The standard values of CTG during pregnancy
Fetal cardiotocography is a study that is conducted for all pregnant women after 28-29 weeks. Most often, the diagnosis is sent to 32-34 week, if there are no complications. What allows us to see the CTG and what are the norms of values, we will tell in this article.
The essence of the method
CTG is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Tiny heart works in full accordance with the general condition of the child. If the baby is healthy and he is well, then his heart is beating rhythmically and clearly. The small heart responds to any disorders, diseases, pathological conditions by increasing or decreasing the rhythm.
Cardiotocography is performed two or three times in the later periods, usually after 30 weeks and then before delivery at 38-40 weeks. If the pregnancy is not proceeding too smoothly, the doctor may recommend additional CTG.
Cardiotocography is done to find out how your baby feels.
At birth, the device is also connected to the abdomen of a pregnant woman in order to monitor the baby’s well-being while she is traveling along an uneasy, but provided by nature path.
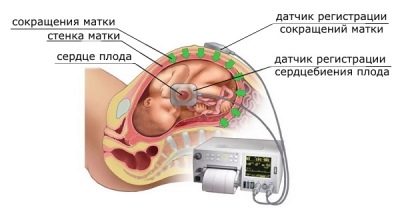
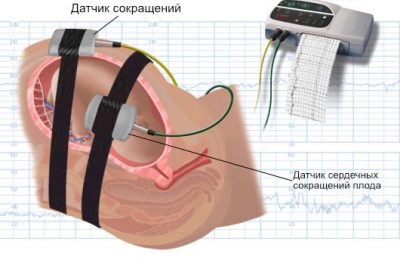
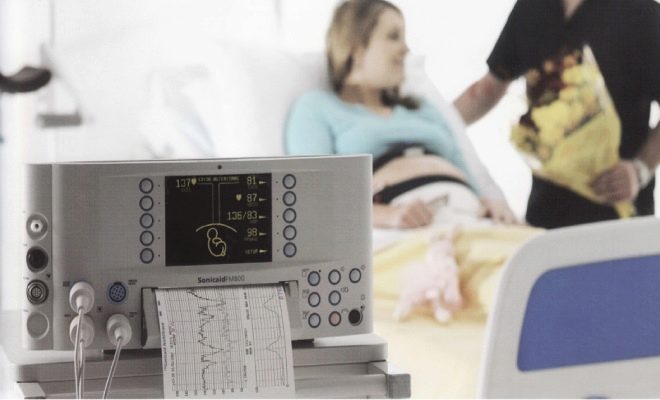
With the help of two sensors occurs measurement of several indicators simultaneously, which are considered together. This is the nature and frequency of the child's heartbeat, uterine contractions and fetal movement.
One of the sensors is a conventional ultrasound recorder. His task - to fix the heartbeat of the child.
The other sensor is called strain gauge, it is a wide belt with velcro that surrounds a woman. His task is to register uterine contractions (or labor contractions, if the method is used in the course of labor) by minor fluctuations in the abdomen volume. The same sensor "catches" and the movement of the fetus inside the uterus.
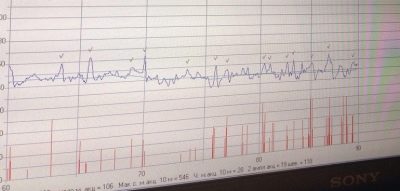
Record of indicators is made at the same time, synchronously in two schedules. On one - data on the child's heartbeat, on the second - uterine contractions and perturbations. The readings of the upper graph on the time scale fully correspond to the lower one, therefore all the parameters are interrelated.
The survey lasts from 30 minutes to 1 hour, sometimes the registration procedure indicators can be extended. Pass CTG in consultation at the place of residence, as well as in any clinic providing pregnancy management services.
Decryption and norms
With the advent of modern fetal monitors, the problem of deciphering difficult terms used in CTG has become a simpler task, because the device itself analyzes the data and gives a conclusion. In it, a woman always sees the most important thing - the cherished record “the fruit is healthy.” But such a record appears, alas, not always.
In addition, expectant mothers really want to know as much as possible about their son or daughter. We will try to explain what the records in the conclusion of cardiotocography mean and what the norms are.
Basal heart rate
Everyone knows that the heart of a child who has not yet been born knocks often - more than 110 beats per minute. But another discovery awaits a woman who first came to CTG - a small heart does not just knock quickly, it knocks at a different pace.
Almost every second the speed changes - 145, 150, 132 and so on.It would be difficult to determine the norm for a particular child, if not average value - The so-called basal heart rate.
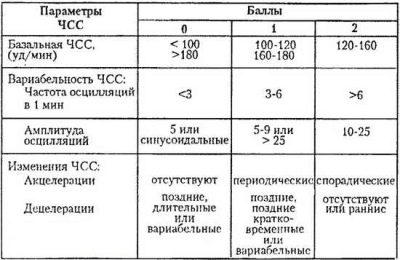
During the first minutes, the program analyzes all incoming values, and then determines the arithmetic average. Normal values for basal heart rate are values from 110 to 160 beats per minute. Excess may indicate tachycardia, heart rate below 110 beats per minute may indicate bradycardia. Both the increase and the decrease to the same extent can be physiological, and can indicate the child’s distress.
Many women mistakenly think that the baby’s heart rate changes by weeks, and therefore they are looking for a match at 33, 36 or 35 weeks gestation. The rates are the same for the entire third trimester. They do not depend on a specific term, and also can not indicate the sex of a child.
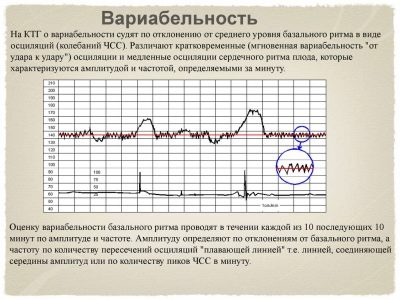
Variability, heart rate
As soon as the base value of the heart rate is derived, the program begins to record the variability or range of heart rate. Under this concept rhythm fluctuations are hidden to a greater or lesser side from the average value.
The readings can change quickly or slowly. Therefore, the oscillations themselves (or, as they are called in the medical environment, oscillations) are also slow and fast.
Rapid vibrations are almost a change in rhythm every second. Slow oscillations are of three types:
- Low - when the baby's heart changed the frequency of the rhythm per minute of real time by no more than three beats. Low episodes look like this: 145, 146, 147, 144, and so on. This phenomenon is called low variability.
- The average oscillations are characterized by a change in the rhythm of the heartbeat by 3-6 beats per minute, and high - more than six. Thus, fluctuations from a baseline value of 140 beats per minute in 60 seconds to values of 145 are the average variability, and up to values of 152 are high variability. Pregnancy rate is fast and high oscillations.
- In addition, a quantitative indicator of oscillations is estimated. A fetal heart rhythm is considered monotonous, in which, within a minute, the heart rate changed by no more than 5 beats. Transition is called the rhythm at which the change per minute occurred at 6-10 beats. The wavelike rhythm is characterized by a change of 11–25 beats, and a galloping rhythm - more than 25 beats per minute. Of all these parameters, a wavy rhythm is considered normal.
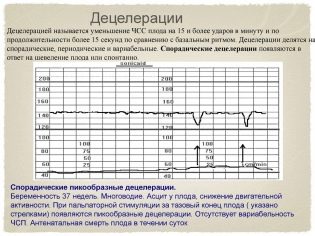
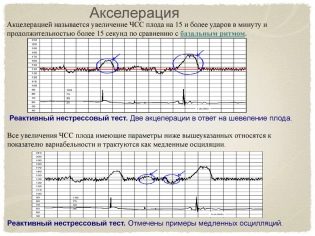
Deleration and Acceleration
These not very clear terms are actually very easy to visualize - these are the ups and downs (high and low episodes) on the chart. Future moms also call them cogs and dips. In this case, accelerations are called elevations, and decelerations, respectively, falls.
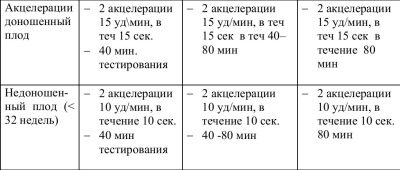
However, acceleration is not considered any increase in the frequency of the heartbeat of a child’s heart, but only such at which the frequency increased by 15 or more beats per minute and lasted at that pace for 15 seconds or more. By analogy with this, deceleration is a reduction in the frequency of 15 or more beats while maintaining the tempo for 15 seconds or more.
A normal and uncomplicated pregnancy is considered to be the norm with 2 or more accelerations in a ten-minute study. There should be no decelerations normally. But single falls at normal other indicators will not be regarded as pathology.
Fetal movements
This is the most controversial parameter of CTG, the rate of which is difficult to derive in certain values.
In the third trimester, children already have their own individual temperament, and some babies are more active, while others prefer to sleep more and gain strength before the upcoming births. That is why there is no rigid regulatory framework that would regulate the number of movements of the crumbs in the womb.
The weather, time of day, personal phases of sleep and rest, as well as the food of the mother, her hormonal background and many other factors can affect the baby’s desire to move. Therefore, it is believed that the child is quite healthy if during the time of the study he performs at least a few movements. For half an hour - three or more, for an hour - six or more.
It is important that the child not only demonstrated perturbations, but also showed a certain regularity between perturbations and accentrations., the so-called myocardial reflex. Normally, if each movement is accompanied by an increase in the frequency of the heartbeat.
Intense frequent movements may be a sign of hypoxia at the initial stage, rare movements may indicate that the crumb is just sleeping or has hypoxia in its advanced form. In general, this parameter in itself does not speak about anything and is always evaluated only in combination with the other norms of CTG.
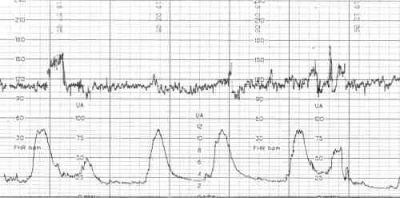
Uterine contractions
The strain gauge, which surrounds the abdomen of a pregnant woman during a diagnostic examination, is sensitive enough to detect even small changes in the abdominal circumference.
Even abbreviations that are not felt by the future mom at the physical level are “drawn” on CTG. Contractile activity is measured in percent: the higher their value, the more likely the onset of labor.
So, labor pains have a value of 98-100%, and training are at the level of 75-80%. If the delivery is still far away, and CTG showed 40%, there is no need to worry, these are normal natural contractions of the uterine muscles, which do not affect the condition of the fetus.
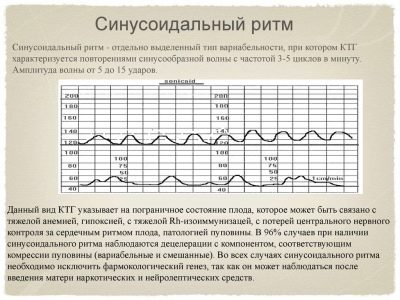
Sinusoidal rhythm
Such a heart rate in a child is recorded quite rarely, and this is good news, because the sinusoidal rhythm itself (when the graph looks like an alternation of sinusoids of equal height and duration) is a sign of a serious condition of the baby.
According to medical statistics, about 70-75% of children who show a sinusoidal rhythm on CTG before birth and it lasts for 15-20 minutes while being examined, are born dead or die immediately after birth.
Sinusoids on the chart appear in babies with severe hypoxia, severe forms of Rh-conflict, serious intrauterine infections that pose a threat to the life of the baby. Therefore the conclusion that states that sinusoidal rhythm = 0 min., means that the child is all right.
Stress and non-stress tests
At the top of the CTG report, a woman can see the inscription “non-stress test”. What does this phrase mean, to understand simply enough. The examination can be carried out as standard when the woman is at rest, and can be administered after physical exertion or the introduction of a small dose of the drug "Oxytocin" to the expectant mother, which causes contractions of the uterine muscles.
Regular cardiotocography is carried out in non-stress mode. This fact is displayed in the record "non-stress test".
If doctors need to arrange additional tests for the baby, he will conduct CTG under stress, but the parameters there will be very different.
CAP
Opposite this abbreviation in the conclusion about the passage of cardiotocography are the main values that are displayed by the program after analyzing all the above parameters. The indicator of the state of the fetus, this is how this value is interpreted - this is the total value.
Norm PSP - 1.0 and less. With such values, it is considered that the baby is comfortable enough, he has no manifestations of hypoxia and other unfavorable factors that may affect his well-being. If the conclusion states that the CAP exceeds the value of 1.1, but does not exceed 2.0, this indicates the initial violations in the state of the little one. Whatever these violations are, they are not considered dangerous to the life of the child. The expectant mother is recommended to visit CTG more often.
PSP values higher than 2.1 are considered dangerous. If the values are in the range of up to 3.0, the woman should be hospitalized and further examined, since such indicators are often found in babies experiencing severe rhesus conflict or hypoxia in utero.
PSP above 3.0 means fatal danger to the child. The future mother will be tried to be delivered as soon as possible, making her a cesarean section so that the baby has a chance to survive.
Reactivity Index
Under this phrase lies an attempt to assess the nervous activity of the fetus during the study. The reactivity index is the ability of the fetus to respond to external stimuli. This value has a close relationship with the number of perturbations: the more the child moves, the larger the number (0.80, 1.0, etc.) can be.
If a woman has no problems with the placenta and uterine blood flow, if the ultrasound showed no entanglement, then you should not pay attention to this index, because in itself, it is “technical information” that does not carry diagnostic value.
STV (short-term variation)
If a woman sees such a foreign abbreviation in her conclusion, you should not be afraid. This is just a mathematical value that evaluates fast oscillations (oscillations) over short periods of time. But if you really want to know what the STV rate is, we are ready to help you - normally the index should be more than 3 milliseconds.
If STV = 2.6 ms, experts estimate the risk of intrauterine injury and the likelihood of a child dying at 4%, but if the index drops even lower, the risks increase to 25%.
Score in points
Fisher Scoring Table
| What shows CTG | +2 points | + 3 points | |
Basal heart rate | Less than 100 units / min or more than 100 beats / min | 100-120 beats / min or 160-180 beats / min | 121-159 beats / min |
The nature of slow oscillations | Less than 3 beats / min | 3 to 5 beats / min | 6 to 25 beats / min |
The number of slow oscillations | Less than 3 for the study period | From 3 to 6 for the study period | More than 6 over the study period |
Number of acceptations | Not fixed | From 1 to 4 for half an hour | More than 5 in half an hour |
Nature of decelerations | Late or variable | Variable or late | Early or not fixed |
Fetal movements | Not fixed at all | 1-2 for half an hour | More than 3 in half an hour |
According to the results of CTG, a child can get a different number of points on this popular table in Russia. If the pussy scored 5 points or less, it is considered that he is in extremely distress, he is threatened with death.
If the score is from 6 to 8, there is a probability of initial violations, but in general the life of the crumbs is not in danger. If the child received 9-12 points - everything is fine with him.
findings
Expectant mothers should not look for which of the parameters in her opinion CTG is normal and which deviate from it. All the analysis for it is done with a special computer program. And the main indicator for women is PSP. In fact, it reflects the entire verdict.
If CTG does not work, if the indicators contradict each other, the doctor will ask you to come for an examination again. You should not worry, this is also not uncommon.
Alarming indicators of cardiotocography are not a reason to worry, but a reason to go in the direction of the hospital where the expectant mother will be examined, including ultrasound and laboratory tests, and will decide on delivery.
Such a variant of the completion of pregnancy, of course, can not suit any of the women. But in consolation it can be said that in terms on which passes KTG, the child is already quite viable, and having been born at 36, 37, 38 or 39 weeks, he will be able to cope with new circumstances.
Refusal of hospitalization on the occasion of "bad" CTG is the risk of losing the baby completely.
See how to interpret cardiotogram (CTG) in the next video.