics will indicate the intrauterine suffering of the child, then the woman will be shown early delivery. This is not always the case, and many expectant mothers with low water receive excellent results of cardiotocography.
Can CTG harm the fetus?
Cardiotocography is considered a method completely safe for the child and the mother. Despite this, many women claim that doing ultrasound is harmful, as well as CTG, which also uses an ultrasonic sensor. The harm of ultrasound radiation for the development of the child is not proven. However, to assess the separated effects of exposure to ultrasound on a person (after ten, twenty or forty years) is also not possible yet.
Thus, only illiterate actions of medical personnel, who can tighten the strain gauge belt on the pregnant belly, causing mechanical pressure and even trauma to the fetus, can harm the baby.
Does CTG change weekly?
There is no difference in how long CTG is performed. The parameters that are determined in this study do not depend on height, circumference of the head, chest, or the length of the child’s limbs, as is done on an ultrasound scan. Therefore, the results of CTG at 33, 35 and 36 weeks will not be any different. If the child is comfortable and good, then this is what the chart will show.
Experienced obstetricians, however, note one curious detail - The baby's heart starts knocking a little less often at 32.34, 36 and 38 weeks.
Is it possible to carry out the procedure at home?
Theoretically and practically it is possible, but the cost of cardiotocography machines is high (several hundred thousand rubles), and small amateur devices that only record the heart rate and do not record and do not analyze other parameters have no special diagnostic value.
Sometimes, when the situation requires daily monitoring, a woman is temporarily given a device for home use, this decision is made by the attending physician. Most often this happens with patients of modern perinatal centers, who are better equipped than consultations.
Home measurements will be able to show the condition of the baby, as well as understand that there will soon be childbirth, if the baby moves very much or, on the contrary, is quiet, and characteristic “waves” appear on the chart, indicating the start of labor and labor. This can happen at any time, starting from 37-38 weeks. Women whose onset of labor activity should not coincide with home stays are advised to go to the maternity hospital in advance. In a hospital setting, if necessary, they will conduct daily CTG, and the expectant mother will not have to worry about the state of her baby.
How is CTG, as well as other useful information on studies of pregnant women, see below.