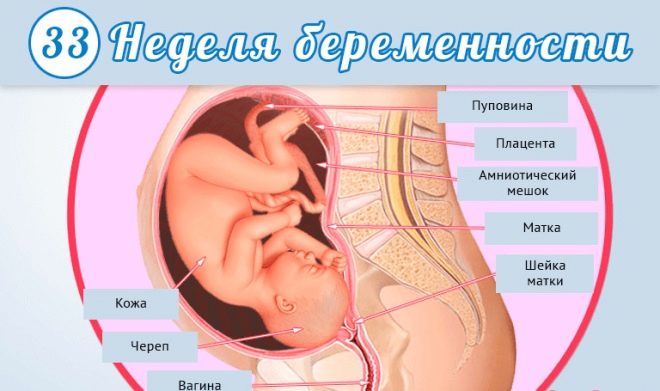
Fetal development at 33 weeks gestation
Before the birth of the baby, quite a bit of time is left. This article will tell about the features of fetal development at week 33.
Anatomical features
Fetometric indicators are important clinical markers to assess the intensity of intrauterine development of the fetus. They provide the doctor with information about what size the fetus has. With the help of such a simple test, the doctor can assess the parameters of the body of the baby, as well as suspect the presence of any emerging pathologies.
Fetometry is the most important diagnostic test that is used throughout the world. For its carrying out special ultrasonic installations are used. Modern devices make it possible to obtain an image of the fetus and study the basic parameters of its body quite easily. The results of studies that are conducted on such equipment are fairly accurate.
The main parameters studied are the length of the body and body weight. For each period of prenatal life, their normal values are different. In their work, doctors use a special table. It contains all the normal values of the studied parameters, characteristic for each week of pregnancy. Such a table is presented below.
Study criteria | Norm for 33 weeks gestation |
Growth | 42-45 cm |
Weight | 1900-2400 grams |
Biparietal size (BPR) | 78-91 mm |
Forearm Bone Length | 47-54 mm |
Bone length of shin | 59-68 mm |
Thigh length | 59-68 mm |
Shoulder length | 54-63 mm |
Abdominal circumference | 26.8-32.5 cm |
Head circumference | 28.8- 33.3 cm |
Frontal-nuchal size | 99-116 mm |
After the fetometry performed, the expectant mother should definitely consult a doctor. In itself, the fetometric conclusion is not a diagnosis. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist, who oversees the development of the course of a particular pregnancy, can assess the intensity of intrauterine development of the fetus.
How is it developing?
Only a few weeks left before the birth of the baby. During this short time, the children's body should have time to prepare for this important event. Most of the internal organs and systems have already been formed, but they are not yet fully functioning. Truly the bodies will begin to carry out their work after the crumb is born.
About the nervous system
Quite specific changes occur in the PNS: every day the work of receptors is improved, which are represented in large numbers in the children's organism. The active development of the senses of the baby contributes to the fact that he has his own feelings.
Baby at 32-33 week already quite well distinguishes tastes. The fetus has such an opportunity due to the fact that there are quite a lot of receptors on its tongue - the papillae. The amniotic fluid, falling on the tongue when swallowed, causes a certain taste in the baby: it can be sweet, salty and even bitter.
Outside the eyes of the child, they cover the eyelids with which he can open and close them.
Another interesting feature of this period of pregnancy is the ability of the fetus to respond to bright light.If it gets on the face of the child, then he will try in every way to turn away from him. The child at the same time experiencing quite significant discomfort.
In the uncomfortable state, the baby changes its motor activity - it starts kicking more and more. This is a kind of signal for his mother that the baby is uncomfortable.
The number of receptors on the skin of the baby increases every day. At 33 weeks, the fetus is already able to respond to the appearance of pain impulses. This reaction is normal. It indicates that the children's body is gradually preparing for new environmental conditions.
The ability to perceive sounds is another manifestation of the work of nerve analyzers characteristic of this period of pregnancy. The range of sounds perceived by the baby at this stage of his intrauterine life is already quite large.
Scientists have found that at 32-33 weeks of pregnancy, the baby with great pleasure perceives lower sounds. Therefore, the baby reacts quite well when his father talks to him.
About the lungs and fetal respiration
The revitalization of the lungs, perhaps, is a very important feature of this period of pregnancy. Every day surfactant accumulates in the alveoli. This particular substance prevents the "sticking" of pulmonary vesicles during breathing. In the absence of surfactant, independent breathing in humans is impossible.
Every day the respiratory muscles of the fetus develops. This is largely due to frequent ingestion of amniotic fluid. When swallowed, the muscles that are part of the fetal respiratory muscles are actively involved.
After swallowing a large amount of amniotic fluid, the baby usually hiccups often. These manifestations of fetal vital activity are felt by his mother. In this case, the woman feels small movements in her stomach. As a rule, they are of moderate intensity. Hiccup in a fetus is a completely normal state and is necessary for its full intrauterine development.
Already fairly well-formed lungs ensure that the baby born at week 33 is viable. In order for the baby to exist independently, it is very important that he could breathe. The presence of surfactant makes breathing possible. However, babies born at this time often have pathology. In this case, you will need special medical care for the newborn, as well as rehabilitation measures for him.
About heartbeat
In order for the baby to exist independently outside the mother's womb, it is very important that his heart work. By week 33, a small heart has almost the same structure as in adults.
A distinctive feature of the fetal heart is the presence of a tiny hole between the atria. This is completely normal. This hole closes when the baby is born and begins to breathe independently.
The main function of the heart is to pump blood through the blood vessels. Scientists have found that a baby who weighs only a couple of kilograms has a heart that can pump quite a lot of blood per day. Normal heart activity allows you to deliver to all internal organs the nutrients and oxygen necessary for their full functioning.
Despite the fact that the fetus is still relatively small, its heart beats much more often than in an adult. This feature is largely due to differences in adult and children's metabolism. A children's growing body requires much more nutrients and oxygen.
You can evaluate the work of the heart with a fairly simple test. To do this, doctors calculate the number of heartbeats per minute. Since the baby is already quite large, it is possible to carry out such a fairly simple study not only with an ultrasound scan, but also using an obstetric stethoscope. The fetal heart rate is shown in the table below.
Heart rate | Norm in the 33rd week of pregnancy |
Heart rate | 120-150 beats per minute |
If the heart of the fetus beats normally, then this clinical condition of the doctors is called normocardia. Tachycardia is too frequent a heart rhythm. If the heart rate is significantly lower than the established norm, then this condition is called bradycardia.
Evaluation of the fetal heart rate is a very important component. It allows you to assess how comfortable a baby feels in the womb.
If the baby's heart beats too fast, then this may be a sign of hypoxia. In this condition, oxygen starvation of the internal organs occurs due to the lack of oxygen in them. Hypoxia is an unfavorable condition for the fetus and is dangerous by the development of a number of undesirable pathologies.
About sex differences
By the 33rd week of prenatal life, babies already have fairly good sexual characteristics. So, boys even have their own testosterone in their blood. The testicles are formed. In some boys, they have even sunk from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum.
The girls formed a set of female germ cells. A sufficient number of eggs is necessary for the woman to have a reproductive function in the future.
Movements
By the 33rd week of pregnancy, the motor activity in a baby changes: the number of active movements performed by the child gradually decreases. This is largely due to the fact that the baby is already quite large and it simply becomes crowded in the uterus. Even in spite of the fact that the child is no longer moving and pushing so strongly, his mother still feels such movements.
As a rule, the child is very active during the day, at night the baby usually sleeps or rests. However, the imperfect structure of the cerebral cortex contributes to the fact that the fetus may confuse the time of day. In this case, he can wake up his mother in the middle of the night with strong kicks.
In this situation, a pregnant woman should breathe deeply, drink some water and try to tell her baby a fairy tale. These actions should calm the baby, and his physical activity will decrease.
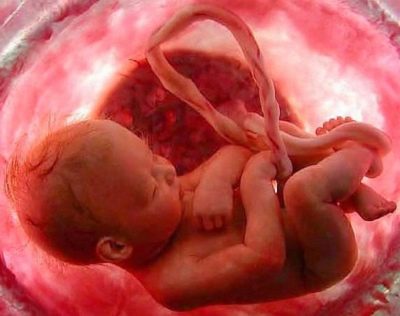
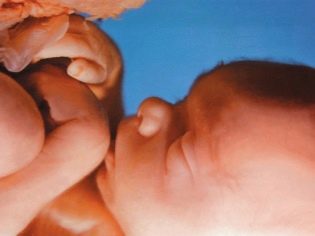
What does it look like?
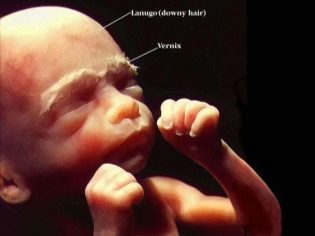
The baby is already quite well defined all parts of the face. The nose of the child has a fairly clear outline. Also pronounced forehead, which no longer looks as flat as before. The auricles of a baby are small and quite clearly contoured.
At 33 weeks of gestation, the cheeks of the fetus are already quite plump. This is due to the fact that under the skin increases the subcutaneous fat.
Note that fat accumulates not only in the projection of the face, but also on the stomach, buttocks, limbs. All this contributes to the fact that the characteristic features of dimples and folds characteristic of all children appear in the fetus.
The body of the baby is covered with a special downy hairline - lanugo. But gradually fluff hairs begin to fall away. This makes the skin of the fetus smoother. Every day more and more hair grows on the head, eyelashes and eyebrows.
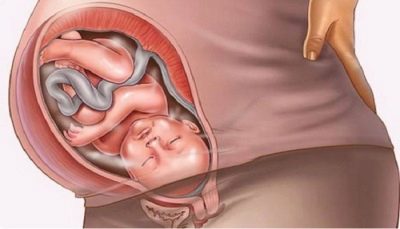
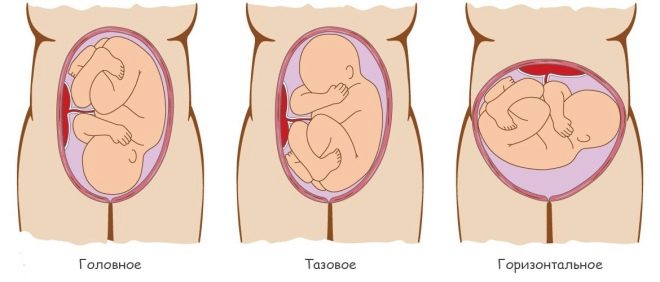
How is the fetus in the womb?
On the location of the baby in the uterus largely depends on the method of technology of obstetrics. If the baby is positioned correctly - in headache, the risk of birth injuries is significantly reduced. By week 33, the baby gradually assumes a stable position in the uterus. Changing the position of the fetus in the womb is possible, but occurs quite rarely at this time.
A less favorable option for the location of the baby is the transverse position. In this case, the fetus is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the uterus. With this arrangement, the baby's natural independent labor can be dangerous by the development of a number of complications. Doctors try to avoid this and resorted to cesarean section.
Another rather unfavorable option of how the baby is in the uterus is pelvic presentation. In this case, the pelvis of the child is located first to the birth canal.Independent labor with this presentation can also be fraught with the development of serious injuries to both the mother and the fetus. If the baby does not turn over before the birth, then doctors can also resort to performing a cesarean section.
The tactics of obstetric aid is chosen individually and depends on many related factors. The obstetrician-gynecologist, who monitors the course of a particular pregnancy and knows its features, makes the decision about the possibility of independent delivery.
About what happens at the 33rd week of pregnancy, see the next video.