Interpretation of CTG during pregnancy
During the child's birth, the future mother learns many new literal abbreviations for herself - ultrasound, BPR, DBK, HCG. They become clear and even familiar. In the last trimester, another diagnostic study, classified as CTG, is assigned to the “secret” in the letter code. His conduct usually does not cause questions, but only a few can decipher the results. How to understand what is written in the conclusion of CTG, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
Cardiotocography (this is how the name of the examination is deciphered) is a non-invasive, safe and painless way to find out the condition of the baby, how he feels. Such a survey is conducted starting from 28-29 weeks of pregnancy. Most often, future mothers refer to KTG for the first time at 32-34 weeks, and then the study is repeated immediately before the onset of the labor process.
During the birth itself, CTG is often used to determine if the baby has acute hypoxia during passage through the birth canal.
If the pregnancy proceeds well, there is no need for additional CTG. If the doctor has concerns that it is proceeding with complications, then CTG is prescribed individually, some of it has to be done weekly or even every few days. There is no harm from such a diagnosis either for the child or for the mother.
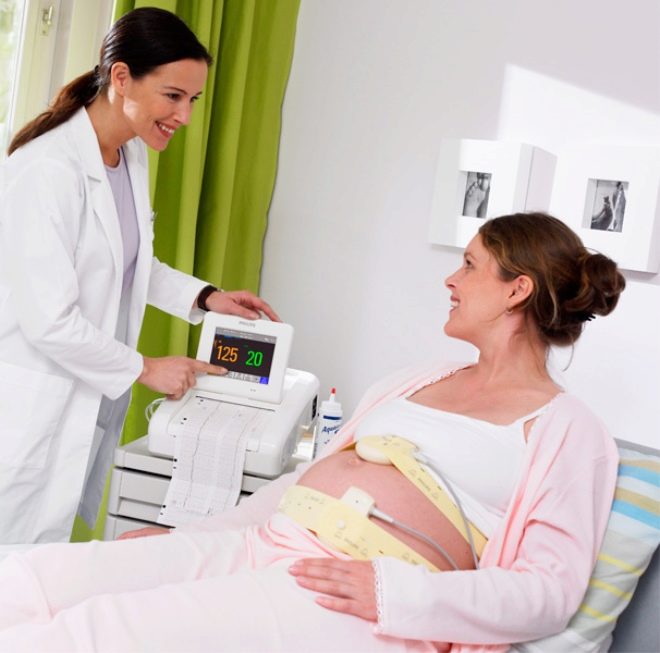
Cardiotocography allows you to find out features of the baby's heartbeat. The child's heart responds immediately to any adverse circumstance, changing the frequency of its heartbeat. In addition, the method determines contractions of the uterine muscles. Registration of changes occurs in real time, all parameters are recorded simultaneously, synchronously and displayed in graphs.
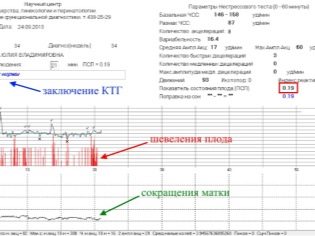
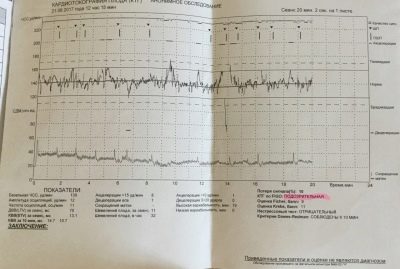
The first chart is a tachogram showing the baby’s heartbeat changes. The second is a graphic depiction of uterine contractions and fetal movements. It is called a hysterogram or togram (women often use the abbreviation "Toko"). The heart rate of the crumbs is determined by a highly sensitive ultrasonic sensor, and the tension of the uterus and perturbations are captured by a strain gauge.
The data obtained is analyzed by a special program that displays certain numerical values on the research form, which we will have to decipher together.
Technique of
The future mother should come to CTG in a calm mood, because any excitement and feelings of a woman can affect the heartbeat of her baby. It is advisable to pre-eat, go to the toilet, because the examination lasts a long time - from half an hour to an hour, and sometimes more.
It is necessary to turn off the cell phone, to sit comfortably in a pose that will allow you to spend the next half hour in comfort. You can sit down, lie down on a couch, take a reclining position of the body, in some cases, CTG can even be carried out while standing, as long as the expectant mother is comfortable.
An ultrasonic sensor is fixed to the abdomen in the area of the child's chest attachment, which will detect the slightest changes in the nature of the heartbeat and heart rate.
A wide belt is put on top of it - a strain gauge, which will determine the time when the uterine contraction or movement of the baby has occurred due to minor fluctuations in the abdomen's abdomen. After that, the program starts and the study begins.
At this stage, a pregnant woman may have two questions - what the percentages on the fetal monitor mean and what the sounds that are heard during CTG indicate. Let's help in this:
- Sounds during the study. The sound of the child's heartbeat, which is already familiar to the expectant mother, does not need explanation. Previously, ultrasound specialists have probably already given the woman a chance to listen to a small heart beating. During CTG, a woman, if the device is equipped with a speaker, will hear it constantly. Suddenly, a woman can hear a long loud sound, like a hindrance. So the baby moves. If the device suddenly starts beeping, it indicates a loss of signal (the baby turned and moved far from the ultrasonic sensor, the signal was disturbed).
- Percentages on the screen. Percentage refers to the contractile activity of the uterus. The more actively the main reproductive female organ is reduced, the more the doctor has reasons to hospitalize a woman. If the values are close to 80-100%, we are talking about the beginning of labor before labor. Indicators in the range of 20-50% to scare a woman should not - give birth to her just early.
Decoding results
To understand the abundance of numbers and complex terms is not as difficult as it seems at first glance at the result of CTG. The main thing is to understand and be well aware of what concepts we are talking about.
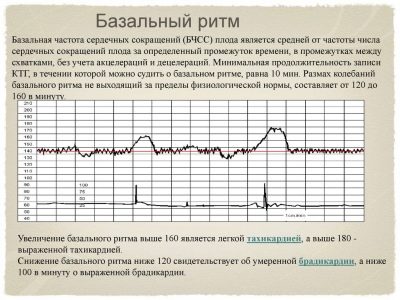
Basal heart rate
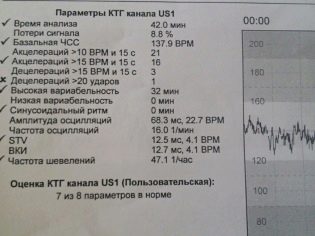
Basic, or basal heart rhythm - the average value of the baby's heart rate. The mother, who will come to CTG for the first time, may be surprised that the heart of the baby beats very unevenly, the indicators change with every second - 135, 146, 152, 130 and so on. All these changes do not slip away from the program, and in the first ten minutes of the survey, it displays the average value, which for a given baby will be basic or basal.
This parameter in the third trimester does not change depending on the particular week, as some pregnant women think. Both at 35-36 weeks, and at 38-40, the basal heart rate only reflects the average values of the frequency of the child's heartbeat and in no way indicates either the gestation period or the sex of the child.
The rate of basal heart rate is 110-160 beats per minute.
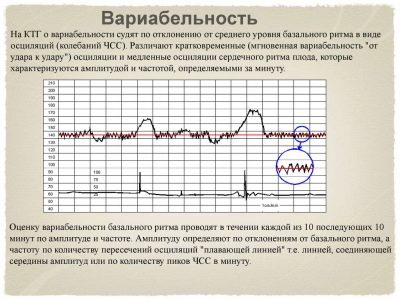
Variability
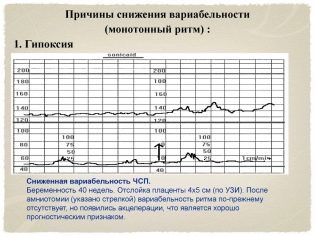
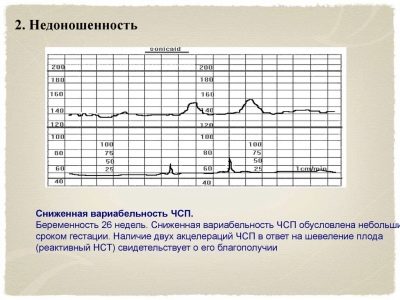
As can be understood from the sound of a word, this concept hides variants of something. In this case, the variants of deviation of the heart rate from the base values are considered. In medicine, another name for this phenomenon is used, which can also occur in conclusion - oscillations. They are slow and fast.
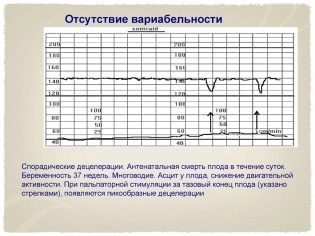
Fast reflect the slightest changes in real time, because, as already mentioned, each heart beat of the fetus displays a different heart rate. Slow oscillations are low, medium and high. If in a minute of real time, the frequency of contractions of a child's heart was less than 3 beats per minute, they speak of low variability and low oscillation. If the range per minute ranged from three to six beats, then we are talking about average variability, and if the fluctuations in one direction or another were more than six beats, the variability is considered high.
To imagine this more clearly, let us give an example: the device registered a change in the fetal heart rate from 150 to 148 per minute. The difference is less than 3 beats per minute, which means that this is a low variability. And if in a minute the heart rate has changed from 150 to 159, then the difference is equal to 9 beats - this is a high variability. The norm for a healthy baby with uncomplicated pregnancy is fast and high oscillations.
Slow oscillations are of several types:
- monotonous (changes in heart rate by five beats per minute);
- transients (heart rate per minute changes to 6-10 beats per minute);
- wavelike (heart rate changes by 11-25 beats per minute);
- galloping (more than 25 beats per minute).
If in a minute the jump in the heart rate looks like this: 140-142 beats / min, then it is a question of monotonous slow oscillation, if in a minute the heart rate changes from 130 to 160, then it is a question of a jumping slow oscillation. Wave-like oscillations are considered to be a normal value for a healthy baby, and other types almost always accompany various pathologies of pregnancy - entanglement with umbilical cord, hypoxia, rhesus-conflict.
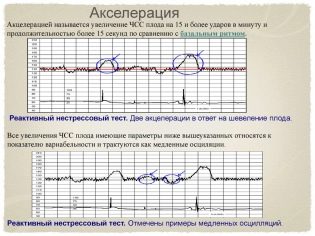
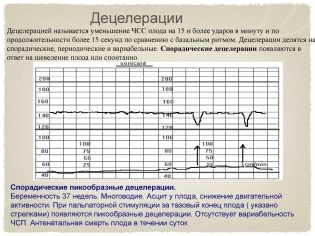
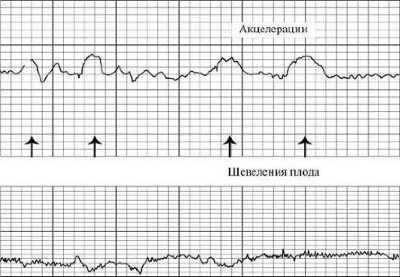
Acceleration and Deceleration
Quantitative change is oscillations, and qualitative change is acceleration and deceleration. Rhythm enhancement - acceleration. On the graph it looks like a peak, a jag. Rhythm deceleration - deceleration, is graphically depicted as peak top down, i.e. failure. Acceleration is an increase in the frequency of the baby's heartbeat by 15 beats per minute or more and the preservation of such a rhythm for more than 15 seconds.
Deceleration is a decrease in the value of the heart rate from the base value by 15 beats in the lower direction and the preservation of such a rhythm for 15 seconds or more.
In the activities themselves there is nothing bad if there are more than two of them recorded in 10 minutes. However, too frequent accelerations of equal duration and occurring at regular intervals are an alarm signal, the child is uncomfortable. Deleration (reduction) is not peculiar in principle to a healthy baby, but a small number of them with other normal indicators of cardiotocography may be a standard variant.
Stirrings
How much movement should be, the question is quite complicated, because there is no definite answer to it. All children have different physical activity, they are influenced not only by their own well-being, but also by factors that are not dependent on him - the mother's diet, her mood and emotional state, and even the weather outside the window.
If the baby wants to sleep at the exact moment when CTG is needed, his movements will be kept to a minimum.
Considered a good sign if during CTG a child has at least a few movements registered: in half an hour - at least three, in an hour - at least six. Too frequent abrupt movements - an alarming sign that can talk about violations in the condition of the crumbs. Too rare movements - not a good indicator either. However, if all the other CTG values are normal, the doctor will assume that the child simply slept through this entire hour, and will ask the woman to come for an examination again after a few days.
What is important is not so much the perturbations themselves, as the relationship between them and the number of accelerations. In a normal healthy child, with movement, the heart rate increases. If this connection is broken and the movements do not accompany the rise of the heart rate, and the accelerations themselves arise spontaneously and are not connected with the movement, the well-being of the child is called into question. On the graph, the perturbations look like dashes in the lower part, where the uterine contractions are marked.
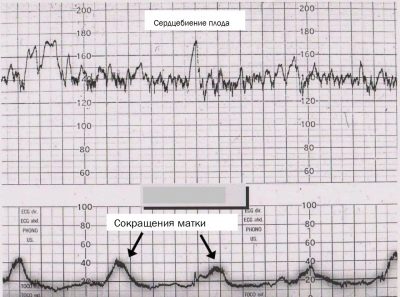
Uterine contractions
Abbreviations of uterine muscles are depicted in the lower graph. Visually, they look like undulating drops, because the reduction begins smoothly and ends no less smoothly. Do not confuse them with the movements, they are marked by short vertical lines. It is interesting that the strain gauge belt detects even those cuts that a woman does not physically feel.
Percentages mean contractile activity.
The uterus tone on CTG is definitely impossible, because the pressure inside the uterus can be measured only in one way - to insert a thin long sensor-electrode into its cavity, but this is impossible until the fetal bladder is intact and the labor has not started. Therefore, the value of the tone of the uterus constant - 8-10 millimeters of mercury are taken as the base rate. A program that analyzes all indicators on the contractility of the main female reproductive organ can “conclude” that this pressure is exceeded. Only then can the doctor suspect a tone, but manual paper on an gynecological chair and ultrasound will be needed to confirm.
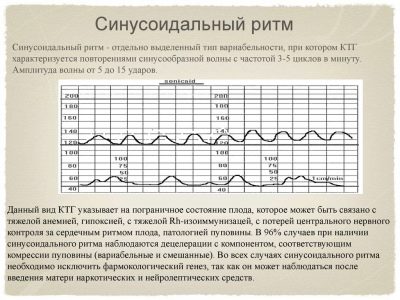
Sinusoidal rhythm
If the conclusion says “sinusoidal rhythm - 0 min”, then this is a very good indicator. Such a rhythm, indicated on the graph as sinusoids repeating at regular intervals, equal in duration, speaks of severe pathologies. At the same time, the number of accelerations and decelerations is minimal or absent altogether. If this graphic picture persists for about 20 minutes, doctors may suspect big problems.
Such a rhythm happens in children with severe uncompensated hypoxia, severe intrauterine infection, and strong Rhesus-conflict. Seven out of ten babies who showed a sinusoidal rhythm on CTG for 20 minutes or more die in utero or immediately after birth.
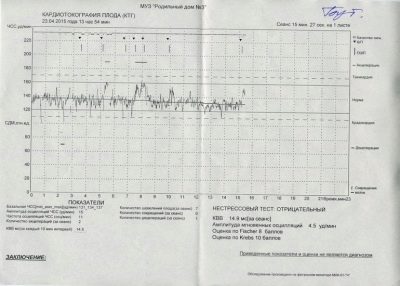
Table of norms of the main indicators:
Measured parameter | Normal value |
Base frequency heart rate | 108-160 beats / min at rest and 120-180 beats / min during stirring |
Variability | Instant high oscillations slow wave-like oscillations, total variability - 5-25 beats / min |
Number of acceptations | Not more than 15 beats / min, at least 2 times per examination |
Decoupling | Missing or do not exceed 15 beats / min |
Stirrings | 6 or more per hour |
Assessment of the fetus - points
To assess the condition of the fetus, doctors use methods of calculating the results in points. In women, they often cause well-founded questions, which means 4 or 5-6 points for CTG, which can be discussed by 10, 11 or 12 points. The interpretation depends on which method of counting the program operated on or how the doctor calculated the result if the evaluation was done “manually”.
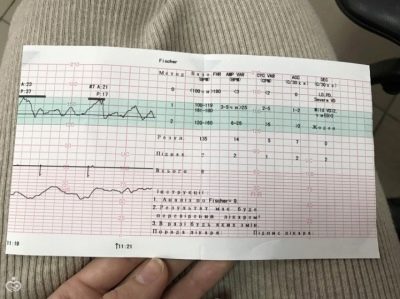
The most commonly used Fisher scoring system.
This is a twelve-point system in which a certain number of points is awarded for each indicator.
By fischer
Fisher scoring table (Krebs modification):
Determined on CTG indicator | Score 1 point if: | Score 2 points if: | Score 3 points if: |
Baseline heart rate | Less than 100 units / min or more than 100 beats / min | 100-120 beats / min or 160-180 beats / min | 121-159 beats / min |
Expressiveness of slow oscillations | Less than 3 beats / min | 3 to 5 beats / min | 6 to 25 beats / min |
The number of slow oscillations | Less than 3 for the study period | From 3 to 6 for the study period | More than 6 over the study period |
Number of acceptations | Not fixed | From 1 to 4 for half an hour | More than 5 in half an hour |
Decoupling | Late or variable | Variable or late | Early or not fixed |
Stirrings | Not fixed at all | 1-2 for half an hour | More than 3 in half an hour |
Interpretation of the results is as follows:
9.10, 11, 12 points - the child is healthy and feels quite comfortable, his condition does not cause concern;
6.7.8 points - the baby’s life is not in danger, but his condition is worrying, since such an indicator may be a sign of initial pathological changes and adverse external influences. Women should do CTG more often to keep track of the baby over time;
5 points or less - The child’s condition is threatening, there is a high risk of fetal death, stillbirth, neonatal death in the early postpartum period. A woman is sent to a hospital where urgent diagnostics is carried out and in most cases everything ends with an emergency cesarean section in order to save the baby's life.
According to FIGO
This assessment table was adopted by the specialists of the International Association of gynecologists and obstetricians. It is less commonly used in Russia than the Fisher estimate, but is more understandable for future mothers.
FIGO interpretation table:
Parameter determined on research | Value - “norm” | Meaning - “doubtful” or “suspicious” | Meaning - "pathology" |
Basal heart rate | 110-150 beats / min | 100-109 beats / min or 151-170 beats / min | Less than 100 or more than 170 beats / min |
Variability | 2-25 beats / min | 5-10 beats / min in 40 minutes | Less than 5 beats / min for 40 minutes or sinusoidal rhythm |
Acceleration | 2 or more in 40 minutes | During the 40-minute survey are absent | Absent altogether |
Decoupling | Not recorded at all or there are rare variable | Variable | Variable or late |
CAP
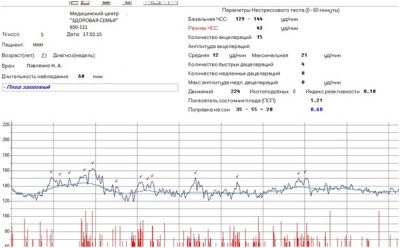
This is a key value that is derived from all measured and analyzed parameters.
It stands for "the indicator of the state of the fetus."
It is very difficult to visualize by what algorithms and mathematical formulas this calculation takes place if there is no diploma of mathematics on the shelf at home. This is not required. It is enough for the future mother to know which PSP indicators are normal and what they mean:
PSP less than 1.0. This result means that the baby is healthy, he is comfortable, his state of health and condition are not disturbed. This is a good result, in which the doctor sends the pregnant woman with CTG home with a clear conscience, because nothing bad should happen to the baby.
PSP from 1.1 to 2.0. Such a result indicates likely initial changes that are different from normal feeling. Violations with such a CAP are not deadly, but they can not be ignored. Therefore, women are asked to come to CTG more often, on average, once a week.
PSP from 2.1 to 3.0. Such indicators of the condition of the fetus are considered very alarming. They may indicate severe discomfort that a child experiences in the womb. The cause of the trouble of the baby can be Rh-conflict, a state of oxygen deficiency, entanglement of the umbilical cord, intrauterine infection. Pregnant sent to the hospital. She is shown a more thorough examination and, possibly, early delivery by cesarean section.
PSP above 3.0. Such results may indicate that the child’s condition is critical, it is threatened with fetal death, which can occur at any time. A woman is hospitalized on an urgent basis, emergency caesarean section is shown to save the baby.
Stress and non-stress tests
Plain CTG, which takes place during pregnancy, is considered to be a non-stress test. But sometimes the situation requires a more careful and detailed study of the features of the work of a small children's heart, for example, with an unsatisfactory result of the previous CTG or with suspected heart defects of the child, then stress tests are performed.
The study in this case is technically carried out in the same way as always, but before attaching sensors to the future mother's belly, she may be asked to walk up and down the stairs several times, breathe deeply and occasionally hold her breath during cardiotocography.
Sometimes, in order to understand how a child’s heart and nervous system will behave in a stressful situation, a woman is given an injection of oxytocin, a drug that causes contractions of the uterine muscles.
Non-stress test eliminates provoking external factors. A woman, on the contrary, is asked to calm down, sit comfortably, not think about anything disturbing and bad. It analyzes how the baby’s heart responds to its own movements, that is, the number of accelerations is calculated.
Deciphering stress CTGs is a task for specialists; the conclusion of the analyzer program alone will not be enough, doctors must make allowances for stress factors. A good result is a negative non-stress test, during which the baby “shows” two or more accelerations in 40 minutes.
Possible problems
The problems that such examination as cardiotocography may indirectly indicate can vary from congenital malformations to pathologies of pregnancy or external adverse factors that a woman herself is exposed to.But they will all be accompanied by one of the following deviations.
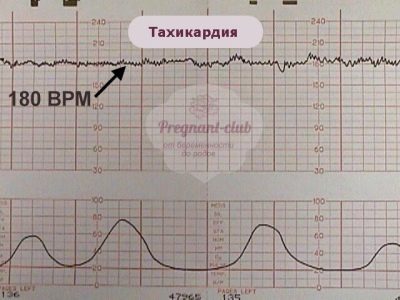
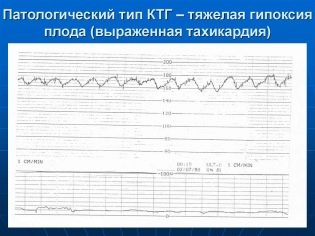
Tachycardia
Such a state can be said if the basic rhythm of the heartbeat exceeds the established norms, and the duration of the violation is 10 minutes and more. Mild tachycardia is indicated by an increase in heart rate to 160-179 beats per minute. Severe tachycardia is considered when the baby's heart beats with a frequency of 180 beats per minute and above.
The most common cause is fetal hypoxia. With an oxygen deficiency, the child begins to experience stress, his hormonal changes are changing, because of this, the heart begins to knock faster. But this is only in the early stages of hypoxia. With severe oxygen deficiency, the baby behaves differently.
Tachycardia is often a companion of intrauterine infection, which struck the baby. Almost like a child born, a crumb in my mother's stomach can get sick. His immune protection will start working, and despite the fact that it is still very weak, the temperature will rise, and this will also immediately affect the heart rate. The cause of the child's tachycardia may also be the unwellness of his parent. If a woman has a fever, then the child has a stronger heart beat.
Also, the heart rate of the fetus is influenced by medications that his mother takes and any violations of her hormonal background.
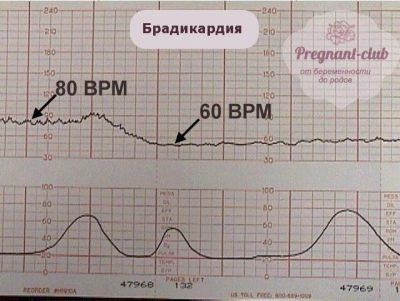
Bradycardia
If the cardiotocography shows that the heart of the baby for 10 minutes or more beats with a frequency below 100 beats per minute, doctors diagnose bradycardia. This is a dangerous symptom that may indicate severe uncompensated hypoxia, in which oxygen deficiency is already critical, the child does not have the strength to move. If the slowing down of the heart rate is fixed on CTG at the time of delivery, then there is nothing dangerous about it, because decrease in heart rate baby reacts to the passage through the birth canalwhen his head is pressed.
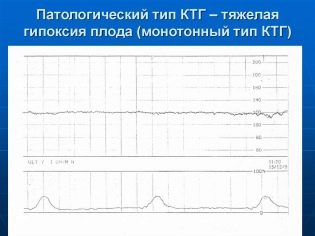
Fetal hypoxia
Oxygen starvation can be very dangerous for a child at any time, it leads to violations of the central nervous system, and sometimes to the death of the fetus. Early hypoxia, while it is still compensated by the protective mechanisms of the baby’s body, is characteristic of tachycardia, and late hypoxia, hypoxia in the advanced stage, is bradycardia. In addition, CTG shows low variability, the same periodic acceleration, sinusoidal rhythm, monotony.
PSP in this situation is in the range of 1.1 - 3.0. According to Fisher, the child’s condition is estimated at 5–8 points, depending on the severity of oxygen deficiency. In severe hypoxia, an urgent delivery is indicated, regardless of how long the pregnant woman is at 37 weeks or only at 33 weeks. The chances of surviving such a baby’s mother’s womb will be greater anyway.
Can it be wrong?
Cardiotocography is not a high-precision diagnostic test. Its accuracy is approximately at the level of 90%, and much depends on how well the examination was conducted, and also on the experience of the doctor and whether he will be able to interpret the results correctly. In general, CTG is the same for everyone. But the reasons that led to the deviations of those or other normative values can be very diverse.
Therefore, it is impossible to treat the conclusion of CTG as the ultimate truth. The survey gives only a general picture., but to confirm or refute the negative results, as well as to establish the reasons for the unusual behavior of the baby will only help additional diagnostics.
Typically, this laboratory blood tests, ultrasound scanning, ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound).
An erroneous CTG may be due to the fact that the woman was not prepared for the examination - she didn’t sleep, she was worried about her personal problems. The doubtful truthfulness of CTG is also seen if the pregnant woman took any medications and did not warn the doctor about this, because some drugs can significantly increase and decrease the heartbeat of not only the mother, but also the fetus.An erroneous CTG may be in the event of a malfunction of the equipment on which the study is conducted.
All questionable results are therefore necessarily rechecked by repeated CTG, as well as using ultrasound. All the bad results of CTG are also rechecked, but already in the hospital, so as not to risk the health of the mother and child.