What should be the weight gain during pregnancy?
You can often hear that a pregnant woman needs to eat for two. From the point of view of medicine, this statement has nothing to do with the truth. There are two - it means quickly gaining body weight. And while carrying a baby extra pounds - an additional burden on the mother's body and high risks of complications. What should be a normal weight gain in different periods of pregnancy, we will tell in this material.
Why does pregnancy increase in weight?
Weight during pregnancy is a fairly individual criterion. In some women, it may decrease in the first and third trimesters, for example, if strong toxicosis is observed. For others, weight is constantly growing. Initially, the weight of the future mother depends on her body and body weight before pregnancy.
For obese women, the total weight gain during pregnancy may be two times less than the total weight gain for skinny, slender girls.
Weight in varying degrees during the period of carrying a child grows constantly. However, the body weight of newborn boys and girls is on average the same - from 3,000 to 4,000 grams. It does not depend on how many women scored for pregnancy - 5 or 15 kilograms. Various increases - an individual trait of expectant mothers.
The growth of body weight consists of several components:
- Kid. Its weight is about a third of the whole mother's increase. Usually babies are born with a weight of 2500 to 4000 grams.
- Placenta. On average, about 5% of the total weight of the pregnant woman is allocated to the “baby seat” The placenta usually weighs about half a kilogram - from 400 to 600 grams.
- Amniotic fluid. Waters in which the baby swims reach a weight of one and a half kilograms by the third trimester. True, closer to childbirth, their number decreases, as does weight. The mass of amniotic fluid is about ten percent of the total increase.
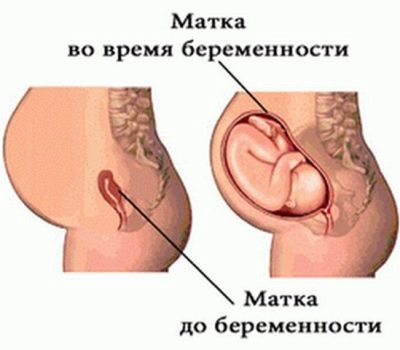
- Uterus. The main reproductive organ of a woman is constantly growing, so that the baby can fit in it until the very birth. The weight of the uterus at the end of the gestation period reaches a full kilogram, and this is about 10% of the total increase.
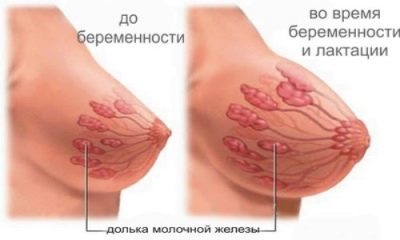
- Chest. The female breast begins to undergo changes from the very first weeks of pregnancy, and for childbirth it most often increases significantly due to the overgrown glandular tissue. It is easier for women to imagine these changes in volume.
But we are talking about weight, and therefore it is worth taking into account that the weight of the grown breast is on average about 600 grams, which is about 2-3% of the total weight gain of the expectant mother.
- Blood volume In a pregnant woman's body, the volume of free circulating blood is about 2 times increased compared with non-pregnant women. On average, the mass of blood that the future mother's heart pumps is about one and a half kilograms.
- Cellular and intercellular fluid. Their weight in the body of the future mother may be close to 2 kilograms. And along with the volume of blood we talked about above, fluids make up about a quarter of the total weight gain.
- Fat reserves. The body of a pregnant woman in advance begins to take care of putting off fat as an energy source for the upcoming delivery and the postpartum period. Fat in the body of the future mother is deposited about 3-4 kilograms, which is about 30% of the total weight gain.
Changes in body weight
Dynamics of growth of body weight of a pregnant woman is not the same at different times:
- During the first half of the gestation period, a woman on average gains about 40% of the total increase.
- For the second half of pregnancy, the increase is about 60% of the total number of kilograms acquired during the entire period of the child's bearing.
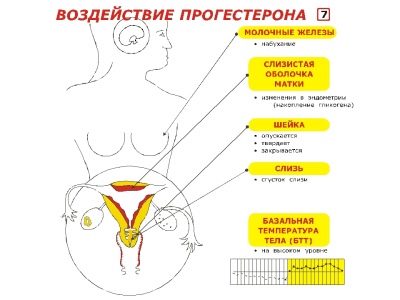
In the early stages, the hormone progesterone is responsible for the accumulation of fat. It starts up a lot of processes in the future mother's body, aimed at the preservation and further development of the embryo. Creating a fat “reserve” is also one of the mechanisms for the preservation and well-being of the fetus.
In the second trimester, the placenta begins to actively grow and develop, the amount of circulating blood increases, which invariably leads to an increase in body weight. Even if in the first trimester there was a weight loss due to toxicosis and lack of appetite, in the middle of pregnancy, when nausea subsides, the woman will be able to gain everything that was not collected in earlier periods.
In the third trimester, the amount of amniotic fluid begins to decrease, but the weight continues to come due to the fact that the child is actively gaining weight. Only in the last two or three weeks the weight begins to decrease somewhat, since the child has already gained its weight, and the amount of amniotic fluid has reached its minimum. In addition, the body of a pregnant begins to prepare physiologically for childbirth, at the natural level, freeing himself from all that is superfluous, which may prevent him from giving birth.
Rates of increase - how to calculate?
A normal increase depends on how much weight the woman had before pregnancy. For a woman with her own normal weight, an increase from 10 to 15 kilograms for the entire gestation period is considered correct. If a woman's own weight is slightly exceeded, her normal increase can be considered a weight not exceeding 11 kilograms. In obese women in nine months, the weight should increase by no more than 7-8 kilograms.
Correctly do the calculation of the individual increase will help the doctor, who will take into account all the factors affecting the weight of this future mother - its complexion, the presence of multiple pregnancy, etc.
On average, for the first trimester, a supplement of 200 grams per week is considered the norm. Up to 12 weeks, the weight of a woman should increase as much as 3-4 pounds. In the second trimester, when the appetite improves, and toxicosis, if it was, retreats, the increase is more intense - up to 400 grams per week. At the very end of pregnancy, the increase is usually not more than 100-150 grams per week.
During the first visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist, when a woman applies for registration, she will be measured in height and weight.
If the expectant mother knows her parameters before pregnancy, you should definitely report them to your doctor.
Based on these two values, the doctor will calculate the BMI (body mass index), which will allow to judge the correct or excessive weight gain during the entire pregnancy. Body mass index is weight divided by height squared.
For example, a woman’s weight is 55 kilograms, and her height is 1 meter 60 centimeters. The calculations will look like this: 55 / (1.6 ^ 2). It turns out that this woman's BMI is approximately 21.5. This corresponds to a normal weight, and an increase of 10-13 kilograms in this case will not be considered pathological.
Depending on how the BMI turns out, the woman will establish the maximum allowable limit of increase:
- A BMI below 18.5 is underweight, for such a woman, weight gain during pregnancy can reach up to 18 kilograms, and this will be quite normal;
- BMI from 18.5 to 25 is a normal weight, the increase can be from 10 to 15 kilograms;
- BMI from 25 to 30 - overweight, the increase should not exceed 9-10 kilograms;
- A BMI of 30 and above is obesity, and weight gain above 7 kilograms for the entire gestation period will be considered pathology.
If a woman bears not one baby, but twins or triplets, then the norms of addition will be completely different in comparison with a singleton pregnancy.
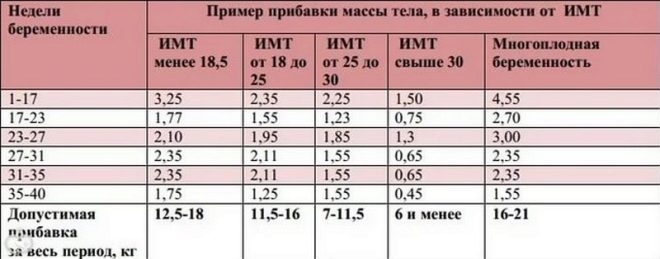
Rate of increase for the entire period - table:
BMI | One fruit | Twins or Triplets |
Less than 18.5 | 13 -18 kg | 18-27 kg |
From 18.5 to 25 | 10-15 kg | 17-25 kg |
25 to 30 | 8-11 kg | 15-23 kg |
Over 30 | 6-7 kg | 10-19 kg |
When calculating the individual norm, different women's clinics use different norms for the ratio of real weight to body mass index. We have reviewed the most popular rating system above. However, in some consultations, doctors use a different system, an international one, according to which a BMI below 19.8 is considered normal weight, above 19.8 to 26 - overweight, and above 26 - obesity.
The body mass index itself is calculated exactly the same as above. Based on the results obtained, it is possible to calculate the individual increase by weeks and months. Depending on which system the BMI was calculated for, the rates of increase may look like this.
Addition table for weeks according to different BMI calculations:
Duration of gestation, weeks | BMI less than 18.5 (kg) | BMI from 18.5 to 25 (kg) | BMI over 30 (kg) | BMI less than 19.8 (kg) | BMI from 19.8 to 26 (kg) | BMI over 26 (kg) |
2 | 0 — 0,2 | 0 – 0,1 | 0 – 0,1 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
3 | 0 — 0,4 | 0 — 0,3 | 0 — 0,2 | 0,7 | 0,6 | 0,5 |
4 | 0 — 0,9 | 0 — 0,7 | 0 – 0,5 | 0,9 | 0,7 | 0,5 |
5 | 0 — 1,2 | 0 — 0,8 | 0 — 0,6 | 1,2 | 0,9 | 0,5 |
6 | 0 — 1,4 | 0 – 1 | 0 — 0,6 | 1,4 | 1 | 0,6 |
7 | 0, – 1,5 | 0 — 1,1 | 0 — 0,6 | 1,5 | 1,1 | 0,6 |
8 | 0 — 1,6 | 0 — 1,2 | 0 — 0,7 | 1,6 | 1,2 | 0,7 |
9 | 0 – 1,7 | 0 — 1,2 | 0 — 0,7 | 1,7 | 1,2 | 0,7 |
10 | 0 — 1,8 | 0 — 1,3 | 0 — 0,8 | 1,8 | 1,3 | 0,8 |
11 | 0 — 1,9 | 0 — 1,4 | 0 — 0,9 | 1,9 | 1,4 | 0,8 |
12 | 0 – 2,0 | 0 — 1,5 | 0 – 1 | 2,0 | 1,5 | 0,9 |
13 | 0 — 2,4 | 0 — 1,8 | 0 — 1 | 2,4 | 1,7 | 0,9 |
14 | 0,5 — 2,7 | 0,5 — 2,0 | 0,5 — 1,2 | 2,7 | 1,9 | 1 |
15 | Not more than 3.3 | No more than 2.6 | Not more than 1.2 | 2,9 | 2,1 | 1,2 |
16 | No more than 3.6 | No more than 3 | No more than 1.4 | 3,2 | 2,3 | 1,4 |
17 | No more than 4.1 | No more than 3.5 | No more than 1.8 | 4,1 | 3,0 | 1,9 |
18 | No more than 4.6 | No more than 4 | No more than 2.3 | 4,5 | 3,6 | 2,3 |
19 | No more than 5.3 | Not more than 4.9 | No more than 2.6 | 5,0 | 4,2 | 2,6 |
20 | No more than 6 | Not more than 5.8 | Not more than 2.9 | 5,4 | 4,8 | 2,9 |
21 | Not more than 6.6 | Not more than 6.4 | No more than 3.1 | 6,1 | 5,3 | 3,1 |
22 | Not more than 7.2 | Not more than 7.0 | No more than 3.4 | 6,8 | 5,7 | 3,4 |
23 | Not more than 7.9 | Not more than 7.8 | No more than 3.6 | 7,2 | 6,0 | 3,6 |
24 | No more than 8.6 | Not more than 8.5 | Not more than 3.9 | 7,7 | 6,4 | 3,9 |
25 | Not more than 9.3 | Not more than 9.3 | No more than 4.4 | 8,1 | 7,0 | 4,4 |
26 | No more than 10 | No more than 10 | No more than 5 | 8,6 | 7,7 | 5,0 |
27 | Not more than 11.8 | Not more than 10.5 | No more than 5.2 | 9,2 | 7,9 | 5,2 |
28 | No more than 13 | No more than 11 | No more than 5.4 | 9,8 | 8,2 | 5,4 |
29 | Not more than 13.5 | Not more than 11.5 | No more than 5.7 | 10,0 | ||
30 | No more than 14 | No more than 12 | Not more than 5.9 | 10,2 | 9,1 | 5,9 |
31 | Not more than 14.5 | Not more than 12.5 | Not more than 6.1 | 10,7 | 9,6 | 6,1 |
32 | No more than 15 | No more than 13 | Not more than 6.4 | 11,3 | 10,0 | 6,4 |
33 | 15 — 15,5 | 13 -13,5 | 6,4 — 6,9 | 11,7 | 10,5 | 6,9 |
34 | No more than 16 | No more than 14 | Not more than 7.3 | 12,5 | 10,9 | 7,3 |
35 | 16 — 16,5 | 14 — 14,5 | 7,3 — 7,6 | 12,9 | 11,4 | 7,6 |
36 | No more than 17 | No more than 15 | Not more than 7.9 | 13,6 | 11,8 | 7,9 |
37 | 17-17,5 | 15 — 15,5 | 7,9 -8,3 | 14,1 | 12,3 | 8,2 |
38 | No more than 18 | No more than 16 | Not more than 8.9 | 14,5 | 12,7 | 8,6 |
39 | 17,5 -18 | 15,5 – 16 | About 9.0 | 14,8 | 12,9 | 8,6 |
40 | No more than 18 | No more than 16 | Not more than 9.1 | 15,0 | 13,0 | 8,7 |
41 | 17,5-18 | 15,5 -16 | 8,9 -9,1 | 15,0 | 13,0 | 8,7 |
According to this table, a woman with any body mass index, no matter how they calculate it, will be enough to simply understand how much she should gain in weight by weeks and months.
However, these values are only basic, averaged, demonstrating the rate of weight gain with different body mass index of the future mother before pregnancy.
The rate of weight gain in each case is individual, and only careful observation of its dynamics allows the doctor to judge whether everything is in order with the future mother and her baby, whether there are any pathologies of pregnancy.
How to control?
The dynamics of change in the body weight of the expectant mother are monitored at each scheduled visit to the doctor in the antenatal clinic. And then the expectant mothers have a lot of questions related to the fact that weighing in the office shows quite different numbers like home scales.
Women should always take into account that at home they are weighed in a minimum amount of clothes, whereas in consultation they are dressed and shod, therefore an experienced doctor will always make allowances for the outfit of a pregnant woman.
In addition, weighing with all the apparent ease of this procedure requires proper preparation, otherwise the scales in the antenatal clinic will show a weight that exceeds the real, and, quite significantly. Before you weigh yourself at home or go to an obstetrician-gynecologist, A woman should remember the rules for proper weighing:
- best weighed in the morning;
- at home weighing it is necessary to take measurements on the same day every week, so the dynamics will be more obvious;
- it is desirable to carry out measurements on an empty stomach;
- home weighing is carried out in a minimum amount of clothes, you can - naked;
- Before weighing, be sure to go to the toilet and rid the bladder of urine, and the intestines - from accumulated fecal masses.
If the data of the weights in the antenatal clinic is more than a kilogram different from home measurements, the woman should definitely have a calendar in which she will indicate her increase, measured according to all the rules at home.
You can take the calendar with you and show to the doctor.In the medical card of a pregnant woman, each appointment draws a schedule of weight gain. The same woman can also draw on her own at home, it will help to notice in time the periods when the expectant mother begins to gain excess, the periods when the weight stops or begins to fall. An uneven schedule is always an alarming sign that must be discussed with your doctor.
A strong and sharp increase may indicate the onset of preeclampsia, the appearance of internal edema, which are not visible during external examination. If the weight grows slowly, changes little, not only weekly but also monthly, this may indicate different pathologies in the development of the child, the placenta, a decrease in the quantity of amniotic fluid and other unpleasant processes.
What is dangerous fast weight gain?
As we have already found out, the norms are individual, but the rate of weight gain is of great importance. Even if a woman has a weight during weighing, which according to the table fits into the standard variant, but only a week ago the weight lagged far behind, then such an increase, although it is quite adequate, is unlikely to please the doctor.
It is important that the body mass of the future mother grows gradually, smoothly, with intervals that are permissible at different times.
Women tend to underestimate such criteria as their own weight during pregnancy. In numerous forums of future mothers, women often speak of the fact that the doctor “terrorizes” them, forcing them to lose weight, and together “competently” advise each other “not to pay attention to it”.
Such behavior cannot be considered responsible and adult. After all, the harm that can cause excess weight, as well as harm from a lack of body weight, represent a serious danger to the health and life of the mother and child.
Extra weight in the period of carrying a child is considered such an increase in which:
- during the week a woman added more than 2 kilograms (for any period of gestation);
- for the first trimester, the expectant mother “has grown heavier” by 4 kilograms and more;
- if in the second trimester a woman each month adds more than one and a half kilograms;
- if in the third trimester weekly increase exceeds 800 grams.
Excess weight is a very real risk of developing late toxicosis. Edemas can be external, which a woman can easily discern by the characteristic marks of the socks, by the inability to put on or take off the wedding ring. Wrists, face and ankles are usually swollen. But even if there is no visible edema, this does not mean that there are no internal, much more dangerous and cunning edemas.
Normal blood flow in the system "mother-placenta-fetus" with edema and changes in blood pressure is broken. As a result the crumb gets less nutrients and necessary for its proper development of oxygen.
Extra pounds and active weight gain above the norm are dangerous and the likelihood of premature birth up to 30 weeks, as well as post-pregnancy after 39 weeks.
Excessive increase in 30% of cases leads to early aging of the placenta, which means that the baby will not receive in the last weeks of pregnancy, which are so important for him, a large amount of nutrients that are very necessary for him in the process of preparing for the upcoming birth.
Extra pounds often lead to the appearance of hemorrhoids, varicose veins, as well as the emergence of weak labor forces during labor, as a result of which doctors have to perform unscheduled emergency cesarean section to save the life of a child.
What is dangerous mass shortage?
Lack of body weight during pregnancy leads to various forms of fetal hypotrophy. The kid does not receive the necessary substances and vitamins. In 80% of cases in women with too small an increase babes are born weaker, with a small body weight, severe hypotrophy (insufficient amount of subcutaneous fat). Such children harder to adapt to the environment, they are more difficult given the processes of thermoregulation.
Intrauterine growth retardation increases the risk of congenital neurological diseases, as well as hormonal disorders, the consequences of which can affect any system and any organ in the body of a baby.
Sometimes a small set or no increase is due to the fact that a woman in the literal sense of the word is starving, not eating up. This happens not only in socially disadvantaged families, but also in expectant mothers with a complete lack of appetite against the background of toxicosis of pregnant women. This leads to a deficiency of estrogen levels, and the probability of miscarriage in the early stages, termination of pregnancy and premature birth in the middle and end of gestation period increases tenfold.
It is considered insufficient to put on weight less than 800 grams in the first trimester, less than 5 kilograms in the second and less than 7 kilograms in the third trimester, closer to week 36 of gestation.
What if the weight is overweight?
If the weight is gained too abruptly, irregularly, intermediate weighings show that the increase is pathological, the woman is prescribed an analysis for hormones, because besides overeating, the reason for this “behavior” of body weight can also be found in hormonal imbalances.
If this version is confirmed, then the woman will hormonal therapy as a result of which the hormonal background is restored, and problems with intensive weight gain are solved.
If the reason is overeating and low physical activity (and many pregnant women, alas, are sure that it is necessary to eat for two, and to burden yourself with hiking and swimming is harmful), then the woman is recommended a universal diet for pregnant women.
There should be a future mother 5-6 times a day, every 3-4 hours except for the time allotted for a night's sleep.
One-time portions should be reduced to such a level that the amount of food can visually fit in the palm of a woman if she folds them with a “boat”.
After 28-29 weeks it is allowed to arrange fasting days. Once a week a pregnant woman is allowed to take either 5–6 times a pound of low-fat cottage cheese, or 400 grams of boiled buckwheat, or a liter of fermented milk products. Sugar and salt on fasting days are completely prohibited.
Depending on how intense weight gain is, a woman is given the number of calories that can be gained per day. Most often it is 2200-2500 Kcal. There are counters on the websites about diet food that allow you to quickly find out the number of calories in both individual products and ready meals. This will help to easily calculate the menu for the week, month and day.
The last meal is carried out no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime. All dishes are prepared without frying, deep-frying, an abundance of spices. Also watching the drinking regime - a woman should consume from 1.5 to 2 liters of clean water per day.
Allowed products and dishes - cabbage, zucchini, cereals, apricots, watermelon, apples, buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, milk, beef, veal, meat of turkey, chicken, rabbit, cottage cheese without high fat content.
Prohibited foods - chocolate, pastry, fatty pork, smoked sausages and fish, all fried, salted, pickled, peas, beans, semolina, pearl barley, fast food, ice cream, condensed milk, grapes, bananas, canned food (meat and fish ).
The amount of salt is reduced to 5 grams per day. It is generally better to give up sugar, replacing it with slow carbohydrates (sweet fruits and cereals). Carbonated drinks, syrups, beer are not allowed.
To help pregnant women who are trying to take their weight under control and reduce it, special gymnastic exercises, walks in the fresh air, swimming, yoga classes come. If there are no contraindications, the doctor will advise you to increase physical activity. This will help, together with the correction of power lead to an increase in the permissible norms.
Actions in case of insufficient increase
If the woman’s weight is insufficient, there is a shortage of it, the doctor will also be obliged to give a referral for examination by a gastroenterologist and an endocrinologist.If a woman does not have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or hormonal "malfunctions", she will also receive correction of nutrition.
Caloric intake of its daily ration should exceed 2500 - 3000 Kcal. The diet must include butter - cream and vegetable, pearl barley and semolina, peas and beans, muffins, fatty fish and meat.
The ban, as with excess weight, applies to smoked, pickled and fried. The rest of the approach to the diet is the same. Preferably a fractional diet, with a normal volume of servings, to ensure that the content of fat, carbohydrates and proteins in her diet was sufficient. In addition to the correction of nutrition, the doctor prescribes vitamin complexes, so that the child with the mother's blood can receive the necessary nutrients.
If a woman has a strong toxemia, in which literally “the piece doesn’t crawl into the throat”, the woman will have to adapt to this unpleasant state and force herself to eat at least in small portions in the intervals between attacks of toxicosis.
Choose for this should be moments in which the appearance of nausea is unlikely.
Many future mothers with painful toxemia eat at night in bed or try to eat only in the open air.
If a fetal development delay is diagnosed together with an insufficient weight gain, the woman will have to undergo treatment in the hospital, where she will be given and dripped the necessary preparations to improve uteroplacental blood flow, vitamins, and give all recommendations on the organization of high-calorie nutrition.
Usually, after such measures, the future mother's body weight increases, and, although the average increase passes through the lower limit of the norm, it still fits into it. Such a pregnant woman can be shown more frequent ultrasound scans to monitor the development of the placenta, the baby, as well as to conduct a preliminary analysis of its intended body weight.
About the important facts about weight during pregnancy will tell the obstetrician-gynecologist in the next video.