Features of large and lightweight fetuses during pregnancy and childbirth
The weight of the child at birth plays an important role. The adaptation of the baby after the birth is partially dependent on him: for example, low-weight babies retain heat worse, but it is necessary.
During the first year of life, the weight with which the peanut was born will leave a serious imprint on the choice of feeding tactics, care, health and mood of the baby. Well, if the weight of the fetus during pregnancy is assessed as normal. But often doctors put the future mother before the fact: a large fetus is expected or, conversely, the weight of the child does not "fall short" to the average statistical norm. What are the features of such deviations in pregnancy and in the birth process, we will tell in this article.
Large fruit (macrosomia)
If the estimated weight of the baby significantly exceeds the norm, they say about macrosomia - a large fetus. Large at birth is considered a fetus whose weight exceeds 4 kilograms. According to statistics, about 5-7% of newborns are born with such “heroes”. The growth of such children usually also exceeds the standard standard values. If the weight of a child at birth is 5 kilograms or more, it is called a giant fruit.
Larger boys are born more often, but this does not mean that the female fetus cannot demonstrate a tendency toward macrosomia. Size is usually diagnosed in the second trimester of pregnancy, more often - at the beginning of the third trimester, when the child begins to actively gain weight and "build up" the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
The reasons
Any baby is a child of its parents, and therefore the genetic predisposition is considered the most common cause of fetal macrosomia. If mom and dad are tall and large, or one of the parents has such a heroic build, then the chances that the fruit will be large, are quite high.
Often the fetus during pregnancy is considered normal, and only in the last weeks before childbirth is determined macrosomia. It is no secret that in the last months of pregnancy the baby is actively gaining weight, so it can become large in the case of a post-term pregnancy: after 42 weeks of gestation, up to 40% of children are born large.
Improper diet, in which a woman passes, eats a lot of sweets, adds extra pounds both to her and her child. The fact is that the pancreas is not able to produce as much insulin as it is needed for the breakdown of sugar obtained through the placenta with the mother's blood.
Also large enough are often children who are harvested by women diagnosed with pre-pregnancy diabetes or detected already during gestational diabetes.
Sometimes large parameters do not indicate the health of the fetus. Excess weight may be due to intrauterine swelling, which is often affected by children with a positive Rh factor who are born with Rh-negative women. Edematous form of hemolytic disease increases the weight of the fetus by 20-25%.
Some placental pathologies also contribute to fetal macrosomia. Thus, the large size of the “children's place” and the increase in its thickness lead to a more intensive exchange through the “fetus-mother-system” system, as a result of which the crumb receives more nutrients, its metabolic products are faster displayed, which accelerates its growth and development. In addition to the nutritional function, the placenta "is engaged" in the production of hormones, and a large placenta can produce them in larger quantities.This is also reflected in the growth rate of the baby.
Children who are second, third, and fourth are almost always larger than their elder brothers and sisters. Obstetricians believe that this is due to stretching of the walls of the uterus: the multiparous woman's walls of the reproductive organ are more elastic, “stretched”, so the fetus has more room for growth and development than he, naturally, cannot but use.
In 60% of cases, obesity in the mother leads to the birth of a large fetus, since metabolic processes are disturbed not only in the woman, but also in the child she carries in the womb.
Preparations for improving uteroplacental blood flow ("Quarantine", "Actovegin»And others) also contribute to an increase in fetal weight. Experienced obstetricians note the connection with the age of the pregnant woman - most often macrosomies affect the children of expectant mothers who have not yet turned 20 years old, as well as women over 35 years old.
Bearing
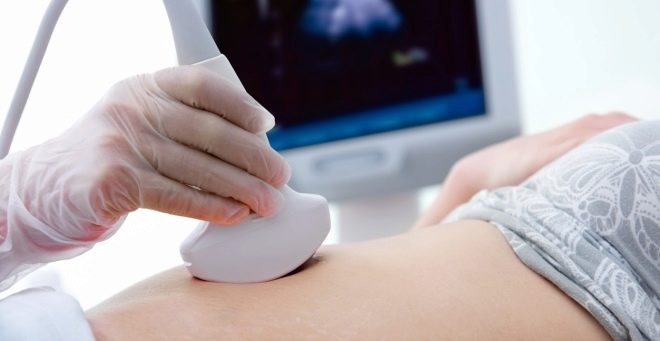
A large belly is not at all a sign of the obligatory presence of a large fetus. Macrosomia is diagnosed not by the size of the abdomen, but by the totality of symptoms, which include the height of the uterus flooring (exceeding more than two weeks), ultrasound data, as well as data obtained by the method of abdominal measurement taking into account the build of the future mother.
In the early stages, the size of the baby does not have much diagnostic value for the definition of macrosomia. It is hard for the baby to gain weight in the mother’s womb after 20 weeks; accordingly, diagnostics is possible only from the middle of the second trimester.
Pregnancy is a big baby for the mother can turn into a real test. A large fetus takes up a lot of space in the abdominal cavity; as a result, all the organs of a woman located in it are squeezed, they have to function at the limit of possibilities in extremely cramped conditions. Therefore, persistent severe heartburn and frequent urination are not excluded. If the baby is trying to behave restlessly in the womb, it is actively moving, the movements of the child cause pain to the pregnant woman.
The load on the legs of the woman with fetal macrosomia is higher, and therefore varicose veins and joint problems are not excluded. Stretching the skin on the abdomen almost always leads to the appearance of stretch marks.
During pregnancy, a large fetus is a risk factor for gestation. A red badge appears on the exchange card of the expectant mother, indicating that the woman is at risk. She is recommended a diet with the exception of sweet and fast carbohydrates, as well as careful monitoring of the amount of fetal movement after 28 weeks and a weekly registration of weight gain.
Vitamin preparations for pregnant women and preparations for improving uterine blood flow are usually canceled so that the child does not grow from large to giant.
Childbirth
How childbirth will proceed depends on the size of the woman’s pelvis, the estimated mass of the fetus, presentation and the mass of other obstetric factors. It is clear that with a narrow pelvis to give birth naturally to a large baby is quite problematic. But if the size of the pelvis is normal and corresponds to the size of the head according to ultrasound data, if the fetus is in the right head position and there are no associated complications of pregnancy, the baby may well be born naturally.
Large births are often accompanied by early discharge of amniotic fluid. The big head of the baby can not tightly press against the exit of the small pelvis and as such, the division of the volume of water into the front and rear does not occur. If the outpouring is not just early but also simultaneous, that is, there is a risk that the umbilical cord or the baby’s limb will fall out, this greatly complicates and delays the birth process.In such cases, with a long anhydrous period, the decision is made to conduct an emergency cesarean section.
A large fetus that goes through the birth canal in the process of childbirth creates the risk of rupture of the uterus, vagina, cervix, injuries of the symphysis. The risks of birth trauma are also considered elevated - due to the fact that the hanger of the child is difficult to pull out, there is a danger of a congenital traumatic fracture of the clavicle, injuries of the cervical spine.
In 80% of cases, doctors decide to conduct a planned caesarean section to women with large fetuses in order to reduce the possible risks that we have listed.
Hospitalization in a planned manner (for childbirth or cesarean section) with a large fetus should be carried out at 38 weeks gestation, these are the recommendations of the Ministry of Health.
Small fruit
The fact that the fetus is lightweight, they say in cases where births occur on time and the weight of the child does not exceed 2.5 kilograms. Hypotrophy (weight loss) is not always accompanied by a parallel decrease in the growth of the child. Most often, a small weight is a sign of unsuccessful fetus in the womb.
Projections for pregnancy and childbirth depend on the cause, which led to the low body weight of the child, if it can be established.
The reasons
First of all, it should be noted that the small size and small weight of the fetus, as in the case of large children, may well be due to genetic features, if the crumbs are thin and low mom and dad. Small children are also often children from twins, triplets. Such reasons are considered physiologically and anatomically substantiated, and do not cause much anxiety among doctors.
In all other cases, diagnostics are carried out in order to establish the reasons why the baby does not gain weight in the womb. The most common diagnosis in this case is “delayed fetal development”. Low weight can be a sign of chronic hypoxia caused by a variety of factors: malnutrition, lack of vitamins and minerals in the required amount, pathology of the placenta, the umbilical cord, entanglement of the umbilical cord.
Any chronic illness of the future mother, as well as her acute infectious diseases transferred to her, contribute to the reduction of fetal weight. Harmful habits during the carrying of the fetus do not add health to either the mother or the child. Most often, low-weight babies are born to women who smoke during pregnancy.
Children who have congenital malformations, as well as anomalies in the genetic set (Down syndrome and other trisomies) are also characterized by low body mass. If screening studies that are mandatory did not show a high risk of having a “special” baby, other reasons for which the child is not gaining weight are considered.
Bearing
Methods of diagnosis of fetal hypotrophy - ultrasound, measurement of the abdomen (VSDM lags behind the standard values by about two weeks). But the reasons will help to understand the ultrasound with Doppler and CTG. If a child has physiological thinness and diminutiveness, then the blood flow in the placental vessels will be within the normal range, and CTG will not reveal signs of disturbance of the fetus.
Depending on what the reasons will be revealed and how great the lag in height and weight is, the woman will be prescribed treatment. It can be carried out at home or in a hospital - this question remains at the discretion of the attending doctor. In the treatment regimen include vitamins, vasodilators ("Curantil", "Actovegin"). Ultrasound monitoring is carried out regularly, which allows you to assess how much the baby has grown during treatment.
A woman carrying a small baby is recommended abundant food, rich in proteins, slow carbohydrates, vitamins. It is important to eliminate the psychological factor: a woman can not be nervous, the child and she needs peace and comfort. Quite often, it is not possible to achieve this at home, and therefore doctors recommend hospitalization.Some pregnant women spend almost all of their pregnancies in the hospital, only occasionally returning home for a couple of weeks.
Birth
The mode of delivery and the timing of delivery are determined depending on the results achieved with the treatment. If the baby starts to gain weight, you don’t need to hurry in the maternity hospital, you need to give the baby a chance to “catch up” with the norm and reach at least 2.5 kg. Therapy aimed at this will continue until the birth. Contraindications for natural childbirth low weight of the fetus is not.
If the child, despite all the efforts and efforts of the doctors, does not gain weight, the pregnancy lasts up to 36-37 weeks. At week 36, a caesarean section can be performed for a fetus.
When choosing the method of birth, it will not be the weight that determines, but the condition of the child. Weak low-weight baby can not cope with serious stress, which is associated with the process of natural birth. Doctors recommend a cesarean section, so as not to lose the baby during labor.
If the child, despite its small size, is quite active and supposedly healthy, childbirth is resolved naturally. Do not think that it is much easier to give birth to a small fruit than a baby with a normal weight. A variety of factors can affect the process of childbirth, and complications can also arise.
But undoubtedly is the fact that in the process of birth a small baby does not create an increased risk of rupture of the uterus and genital tract of the mother, and the risk of getting a birth injury to them is also slightly lower.
Natural childbirth in this case, try to carry out with the use of spinal (epidural) anesthesia, to achieve maximum relaxation and uniform dilation of the cervix. The child is placed in a special crib with heating, discharged him home only after he gets the weight to 2700 or 2800 grams.
findings
Gestation and childbirth of both large and low-weight children, has its own characteristics, with which a woman will have to put up. But in most cases, everything ends quite safely - the birth of a normal child. During pregnancy, it is important to follow all the recommendations of the doctor and in no case do not set yourself diagnoses yourself - according to the ultrasound tables or other data.
A large fetus or a small one, can only be determined by the doctor, as well as the tactics of further management of the patient. Remember that a small belly is not a cause for alarm, because it does not mean that the fetus is also small.
About what to expect with a large fruit, see the following video.