What does a fertilized egg look like and what size should it be normal?
Detection of the ovum in the uterus means pregnancy. A woman can accept congratulations. However, in practice, joy almost immediately gives way to anxiety - is everything in order with the baby, does the fertilized egg meet the standards? In this article we will tell about how the fertilized egg is arranged and what its size should be in normal development.
Appearance and structure
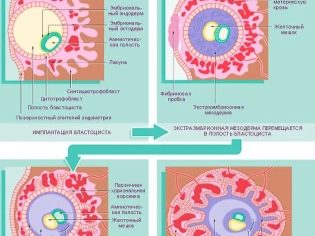
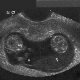
By the third week of its development, if we count from the day of fertilization, the so-called fertilized egg is formed. This is a rather complicated "construction" of a rounded shape, which consists of the embryo, the yolk sac, the chorion and the amnion.
Amnion is the inner lining of the pouch. It produces an amniotic fluid - a special nutrient medium in which the embryo and other embryonic structures are located. Chorion - the outer shell. It contains villi with which the fertilized egg is attached to the endometrium of the uterus.
The yolk bag is a “food storage” that contains nutrients. It looks like a small yellowish pea, located between the chorion and the amnion in the place of the umbilical cord.
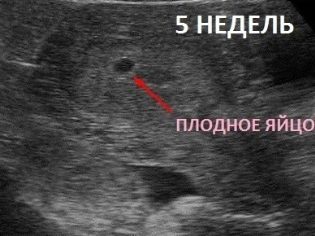
It is possible to examine the fertilized egg only from the 5th week of pregnancy, when its size becomes sufficient for imaging on ultrasound. In other words, it can be seen only after a week or more from the moment the next menstruation occurs.
The color of fetal membranes is grayish, the shape is oval or rounded. Since the membranes are quite elastic, under the influence of various factors (for example, the tone of the uterus), the ovum can change shape, but when these factors are eliminated, it quickly returns to its original appearance. The embryo looks like a small strip in it.
Having one gestational egg does not guarantee that one child will be born. In the case of monozygous twins, the embryos develop in one fetal egg. If two fetal eggs are found, this means that the woman is not expecting twins, similar to each other and having the same sex, but twins, each of whom will have a separate “house” - fetal egg, placenta, in the period of prenatal development.
Usually the gestational egg at the onset of pregnancy is determined in the upper third of the uterine cavity. If it is located low, this can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy, since it is dangerous complete or partial placenta previa, which is formed in the place of attachment of the chorionic villi to the endometrium of the uterus. The process itself is called implantation or nidation and occurs approximately a week after fertilization.
Weekly sizes
The size of the ovum in the initial stages of pregnancy is the main parameter by which the doctor can judge how the baby develops. The fetus is still very small, it is not possible to measure it and its individual parts, but the growth rate of the ovum is a very informative indicator of the development of pregnancy in general.
The size of the ovum speaks not only about development, but also according to certain obstetric terms. The fact is that at the very beginning of pregnancy, when the embryo is just emerging, there is not much difference in height and weight.It is much later that children in the mother's womb begin to grow in different ways, in accordance with their genetic program (some are tall, others are small). In the meantime, all babies develop almost identically, so the growth rate of the ovum is almost the same.
Errors and range of values in diagnostic tables are related to the likelihood of late implantation, as well as other factors that may affect the size of the ovum, but do not pose a threat to the development of the baby.
To measure using a special technique. The diagnostician of ultrasound scans a straight visual line through the fetal egg, which sees on the monitor, so that the ends of the segment are located at opposite points of the inner shell of the fetal sac. This size is called SVD - the average internal diameter.
This size is determined by the very first. Then the size of the embryo itself is added to it. The size of the yolk sac is also considered important.
It is very bad if it is not visualized at all. If it is visible and its dimensions meet the standards, it still does not guarantee that the baby will be healthy, that the pregnancy will proceed without problems.
Growth rates can be seen in the table.
Table of sizes of fetal eggs.
Obstetric term, weeks | SVD, mm | KTR, mm | Yolk sac, mm | Area of the ovum, mm ^ 2 | The volume of the ovum, mm ^ 3 |
5 | 5-18 | 1-2 | - | 245 | 2187 |
6 | 13-22 | 4-5 | 3,0 | 363 | 3943 |
7 | 21-24 | 5-17 | 4,0 | 432 | 6912 |
8 | 29-30 | 10-25 | 4,5 | 675 | 13490 |
9 | 33-36 | 16-36 | 5,0 | 972 | 16380 |
10 | 39-44 | 24-49 | 5,1 | 1210 | 31870 |
11 | 47-51 | 34-58 | 5,5 | 1728 | 55290 |
12 | 56-57 | 42-73 | 6,0 | 2350 | 87080 |
13 | 63-65 | 51-87 | 5,8 | 3072 | 131070 |
Thus, it is considered perfectly normal, if in 5 obstetric weeks - a week after the start of the delay, the woman will have a fertilized egg, the size of which will be 4-5 mm. And in 7 obstetric weeks, the egg of 20 mm will be completely normal. Detection of inconsistencies in the size of the timing may indicate certain pathologies. But under the lag should be understood a significant deviation, for example, with a gestational age of 7 weeks, the size of the gestational sac is 4-5 mm. Let's look at the pathologies of the ovum and the prognosis.
Pathologies
When the doctor says that the fertilized egg is located, but it is stretched, deformed, you should not panic. In most cases, this is the fault of the increased tone of the uterine muscles, with the elimination of this phenomenon, the membranes will take on completely normal forms. Medicine has a ton of ways to remove an increased tone and prevent miscarriage in the early stages. Among other problems that may appear during the passage of ultrasound, the following can be noted.
Hypoplasia
This is an anomaly in which the development of fetal membranes lags behind the growth rate of the embryo itself. A fetal egg, therefore, differs from the embryo in size and timing. According to the diameter of the sac of the sac, the doctor puts only 7 weeks, and the size of the embryo - 9 weeks.
The reasons for which hypoplasia happens are multifaceted. This may be taking antibiotics in the early stages, postponed during the initial stages of pregnancy, influenza or ARVI, hormonal disorders in the woman’s body (endocrine diseases, hormonal stimulation carried out within the framework of the IVF protocol), as well as fetal malformations. Forecasts, alas, are unfavorable. In most cases, the embryo becomes too crowded in small shells and it dies. There is a frozen pregnancy.
A fetal egg that does not grow or grow too slowly gives an inadequate increase in the blood of the hCG hormone during pregnancy, because the chorion's villus does not cope with its responsibilities, including the production of this substance necessary for carrying the fetus.
Bubble skid
A gross and total anomaly in which the embryo does not develop, but the chorionic villi expand and turn into a mass of small bubbles resembling clusters of grapes. With full importation, the embryo is absent altogether, with an incomplete embryo and other structures of the ovum may be present, but they cannot develop normally.
The reasons for this phenomenon - as a female germ cell. If a sperm cell fertilizes an oocyte devoid of DNA, it is this pathology that develops. Only the paternal chromosomes are doubled, such a germ is not viable in principle. If one ovum is fertilized by two spermatozoa at once (which happens, although rarely), an incomplete vesicle drift will be formed.
HCG will “go off-scale” at the same time, because the overgrown villi of the chorion will produce it in excess, which can cause the development of cysts in the female genital glands. But it is dangerous not only by this - in 17-20% of cases the drift goes into the chorionepithelioma. This is a malignant tumor that causes cancer and quickly gives multiple metastases.
When a vesicle skid is detected, the uterine cavity is cleared from formation, vacuum aspiration (essentially an abortion) or curettage (curettage of the uterine cavity) is performed.
Anembrionia
This is the pathology in which the fertilized egg is, it grows, but the embryo inside it is completely absent. Anomaly is also called empty egg sac syndrome. This is found on the ultrasound after 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, when the doctor can not hear the baby's heartbeat and see the fetus.
Up to 80% of cases of anembryony are the consequences of gross genetic pathologies during conception. Also, the reasons may lie in the woman's flu and other acute viral ailments. Anembrionia can be the result of an untreated bacterial infection of the reproductive tract, as well as endometriosis.
More often the pathology is found in women living in regions with unfavorable radiation conditions. Also, pathology is often found in women with metabolic disorders (especially with deficiency and disorders of progesterone production).
If anembrionia is suspected, a woman is prescribed several control ultrasounds with a difference of several days. If the suspicions are confirmed, the embryo is still not visible, is scraping or vacuum aspiration.
False Fertile Egg
This situation is one of the most difficult in the diagnostic plan. A fetal egg is found in the uterus, but it is categorically inconsistent with the term, there is a significant growth lag. It also fails to detect an embryo, as is the case with the empty egg. However, deceit does not lie in this, but in the fact that outside the uterus the second fertilized egg is likely to develop, that is, an ectopic pregnancy takes place.
Low location
If the fertilized egg is not found in the upper third of the uterus, but lower, this requires careful medical observation. But the findings do early. The uterus in the process of growth during pregnancy increases, and the fertilized egg can "migrate" higher. If it develops normally, according to the terms of gestation, then nothing but observation is required in this situation.
Amniotic septum
This pathology occurs in about one and a half thousand pregnancies. Amnion forms cords - a septum is formed inside the ovum. This, of course, requires careful observation by doctors.
The reasons for the development of anomalies are not fully understood, but doctors tend to believe that cords are formed due to damage to the ovum at the earliest stages of development. It is quite possible to carry out and give birth to a child with a septum inside the membranes, but the birth of a child with clefts ("cleft palate", "cleft lip") is not excluded. The limbs of the baby may also suffer due to prolonged squeezing. Sometimes it leads to necrosis of the limbs and their subsequent amputation after the birth of a child.
Quite often, children born after an intrauterine stay in the bladder with a septum suffer from valgus deformity of the feet. The frequency of such negative outcomes is 12-15%. The rest of the women are carrying a child without terrible consequences for his health.
In addition, it is not necessary that the partition will be maintained throughout pregnancy.If on one ultrasound it was found, then on the next it might not be there anymore, because the partition is as thin as it could well be torn.
Big Fertile Egg
Too big fertilized egg in the early stages can speak about various pathologies of both the fetus itself and this pregnancy. Often, oversizing is a harbinger of missed abortion, quite often it is combined with fetal heart rhythm disturbances, with the embryo lagging behind in standard sizes.
A slight increase in the ovum on a period of 5-6 weeks may indicate that one egg is visualized, but there may well be two embryos (monochorial twins, twins). Usually, in this case, a blood test for hCG is done and an ultrasound scan is repeated a week later to examine both embryos.
Retrochorial hematoma
Due to partial detachment of the chorion from the uterine wall, a hematoma may develop - blood accumulates between the chorion and the endometrium. This pathology is usually manifested by the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital organs, as well as weak pulling pains in the lower abdomen.
The prognosis depends on the size of the hematoma. If there is a discharge - this is a favorable sign, which suggests that it decreases, the blood goes. Subsequently, the pregnancy will proceed quite normally.
If the hematoma grows, but there is no discharge or it is very abundant, there is a chance that complete detachment of the ovum will occur (or has already happened). To preserve a pregnancy in such a situation is not possible.
In most cases, retrochorial hematoma develops in women who are nervous a lot, are in a state of constant stress, in women with an impaired hormonal background, with endometriosis and other pathologies of the reproductive system. Excessive physical exertion, as well as unreasonably taken medications, for which the attending physician did not give permission, can become the cause of the detachment.
What to do when anomalies are detected?
First of all, a woman needs to calm down and trust her physician. If the fertilized egg shows too little growth now, it is possible that in a week or two it will fully comply with the norms. Therefore, a woman is assigned several ultrasound examinations. Any pathology, if it occurs, requires repeated confirmation.
A fruit egg is so small and elastic that an inexperienced doctor may well see something in it that is not really there, or vice versa. And because a woman is quite acceptable to turn to another specialist to conduct a re-examination, quite often she does not confirm the disappointing and alarming results of the first ultrasound.
With the deformation of the ovum, if the embryo is of normal size, its heartbeat is heard well, the woman is prescribed moral and physical rest, taking vitamins, as well as drugs that reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus - “But-Shpy”, “Papaverina”, magnesium and iron preparations .
If gross abnormalities such as a blistering, anembryony, etc. are detected, it is not possible to save the pregnancy. A woman should know that she can still have children, the main thing is to find the cause of the development of the anomaly in this case. This will help in planning subsequent pregnancies. Be sure to check with your doctor, will be carried out with a genetic study aborted mass of fetal membranes. If genetic disorders are established, you should definitely visit a geneticist before planning your next pregnancy.
How the conception and development of the ovum occurs, see the next video.