Why is colostrum released during pregnancy and at what time it occurs most often?
Colostrum during pregnancy in different women appears at different times. In some, earlier, in others, immediately before birth. And not always the future mother understands the mechanisms of his education and purpose, because before the birth of the baby there is still so much time.
In this material, we will talk about what constitutes colostrum, when it normally stands out and whether it should be squeezed out.
What it is
Colostrum is a dense secretion of the mammary glands. It is produced in all mammals: cats, dogs, cows and goats. People are no exception. A few days after giving birth, thick and viscous colostrum is replaced first by transitional milk, and then by full breast milk, which in medicine is called mature.
In pregnant women, colostrum is released under the influence of the changed hormonal background, because the mammary glands of the expectant mother begin to rearrange themselves for the upcoming breastfeeding in advance. Colostrum is a thick, sticky, brackish liquid.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it can be transparent, a little later its color changes to various shades of yellow, closer to the birth, the colostrum begins to lighten again, to become white and opaque after birth, becoming a transitional milk. It usually takes from 2 to 5 days.
Colostrum is completely unlike milk: they have nothing in common either in composition or in consistency or in properties. By its chemical structure, this liquid is more like the composition of blood. Despite the fact that in late periods and immediately after birth it looks almost like breast milk, it differs in color and quantity.
The most important function is assigned to colostrum by nature - it should provide the child with a smooth transition from feeding through the placenta to feeding in the usual traditional way. Colostrum will give the crumbs the necessary protective antibodies, antitoxins, so that the tiny body can survive as much as possible the tremendous stress with which its birth into this world and its adaptation to completely different conditions of existence will be associated.
Composition and properties
In terms of its energy value, colostrum significantly exceeds breast milk and any artificial milk formulas. It is thick and viscous, there is not enough water in it (an excessive load on the weak kidneys of the newborn will not benefit him).
But the density of nutrients in it is several dozen times higher than in high-grade breast milk, which the baby will be fed about a week after his birth.
Colostrum not only effectively removes the feeling of hunger, nourishes the baby, but also contributes to a soft and fast bowel movement.. It contains natural laxatives that help the baby in the very first day to release the intestines from meconium - the original feces of a dark green color, which accumulated in it even during the prenatal period of development.
Colostrum mitigates the effects of red blood cell destruction: it reduces the level of bilirubin, as a result of which the baby may not have physiological jaundice, or it will flow in its softest and simplest form.
If we consider colostrum from the point of view of chemical composition, then, in essence, it is a mixture of easily digestible proteins - albumin and globulins. Unlike regular milk, colostrum contains less goat, lactose and fats, which are quickly absorbed.It contains a large amount of natural antioxidants - vitamins A and E, as well as zinc and selenium.
Besides the fact that these substances are involved in the prevention of "oxygen stress" in the newborn, they also help the difficult processes of establishing the independent work of children's immunity.
By chemical composition and properties, colostrum has no analogues in nature - it is a unique, valuable and important fluid, which increases the chances of a newborn to survive and normal subsequent development.
Protective factors
Everyone knows that with breast milk, the mother transmits antibodies to her child, which in the first months of his life form passive (or innate) immunity. But not everyone knows that the content of immune factors is higher in colostrum than in milk. In particular, this applies to substances such as: immunoglobulin A, lactoferrin. Colostrum is rich in living macrophages, leukocytes, neutrophils and lymphocytes.
All these "tenants" of a secret of a mammary gland do not participate in digestion of the baby, are not digested by its organism. They, getting into the stomach, remain in the gastrointestinal tract, it is there that they come to "alert", protecting the baby from the invasion of pathogenic bacteria and aggressive viruses that penetrate through the mouth.
T-lymphocytes in the composition of colostrum exceed in number the number of similar cells in the blood. Leukocytes from colostrum are able to help the child form protection against viruses. Some polysaccharides, which are part of the secretion of the mammary glands, play the role of antiklei - they prevent the attachment of harmful microorganisms to the intestinal walls and mucous membranes of other organs.
Laboratory studies have demonstrated interesting facts: It turns out that female colostrum is a unique natural antibiotic and antiviral agent “in one bottle”. It is actively opposed to Escherichia coli, salmonella, cholera pathogens, dysentery bacillus, and can also destroy the structure of many viruses - rotavirus, Koksaki, polio pathogen, herpes virus.
That is why it is customary to apply the baby to the breast even in the delivery room so that from the first minutes of life in a world filled with bacteria and viruses, it is ready to give them a rebuff.
From this point of view, it is important to put the baby to the breast in the first days after birth, even if there is no milk yet. Even a few drops of colostrum is quite enough for the crumb to be saturated, because all its energy needs will fully satisfy this fluid, moreover, these days are very important for future health.
The immunity of the children who were given colostrum is always stronger and stronger than the immunity of the children who were given donor milk or artificial adapted milk formulas from the first days. And this means that such children get sick less easily and grow stronger and stronger.
Causes of
Under the influence of progesterone from the very first hours after conception of the baby in the body of the future mother, who doesn’t realize at all what is really happening, large-scale changes begin. They concern also mammary glands.
Of course, other hormones help progesterone. That is why sometimes a woman begins to guess about the accomplished conception before the menstruation is delayed - due to the characteristic swelling of the breast and pain in the nipple area.
The ducts located inside the mammary gland, gradually expanding, glandular tissue grows, which is why the breast increases in size. Colostrum begins to be produced by the mammary gland when the level of the hormone prolactin allows it.
Prolactin increases gradually, which is why some women get colostrum in the first trimester, and others only for a couple of months before childbirth. The pituitary gland “knows” prolactin, the process itself is the first stage of lactogenesis.
Very often, a pregnant woman can hear the opinion that a small amount of colostrum during pregnancy can be a sign of future problems with the amount of breast milk. This statement is an error or profanation.
Neither the quantity, nor the quality, nor the color of the colostrum, nor its absence or presence during the period of gestation of a child, affect how much milk will be after birth. After the baby is born, the second stage of lactogenesis will begin, during which colostrum will begin to change the chemical composition under the action of oxytocin.
In some women, colostrum does not appear during pregnancy, it begins to stand out only after childbirth, and this in no way affects lactation - such moms do well in breastfeeding their babies.
Terms of appearance
There are no uniform norms regarding the period at which gestation, which week the release of colostrum should begin, does not exist. In primiparous women, whose prolactin levels are initially small and their nipples are stronger, colostrum may begin to stand out shortly before birth or even after them.
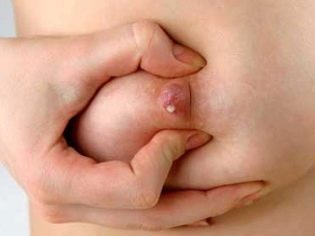
In this case, the chest will hurt, swell and in earlier periods, it is possible that when pressing on the nipples, a small, barely noticeable amount of thick liquid will be released.
Most often, primiparous women indicate that the first signs of the appearance of colostrum were found in them at about 10–12 weeks of gestation. More often indicated time - 16-18 weeks. It did not flow out to the majority and was found exclusively by mechanical pressure on the nipple with fingers on both sides.
If a woman already has experience of breastfeeding, she had a birth, then in subsequent pregnancies colostrum will arrive earlier. The fact is that the level of prolactin in the body of a woman who has given birth is always higher than that of a non-birth woman. In addition, the ducts of the mammary gland are already dilated after the firstborn, and therefore the colostrum will be more, it can leak, causing hygienic inconvenience to the woman.
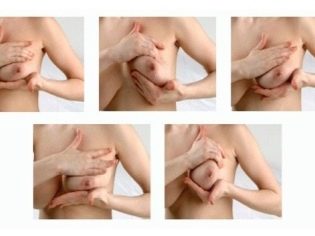
Is it possible to squeeze?
The answer to this question is unequivocal - it is strictly prohibited to squeeze the colostrum. With mechanical stimulation of the nipples, the production of oxytocin, a hormone, is activated, which leads to the smooth muscles of the uterus. Increased tone creates a threat of miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth at a more significant period of gestation.
Increased uterine tone increases the likelihood of developing placental insufficiency, and also contributes to the development of oxygen starvation of the fetus.
From this point of view, it is necessary to avoid not only extrusion of colostrum, but also accidental mechanical action on the nipples, for example, during massage, washing the mammary glands, preparing them for breastfeeding, during sex. Oxytocin levels can increase with hot drinks and hot baths.
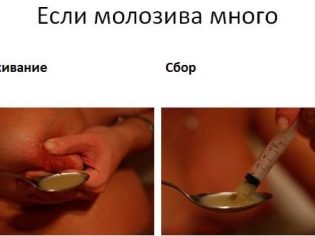
The extrusion of colostrum does not make sense even after childbirth - usually the processes of lactogenesis proceed independently. The exceptions are cases when a woman already has transitional milk, and her nipples are too “tight” and the baby cannot “dissolve” them.
Also, pumping is shown when converting colostrum into milk in the absence of the opportunity to fully feed the baby (the child eats little, the nipples have individual anatomical features, in which their capture by the child is difficult, and also if the baby is not brought to the feed (he is in intensive care or )). Stinging in this case will stimulate the production of milk, and then the child will not need a full, healthy and much-needed nutrition.
If colostrum occurs during pregnancy intensively, soils pregnant clothes and underwear, it is best to use a special bra. Such sew especially for nursing mothers.They provide space for liners that will absorb excess liquid, preventing unpleasant stains on clothing.
Possible problems
Colostrum, which was unexpectedly gone, may be an indirect sign of a frozen (non-developing) pregnancy. Together with the disappearance of colostrum, other symptoms of the “interesting situation” usually disappear - toxicosis, increased appetite. At a later date - the fetal movements stop, his heartbeat is not heard.
It should be noted that in the case of fetal death, the colostrum does not disappear immediately, but a few days after the tragedy. In the early stages a woman may not feel the death of the fetus for a long time. Therefore, the disappearance of colostrum should alert the pregnant. Be sure to visit your doctor and undergo an urgent examination.
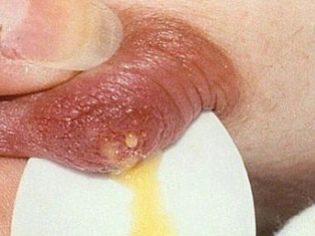
If a woman in the colostrum notices pinkish impurities, as well as fragments of blood, do not panic. The secret of the mammary glands with blood may be a variant of the physiological norm. This is due to the expansion of the milky ducts. Sometimes this process is so intense that the capillaries (small blood vessels) do not stand up and burst. So in the colostrum appear blood impurities.
But if the colostrum has become greenish, gray, on the nipples are formed crusted crusts from such a liquid, the colostrum has acquired an unpleasant odor, then this may indicate an infection, most often a bacterial infection. At the same time, the chest becomes more painful, and touching it causes great anxiety.
Such pathological changes can be a sign of mastitis, staphylococcal infection, tumor in the mammary gland. The most attentive should be women who have previously undergone surgery on the breast.
When changing the color and smell of the secretion of the mammary glands should immediately consult a doctor, get tested and receive treatment. Many problems are successfully solved even during pregnancy, if the doctor prescribes proper and proper treatment on time.
Reviews
In Internet-themed forums, pregnant women often deal with issues of the presence or absence of colostrum in the process of carrying a baby. However, the comments are so contradictory that they themselves confirm the fact that colostrum does not affect the amount of breast milk.
Often pregnant women are faced with the problem of removing dry "dried" crusts on the nipples. Experienced mothers recommend soaking them with warm water and not trying to remove them in any way - this increases the likelihood of injury to the nipples, cracking, and microscadins. If bacteria then get into them, then severe inflammation cannot be avoided, because colostrum is a good nutrient medium rich in proteins.
In case of abundant release of colostrum, it is best for women to carry dry liners and a pack of wet wipes with them so that hygiene procedures are available at any place and at any time.
By the way, the quality of nutrition and the amount of liquid drunk do not affect the quantity and density of colostrum either. This is the answer to another common question for pregnant women.
For the properties and causes of colostrum, see the following video.